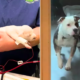
Pets
Are Moles Good Pets? An In-Depth Exploration

Pets
Effective Pet Training Methods: Tips for Success

Effective Pet Training Methods: Tips for Success
Pet training is a crucial aspect of owning a pet. It not only helps in building a strong bond between you and your furry friend but also ensures their safety and well-being. However, training a pet can be challenging, especially if you are new to it. In this guide, we will discuss some effective pet training methods and tips to help you succeed in training your beloved pet.
Understanding Your Pet’s Behavior
Pets, like humans, exhibit a wide range of behaviors that are influenced by their genetics, environment, and past experiences. Understanding your pet’s behavior is crucial for effective training and building a strong bond with them. Here are some key aspects to consider when trying to understand your pet’s behavior:
1. Breed Characteristics: Different breeds have different temperaments and behavior traits. For example, herding breeds like Border Collies may be more energetic and prone to chasing, while lap dogs like Pomeranians may be more affectionate and needy.
2. Body Language: Pets communicate largely through body language. Understanding their body language can help you interpret their feelings and respond appropriately. For example, a wagging tail in a dog may indicate excitement or happiness, while a tucked tail may signal fear or submission.
3. Socialization: Socialization plays a crucial role in shaping your pet’s behavior. Exposing them to various people, animals, and environments at a young age can help them become well-adjusted adults. Lack of socialization can lead to fearfulness and aggression.
4. Past Experiences: Like humans, pets can be deeply affected by their past experiences. A pet that has been abused or neglected may exhibit fear, aggression, or other behavioral issues. Understanding their past can help you provide the right environment and training to help them overcome these issues.
5. Environmental Factors: Your pet’s behavior can also be influenced by their environment. Factors such as the presence of other pets, the amount of exercise they get, and the quality of their diet can all impact their behavior. Providing a stimulating and enriching environment can help prevent boredom and destructive behavior.
6. Health Issues: Sometimes, changes in your pet’s behavior can be a sign of an underlying health issue. It’s essential to monitor your pet’s behavior and consult with a veterinarian if you notice any sudden or significant changes.
7. Training and Reinforcement: Training plays a significant role in shaping your pet’s behavior. Using positive reinforcement techniques, such as treats and praise, can help reinforce desired behaviors and discourage undesirable ones.
By understanding your pet’s behavior and the factors that influence it, you can create a positive and supportive environment that promotes their well-being and strengthens your bond with them.
Common Behavioral Issues in Pets
Pets, like humans, can sometimes exhibit behavioral issues that can be challenging for pet owners to address. Understanding the underlying causes of these behaviors can help in managing and resolving them effectively. Here are some common behavioral issues in pets:
1. Aggression: Aggression in pets can manifest in various forms, such as growling, biting, or lunging. It can be caused by fear, territoriality, or past trauma. Addressing aggression often requires the help of a professional trainer or behaviorist.
2. Separation Anxiety: Pets can experience anxiety when left alone, leading to destructive behavior, excessive barking, or house soiling. Providing your pet with toys, treats, and a comfortable space can help alleviate separation anxiety.
3. Excessive Barking: Dogs may bark excessively due to boredom, attention-seeking behavior, or anxiety. Providing mental and physical stimulation, along with training and positive reinforcement, can help reduce excessive barking.
4. Destructive Behavior: Pets may exhibit destructive behavior, such as chewing furniture or digging, due to boredom, anxiety, or lack of exercise. Providing appropriate outlets for their energy, such as toys and exercise, can help prevent destructive behavior.
5. Fear and Phobias: Pets can develop fears or phobias of certain stimuli, such as thunderstorms or fireworks. Desensitization techniques and creating a safe space for your pet during these times can help reduce their fear response.
6. Compulsive Behavior: Some pets may develop compulsive behaviors, such as excessive licking or tail chasing, which can be a sign of underlying stress or boredom. Providing mental and physical stimulation, along with veterinary guidance, can help manage compulsive behaviors.
7. House Soiling: Pets may soil the house due to incomplete house training, medical issues, or stress. Consistent training, regular bathroom breaks, and addressing any underlying medical issues can help prevent house soiling.
8. Leash Reactivity: Dogs may exhibit reactive behavior, such as barking or lunging on the leash, towards other dogs or stimuli. Training and desensitization techniques can help reduce leash reactivity and improve walking behavior.
9. Resource Guarding: Pets may exhibit resource guarding behavior, such as growling or snapping, to protect their food, toys, or sleeping areas. Training and behavior modification can help address resource guarding behavior.
10. Attention-Seeking Behavior: Pets may exhibit attention-seeking behavior, such as pawing or whining, to seek interaction or affection from their owners. Providing regular exercise, mental stimulation, and positive reinforcement for desired behaviors can help address attention-seeking behavior.
It’s essential to address behavioral issues in pets promptly and effectively to ensure their well-being and strengthen the bond between pet and owner. Seeking guidance from a professional trainer or behaviorist can be beneficial in addressing complex behavioral issues.
Effective Training Methods for Pets
Training is an essential part of owning a pet, helping to establish boundaries, improve behavior, and strengthen the bond between pet and owner. Here are some effective training methods for pets:
1. Positive Reinforcement: Positive reinforcement involves rewarding your pet for desired behaviors, such as sitting or staying. Rewards can include treats, praise, or toys, reinforcing the behavior and encouraging your pet to repeat it.
2. Clicker Training: Clicker training is a form of positive reinforcement that uses a clicker to mark desired behaviors. The sound of the clicker is paired with a reward, helping your pet associate the click with the reward and reinforce the behavior.
3. Operant Conditioning: Operant conditioning involves using rewards and punishments to shape behavior. Positive reinforcement is used to encourage desired behaviors, while negative reinforcement is used to discourage undesirable behaviors.
4. Desensitization and Counterconditioning: This method is used to help pets overcome fears or phobias by gradually exposing them to the feared stimulus while providing positive experiences. For example, if your dog is afraid of loud noises, you can gradually expose them to the noise at a low volume while giving treats or praise.
5. Luring: Luring involves using a treat or toy to guide your pet into performing a desired behavior. For example, you can use a treat to lure your dog into a sitting position, then reward them when they sit.
6. Capturing: Capturing involves rewarding your pet when they naturally exhibit a desired behavior. For example, if your cat uses the scratching post instead of the furniture, you can reward them with treats or praise.
7. Shaping: Shaping involves rewarding successive approximations of a desired behavior. For example, if you want your dog to fetch a ball, you can reward them for looking at the ball, then for moving towards it, and finally for picking it up and bringing it back to you.
8. Consistency: Consistency is key to effective training. It’s important to be consistent in your commands, rewards, and expectations to avoid confusing your pet.
9. Patience and Persistence: Training takes time and patience. It’s important to be patient with your pet and to persist in training even if progress is slow. Consistency and positive reinforcement will eventually lead to success.
10. Professional Training: In some cases, professional training may be necessary, especially for complex behavioral issues or for specific training needs. A professional trainer or behaviorist can provide guidance and support to help you train your pet effectively.
By using these effective training methods, you can help your pet learn new behaviors, overcome challenges, and become a well-behaved and happy member of your family.
Tips for Successful Pet Training
Training your pet can be a rewarding experience that strengthens your bond and improves their behavior. Here are some tips for successful pet training:
1. Start Early: Begin training your pet as soon as you bring them home. Early training helps establish good behavior patterns and prevents bad habits from forming.
2. Be Consistent: Use consistent commands and rewards to reinforce desired behaviors. Inconsistency can confuse your pet and make training less effective.
3. Use Positive Reinforcement: Reward your pet with treats, praise, or playtime when they exhibit desired behaviors. Positive reinforcement encourages your pet to repeat those behaviors.
4. Keep Sessions Short and Fun: Training sessions should be short (5-10 minutes for puppies and 10-15 minutes for adult dogs) and enjoyable for your pet. Use toys and treats to keep them engaged.
5. Be Patient: Training takes time, and not all pets learn at the same pace. Be patient and persistent, and avoid getting frustrated if progress is slow.
6. Use Clear, Simple Commands: Use clear, simple commands that your pet can easily understand. Avoid using long or complicated phrases.
7. Practice Regularly: Regular practice helps reinforce training and keeps your pet’s skills sharp. Practice commands in different environments to generalize the behavior.
8. Gradually Increase Difficulty: As your pet learns basic commands, gradually increase the difficulty by adding distractions or distance. This helps reinforce their training in different situations.
9. Use Different Types of Rewards: Mix up the rewards you use during training to keep your pet motivated. Some pets may prefer treats, while others respond better to praise or playtime.
10. Seek Professional Help if Needed: If you’re struggling with training or dealing with a specific behavior issue, don’t hesitate to seek help from a professional trainer or behaviorist. They can provide guidance and support tailored to your pet’s needs.
By following these tips, you can help ensure that your pet’s training is successful, enjoyable, and beneficial for both you and your furry friend.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding your pet’s behavior is key to successful training. By starting early, being consistent, and using positive reinforcement, you can effectively train your pet and strengthen your bond. Remember to keep training sessions short and fun, use clear commands, and practice regularly.
If you encounter challenges, seek professional help to address specific issues. With patience, dedication, and the right approach, you can successfully train your pet and enjoy a happy, well-behaved companion for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long does it take to train a pet?
The time it takes to train a pet varies depending on the pet’s age, breed, and temperament. Some pets may learn quickly, while others may take longer.
Is it possible to train an older pet?
Yes, older pets can be trained, but it may take more time and patience. Consistency and positive reinforcement are key.
Can I train my pet myself, or do I need professional help?
You can train your pet yourself using the right techniques and methods. However, if you’re struggling or dealing with complex behavior issues, it may be helpful to seek professional help.
What should I do if my pet is not responding to training?
If your pet is not responding to training, try to identify any underlying issues that may be causing the behavior. Consult with a professional trainer or behaviorist for guidance.
How often should I train my pet?
Training sessions should be short and frequent, ideally 5-10 minutes a few times a day. Consistency is more important than the length of the session.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Effective Pet Training Methods: Tips for Success!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Pets
Differences Between Cat Paws and Dog Paws: Unveiling the Mysteries

Differences Between Cat Paws and Dog Paws: Unveiling the Mysteries
If you’ve ever found yourself marveling at the adorable little paws of your feline friend and furry canine companion, you’re not alone.
Cat paws and dog paws are not just cute; they also serve various functions tailored to the specific needs of each species.
In this in-depth exploration, we’ll delve into the {differences between cat paws and dog paws} that make these furry appendages unique.
Anatomy 101: Cat Paws – The Marvels Unveiled
Cats are enchanting creatures, and nowhere is their mystique more evident than in their paws. These multifunctional appendages are not just adorable; they are a masterpiece of evolutionary design.
In this exploration of “Anatomy 101: Cat Paws,” we’ll unravel the intricacies that make these feline footprints truly remarkable.

1. Paw Pads: The Silent Stalkers
1.1 Sensitivity Beyond Compare
Cat paw pads are a sensory wonder. The soft, cushioned undersides of their paws, known as paw pads, serve a myriad of purposes. These pads are incredibly sensitive and play a crucial role in a cat’s ability to navigate the world around them.
1.2 Scent Glands: The Signature Markers
Embedded within these paw pads are scent glands, creating a feline fingerprint with every step. As cats walk, they release unique pheromones, marking their territory and communicating with other feline friends.
The intricacy of this scent messaging system is unparalleled in the animal kingdom.
2. Retractable Claws: Nature’s Hidden Weapons
2.1 Stealthy Hunting Tools
One of the most distinctive features of cat paws is the presence of retractable claws. Unlike their canine counterparts, cats can retract and extend their claws at will. This adaptation is a marvel of nature, allowing cats to keep their claws sharp and hidden when not in use.
2.2 The Mechanism Unveiled
The retractable mechanism is facilitated by an intricate system of tendons and muscles. When a cat needs to climb, hunt, or defend itself, the claws effortlessly extend, ready to grasp and pierce. This feature sets cats apart as skilled predators in the animal kingdom.
3. Paw Pad Functionality: More Than Meets the Eye
3.1 Shock Absorbers in Action
Beyond their role in marking territory, cat paw pads act as shock absorbers. This is especially crucial for cats, who are known for their stealth and agility.
The soft, padded undersides help reduce the impact on their joints when landing, allowing them to move silently and efficiently.
3.2 The Balancing Act
These pads also contribute to a cat’s remarkable sense of balance. Whether walking along narrow surfaces or making daring leaps, the paw pads provide stability and control.
The combination of sensitivity and functionality makes cat paws a masterpiece of natural engineering.
4. The Elegance of Cat Walking: Direct Registering
4.1 The Art of Silence
Cats move with a unique walking style known as “direct registering.” In this elegant gait, a cat’s back foot steps into the same spot as its front foot. This minimizes noise and makes their movements exceptionally stealthy—an evolutionary advantage in the wild.
4.2 Stalking with Precision
Direct registering is not just about silence; it’s a hunting strategy. This walking style allows cats to approach prey with utmost precision, reducing the chances of detection. It’s a testament to the adaptability and strategic prowess of our feline friends.
5. Grooming Rituals: A Paw-fect Affair
5.1 Self-Grooming Mastery
Cats are renowned for their meticulous grooming habits, and their paws are no exception. Using their tongues and teeth, they engage in a ritualistic cleaning process that goes beyond mere hygiene.
5.2 Tongue as a Cleaning Tool
The tongue’s rough texture acts as a natural brush, aiding in the removal of dirt, loose fur, and any foreign particles. The thoroughness of their grooming ritual ensures that their paws remain pristine and ready for any adventure.
In the grand tapestry of feline anatomy, cat paws stand out as a testament to the elegance and efficiency of nature’s design. From silent stalking to precision grooming, every aspect serves a purpose in a cat’s life.
The next time you marvel at your cat’s graceful movements, take a moment to appreciate the intricate wonders that lie beneath those soft and adorable paws.
Canine Wonders: Dog Paws – Unraveling the Paw-sibilities
Dogs, our loyal companions, come equipped with a set of paws that are as fascinating as they are functional. In this exploration of “Canine Wonders: Dog Paws,” we’ll delve into the unique features that make these paw prints an essential part of a dog’s identity.

1. Paw Pads: Calloused Versatility
1.1 Built for Durability
Dog paw pads are a testament to durability. Unlike the soft and sensitive pads of cats, a dog’s paw pads are thick and calloused. This design serves a dual purpose, providing protection and insulation against various terrains and temperatures.
1.2 A Shield Against the Elements
Whether traversing hot asphalt in the summer or icy sidewalks in the winter, a dog’s paw pads act as resilient shields. The calloused texture helps prevent injuries from rough surfaces and provides a level of insulation from extreme temperatures.
2. Non-Retractable Claws: Tools of Adaptation
2.1 The Constant Companion
Unlike the stealthy retractable claws of cats, a dog’s claws are non-retractable and ever-present. This design is a reflection of their diverse roles as diggers, grippers, and stabilizers. Dogs rely on their claws for various activities integral to their daily lives.
2.2 A Digging Dynamo
Digging is a behavior deeply ingrained in many dog breeds. Whether unearthing buried treasures or creating a comfortable sleeping spot, the non-retractable claws play a pivotal role in these digging endeavors.
They act as efficient shovels, allowing dogs to manipulate their environment.
3. Paw Pad Functionality: A Comfortable Traverse
3.1 Traction and Stability
The texture of a dog’s paw pads is designed for optimal traction. This is especially crucial for breeds involved in activities like running, herding, or assisting in search and rescue missions. The paw pads provide a secure grip, ensuring stability on various surfaces.
3.2 Sweating It Out
While dogs primarily cool down through panting, their paw pads also play a minor role in temperature regulation. Dogs have sweat glands in their paw pads, allowing for minimal heat dissipation.
Although not as significant as panting, this mechanism contributes to their overall cooling process.
4. The Walk of Canines: Pacing with Purpose
4.1 The Pacing Stride
When it comes to walking, dogs employ a style known as “pacing.” In this gait, the back foot steps into a different spot than the front foot. This distinctive walking style enhances stability and energy efficiency, making it well-suited for endurance and prolonged walks.
4.2 From Playful Trot to Graceful Stride
Whether trotting beside their human companions or gracefully prancing during play, a dog’s pacing stride is a testament to their adaptability. This walking style is not only efficient but also showcases the diversity of canine movement.
5. Grooming Rituals: A Dog’s Paw-care Routine
5.1 Licking and Chewing Habits
Dogs, being less flexible than cats, resort to licking and chewing as their primary means of paw maintenance. Regular grooming is essential for preventing infections and maintaining overall paw health.
Some dogs may even nibble at their paws to remove stuck objects or dirt.
5.2 Partners in Paw Health
As responsible pet owners, understanding and assisting in your dog’s paw care is crucial. Regularly inspecting for cuts, debris, or signs of infection can contribute to their overall well-being.
It’s a collaborative effort to ensure your canine companion’s paws are happy and healthy.
In the grand tapestry of canine anatomy, dog paws emerge as versatile tools that enable dogs to navigate and thrive in diverse environments.
From the calloused pads that withstand different terrains to the non-retractable claws aiding in digging and stability, each aspect tells a unique story of adaptation.
So, the next time your furry friend leaves paw prints on your heart, take a moment to appreciate the wonders beneath those loyal paws.
Gait and Movement: The Walk of the Species – A Pawspective Unveiled
The distinctive gait and movement of both cats and dogs contribute significantly to their unique characteristics and behaviors. In this exploration of “Gait and Movement:
The Walk of the Species,” we’ll unravel the subtle nuances that make the walks of cats and dogs fascinating windows into their evolutionary adaptations.
1. Cat Walk: Direct Registering in Silence
1.1 The Stealthy Approach
Cats, the epitome of grace and precision, showcase a unique walking style known as “direct registering.” In this method, the back foot steps precisely into the same spot as the front foot, creating a silent and stealthy approach.
This walking style is an evolutionary adaptation honed through centuries of hunting prowess.
1.2 A Stalker’s Strategy
Direct registering is not just about silence; it’s a strategic approach to hunting. Cats, as natural predators, use this gait to minimize noise and maximize surprise when approaching prey.
The synchronized steps enhance their ability to sneak up on potential meals without alerting them to their presence.
2. Dog Stride: Pacing for Endurance
2.1 The Efficient Pacing Stride
Dogs, our loyal companions in various roles, exhibit a walking style called “pacing.” In this gait, the back foot steps into a different spot than the front foot, creating a more stable and energy-efficient stride.
This walking style is particularly beneficial for endurance, allowing dogs to cover long distances with efficiency.
2.2 A Versatile Walk
The pacing stride is not limited to a single purpose. Dogs employ this walking style during various activities, from leisurely strolls with their owners to more purposeful walks, such as herding or participating in search and rescue missions.
It showcases the adaptability of dogs in different environments.
3. The Silent Stalkers vs. The Endurance Masters
3.1 Evolutionary Adaptations at Play
The contrasting walking styles of cats and dogs are a result of their distinct evolutionary paths. Cats, as solitary hunters, developed a silent and precise approach to stalking prey.
On the other hand, dogs, with their history of working alongside humans, evolved a gait that prioritizes stability and endurance.
3.2 A Glimpse into Behavioral Traits
Observing the walk of a cat or dog provides insights into their natural behaviors.
The silent, direct registering walk of a cat reflects its predatory instincts, while the efficient pacing stride of a dog highlights its versatility and cooperative nature developed through centuries of companionship with humans.
4. The Pawsome Ballet of Movement
4.1 Grace and Precision in Cat Movements
Cats are renowned for their graceful movements, and their walk is no exception. The direct registering gait, combined with the flexibility of their spine, allows for fluid and precise motions.
Whether navigating tight spaces or leaping gracefully, cats exhibit a balletic quality in their movements.
4.2 Strength and Stamina in Dog Strides
Dogs, with their pacing stride, showcase strength and stamina. The efficient use of energy allows them to cover long distances without tiring quickly.
Whether trotting alongside their owners during a jog or maintaining a steady pace during work tasks, dogs exhibit a robust and purposeful stride.
5. Embracing Diversity in Motion
5.1 Appreciating Individuality
While cats and dogs share commonalities in their domestic roles, their walks reflect the diversity of their species. Each individual, whether a graceful cat or an energetic dog, brings a unique flair to their movements.
Embracing this diversity adds to the richness of the human-animal bond.
5.2 A Paw-spective Conclusion
In the grand tapestry of gait and movement, the walks of cats and dogs tell stories of adaptation, evolution, and the intricate dance between predator and companion.
Whether silently stalking or pacing with purpose, each species has honed its walk to suit its ecological niche.
So, the next time you witness your feline friend’s stealthy approach or your canine companion’s enduring stride, appreciate the evolutionary tales embedded in every step.
Fun Facts: Quirky Paw Tidbits – Paws and Wonders Unleashed
Beyond their essential roles in walking and hunting, the paws of cats and dogs harbor quirky and delightful secrets. In this exploration of “Fun Facts:
Quirky Paw Tidbits,” we’ll uncover the charming and fascinating aspects of our furry friends’ paws that add an extra layer of wonder to their already enchanting personalities.
1. Cat’s Paw Imprints: A Miniature Cheetah Connection
1.1 The Resemblance Unveiled
Ever noticed that a cat’s paw imprint bears a striking resemblance to a miniature cheetah print? This intriguing similarity is not a coincidence.
Both cats and cheetahs share a retractable mechanism in their claws, allowing for efficient hunting. The paw imprint becomes a charming reminder of their wild ancestry.
1.2 The Echo of Evolution
The retractable claws, a feature in both domestic cats and their larger feline relatives, showcase the evolutionary success of this hunting mechanism.
The paw imprint not only reveals a bit of a cat’s wild heritage but also echoes the efficiency that has made them skilled predators.
2. Dogs’ Paw Preferences: Canine Handedness
2.1 Left Paw, Right Paw, or Both?
Much like humans favoring one hand over the other, dogs often display paw preferences. Some dogs may show a preference for using their left paw, while others lean toward their right. This canine handedness adds a touch of individuality to their personalities.
2.2 Unveiling Unique Personalities
Observing a dog’s paw preferences can provide insights into their unique personalities. While some dogs may be ambidextrous, others may consistently use one paw more frequently, showcasing a charming aspect of their individual quirks.
3. Cat’s Paw Grooming: A Meticulous Affair
3.1 Tongue as a Cleaning Brush
Cats are renowned for their meticulous grooming habits, and their paws receive special attention. During grooming sessions, cats use their tongues and teeth to clean their paw pads thoroughly.
The tongue’s rough texture acts as a natural brush, ensuring every nook and cranny is free of dirt and debris.
3.2 A Ritual of Comfort and Contentment
Beyond hygiene, paw grooming is a comforting behavior. Cats often engage in paw cleaning as a sign of relaxation and contentment. Observing this ritual provides a glimpse into the emotional well-being of our feline friends.
4. Dogs’ Paw Ticklishness: A Playful Sensation
4.1 Ticklish Responses Unleashed
Just like humans, many dogs are sensitive to touch, and their paws can be particularly ticklish. Light touches, gentle strokes, or playful taps can elicit adorable and often comical responses, including paw lifting or gentle nibbling.
Discovering your dog’s ticklish spots adds a playful dimension to your interactions.
4.2 Bonding through Playfulness
Understanding and respecting a dog’s sensitivity to touch fosters a stronger bond between pet and owner. Incorporating playful interactions that respect their ticklish tendencies creates positive associations and enhances the joy of companionship.
5. Paw-some Revelations: A Tapestry of Charm
5.1 Embracing the Quirks
In the delightful tapestry of cat and dog behaviors, these quirky paw tidbits add layers of charm and individuality.
Whether it’s the imprint reminiscent of a wild counterpart, the unique handedness of dogs, the meticulous grooming rituals of cats, or the playful ticklishness, each revelation invites us to appreciate the multifaceted personalities of our furry companions.
5.2 Paws and Wonders Unleashed
As you observe your pets’ playful antics and grooming rituals, remember that each paw print tells a story of adaptation, evolution, and the delightful quirks that make our feline and canine friends truly one-of-a-kind.
In the world of paws and wonders, every revelation adds to the joy of sharing our lives with these enchanting creatures.
Conclusion: Embracing Diversity in Paw-perfect Harmony
In the grand tapestry of nature, the diversity between cat paws and dog paws is a testament to the unique adaptations that have allowed these species to thrive.
While cats’ stealth and precision have made them skilled hunters, dogs’ endurance and stability have made them reliable companions in various roles.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs): Paw Edition
Can cats and dogs have the same paw size?
Paw sizes vary widely between individual cats and dogs. While some may have similar-sized paws, it’s not a strict rule.
Why do cats knead with their paws?
Kneading is a behavior carried over from kittenhood when they kneaded their mother’s belly to stimulate milk flow. It signifies comfort and contentment in adulthood.
Do dogs feel ticklish on their paws?
Yes, many dogs are sensitive to touch on their paws, and some may exhibit a ticklish response when their paws are touched.
Can cats walk on two legs?
While it’s not natural for cats to walk on two legs, some may learn to do so for short distances, especially if trained from a young age.
Q5: How often should I check my pet’s paws for issues?
Regular paw checks are essential. Aim for once a week, examining for cuts, debris, or signs of infection. Consult your vet if you notice anything unusual.
Explore the vast world of cat and dog paws, appreciating the subtle yet significant differences that make each furry companion truly one of a kind.
Whether they’re leaving their mark in the wild or cuddled up on your couch, their paws tell a unique tale of adaptation and evolution.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Differences Between Cat Paws and Dog Paws: Unveiling the Mysteries!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Pets
The Granular Glass Frog: A Unique and Enchanting Pet
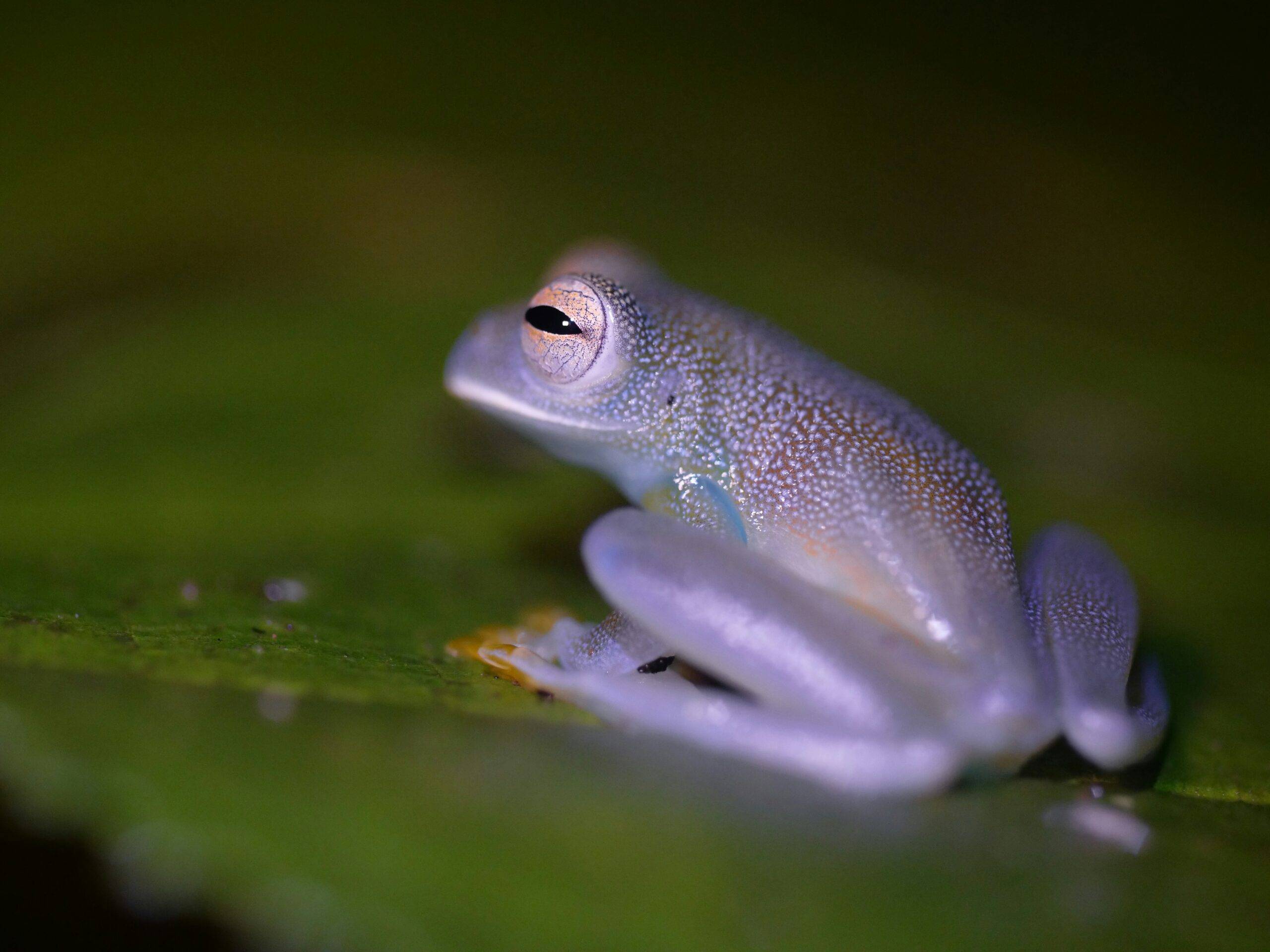

The Granular Glass Frog: A Unique and Enchanting Pet
Are you looking for a pet that is both fascinating and visually stunning? Look no further than the Granular Glass Frog. This captivating amphibian is not only a joy to behold but also relatively easy to care for.
In this article, we will explore the world of Granular Glass Frogs, providing you with up-to-date information on their habitat, care, and characteristics.
What is a Granular Glass Frog?
The Granular Glass Frog, scientifically known as Sachatamia punctulata, is a species of tree frog native to the rainforests of Central and South America.
Its name derives from its translucent skin, which allows you to see its internal organs, making it appear as if it is made of glass. This unique feature has captivated pet enthusiasts around the world.
Habitat and Enclosure
In the wild, Granular Glass Frogs are primarily found in the lowland rainforests near streams and rivers. When creating an enclosure for your pet, it is crucial to replicate their natural habitat as closely as possible.
A terrarium with a vertical setup is ideal, as it mimics their natural tree-dwelling behavior. Ensure the enclosure has plenty of live plants, branches, and a small water feature to provide a comfortable and stimulating environment.
Diet and Feeding
Granular Glass Frogs are insectivores, meaning their diet consists mainly of small insects such as crickets, fruit flies, and pinhead crickets.
It is important to provide a varied diet to ensure they receive all the necessary nutrients. Dusting their food with calcium supplements is also crucial for their bone health.
Always ensure that the insects you feed them are gut-loaded, meaning they have been fed a nutritious diet before being offered to your frog.
Handling and Temperament
While Granular Glass Frogs are captivating creatures, they are best admired from a distance. These frogs are highly sensitive to touch and can easily become stressed or injured if mishandled.
It is recommended to minimize handling and only do so when necessary, such as during enclosure maintenance or veterinary check-ups.
Always remember to wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling your pet to prevent the transmission of any diseases.
Health and Care
To ensure the well-being of your Granular Glass Frog, it is essential to monitor its health and provide proper care. Regularly check for signs of illness, such as loss of appetite, lethargy, or changes in skin color.
Maintaining appropriate temperature and humidity levels within the enclosure is crucial for their overall health. Regularly clean the enclosure and provide fresh, dechlorinated water for drinking and soaking.
Conservation Status
As with many amphibian species, Granular Glass Frogs face threats in the wild due to habitat destruction and pollution.
It is important to support conservation efforts and ensure that any frogs kept as pets are sourced responsibly from reputable breeders. By doing so, you can contribute to the preservation of this captivating species and its natural habitat.
Conclusion
The Granular Glass Frog is a truly enchanting pet that offers a unique and captivating experience for amphibian enthusiasts. With their translucent skin and intriguing behaviors, these frogs are sure to be a conversation starter.
By providing proper care and attention, you can enjoy the company of this extraordinary creature while contributing to its conservation.
Remember, responsible pet ownership is key to the well-being of any animal, so always strive to provide the best care possible for your Granular Glass Frog
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”The Granular Glass Frog: A Unique and Enchanting Pet!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
-

 Pet Care2 years ago
Pet Care2 years agoThe Best Dog Collars For 2022
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoBichon Frise: The Happy, Playful, and Cuddly Companion
-

 Trending Pet Stories1 year ago
Trending Pet Stories1 year ago2023 ‘World’s Ugliest Dog’ Winner: Scooter’s Tale of Resilience
-

 Animals2 years ago
Animals2 years agoAre There Animals Having Down Syndrome?
-

 Pets2 years ago
Pets2 years agoThe Fascinating World Of The Red Chameleon
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Dog Breeds According To AKC.
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years ago21 Dog Breeds That Resemble Bears Or Teddy Bears!
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoEskimo Dogs from Canada – What Are They? – Find Out!