Birds
How To Recognize A Female Blue Jay From A Male Blue Jay Bird

How To Recognize A Female Blue Jay From A Male Blue Jay Bird
Observing the patterns of behavior displayed by male and female blue jays is the only way to tell them apart from one another.
You can tell males from females by observing which birds court the other birds (the males court the females) and then which birds brood the eggs.
Males will court the females, while females will tend to the eggs (the female will incubate the eggs). Blue jays are stunning birds that can be found in the eastern and central parts of the United States.
They are distinguished by the brilliant blue color of their feathers and the crest that sits atop their heads. Even though blue jays are quite distinctive, it can be challenging to distinguish between male and female blue jays.
What characteristics distinguish male blue jays from female blue jays and vice versa?
It would be beneficial to know a little bit about the general behavior and characteristics of blue jays to learn how you can identify the females and males of the series.
This would allow you to learn how to tell which members of the series are which.
A Few Facts Regarding Blue Jays:
- It can be found in various environments, such as urban areas, towns, deciduous forests, and gardens.
- It consumes a wide variety of foods, but its favorite foods are fruits, nuts, and grains.
- Produces a unique “Jay! Jay!” sound but is also capable of producing a wide variety of other vocalizations.
- Produces three to seven eggs at a time when it does so.
Different Varieties Of The Blue Jay
Depending on the classification system, blue jays can be broken up into four or even more subspecies. There are four subspecies of blue jays that are commonly recognized.
These subspecies are the Northern Blue Jay, the Interior Blue Jay, the Florida Blue Jay, and the Coastal Blue Jay.
Physical Traits And Qualities
The length of a blue jay ranges from about 9 to 12 inches (21 to 30 centimeters), and its weight can range from about 13 to 17 inches (34 to 43 inches).

Blue jays are considered to be small to medium-sized birds. The head of the blue jay is adorned with a crest that looks like a crown and is covered in feathers.
The bird’s mood causes these feathers to rearrange themselves in different configurations.
The feathers on a blue jay’s head will bristle in response to fear, the crest will be raised in response to excitement, and it will be lowered when the bird is resting or when it is in the company of other blue jays.
The distinctive blue color of a blue jay’s back feathers, which comes from how their feathers are structured, is one of the bird’s most recognizable characteristics.
Due to the structure of their feathers, certain wavelengths of light are absorbed while others are reflected, causing interference that gives the impression that they are blue.
This phenomenon is referred to as “structural coloration.” The underside of the bird and its face are typically white.
Habitat
The blue jay inhabits most of the eastern half of the United States and parts of Texas and Canada. It can also be found in a few places in Mexico.
The states located in the Great Plains form the westernmost part of the blue jay’s range.
During the cold months of the year, blue jays native to the northern parts of the United States and Canada might move southward to warmer climates.
Diet
The blue jay eats a diverse array of foods to sustain itself. Their beaks were designed primarily for cracking open nuts and seeds, so acorns and other similar foods are among their favorite foods to consume.
They are also willing to consume grain, fruit, and berries without hesitation. Blue jays are omnivores, meaning they will consume insects such as grasshoppers, beetles, caterpillars, and spiders when they have the opportunity.
Blue jays have a reputation for being quite aggressive and will compete fiercely with other species of birds, including jays, grackles, and woodpeckers.
(If you want to lure birds to your yard, keep this in mind when hanging bird feeders.)
Behavior
As was just mentioned, blue jays have a reputation for being quite aggressive, a trait also found in other species of birds, such as starlings.
They are also quite intelligent, as evidenced by the fact that they frequently collaborate and communicate with one another to drive off potential rivals or to frighten away potential prey.
Because of the nature of blue jays, their relationships with other bird species can be quite complicated. To protect their territory, they frequently chase away members of other bird species.
People who would rather have a wider variety of bird species in their backyards may view them as a nuisance because of the presence of these animals.
On the other hand, blue jays have been known to drive away larger predators, making the environment safer for other species of small birds to live in.
The blue jay is a curious bird that has been observed to have an unusual fixation on shiny objects such as coins and bottle caps, even going so far as to steal these items and mess around with them.
Blue jays can communicate with one another using a wide range of vocalizations, including a variety of tweeting and chirping sounds.
These sounds also warn one another about potential dangers, such as predators. They are frequently the target of predatory birds such as owls and hawks.
(It can imitate the noise that raptors make to scare away other birds and investigate whether or not raptors are present.)
Reproduction
In contrast to many other birds, blue jays typically form monogamous mating pairs that remain together throughout their lives.
Observing the bird’s behavior while it is engaged in courtship is one of the most reliable methods for distinguishing a female Blue Jay from a male Blue Jay.
Blue jays will typically congregate in small groups of three to ten individuals most of the time. The female takes charge of the flock, and the male birds will immediately take flight in response to any direction she takes them.
As soon as the female has landed, she will remain still and observe the other birds, while the males of the species will bobble their heads back and forth to attract the female’s attention.
The blue jay’s mating season begins in the middle of March and can last as late as July if conditions are favorable. In general, female blue jays will lay between three to eight eggs in their clutches, with an average of four to five eggs being laid.
After a few weeks, the chicks will emerge from these eggs. Observing male and female Blue Jays as they construct their nests is yet another method for telling them apart.
Even though males and females frequently work together to construct practice nests, females take the lead in constructing the actual breeding nest.
In addition, the female is responsible for incubating the eggs most of the time, while the male brings the food to the female.
After approximately 18 to 21 days, the young birds can fly; however, they will continue to remain close to their parents to continue learning from them until the beginning of fall, at which point the young birds will disperse and begin their independent lives.
In conclusion:
Because male and female blue jays have extremely similar appearances, the best way to tell them apart is by observing how they behave.
Keep an eye out for the female bird taking charge of the flock, as the males will follow closely behind her and bobbing their heads to get her attention.
Immediately after the nest has been constructed, the female will begin incubating the eggs, and the male will bring her food.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”How to Recognize A Female Blue Jay From A Male Blue Jay Bird!?”
Please you should feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Birds
Mastering Parrot Behavior Training: A Comprehensive Guide

Mastering Parrot Behavior Training: A Comprehensive Guide
Parrot behavior training is a fascinating journey that allows you to unlock the full potential of your feathered friend.
Whether you’re a seasoned parrot owner or a newbie, understanding the intricacies of training is essential for building a strong and fulfilling bond with your parrot.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of parrot behavior training, covering everything from basic commands to addressing common behavioral issues.
Our goal is to provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to nurture a happy and well-behaved parrot companion.
Why Parrot Behavior Training Matters
Parrot behavior training is not just a hobby; it’s a crucial aspect of parrot ownership that can significantly impact your feathered companion’s life. Let’s explore why parrot behavior training matters in detail:
Enhanced Communication and Bonding
- Parrots are intelligent creatures capable of understanding and expressing themselves. Behavior training serves as a bridge for effective communication between you and your parrot.
- It strengthens the bond you share with your parrot, creating a deeper and more meaningful connection.
Stress Reduction
- Parrots are highly sensitive to their environment and can become easily stressed by changes or disruptions.
- Through training, you can help your parrot adapt to different situations, reducing anxiety and minimizing the likelihood of stress-related issues.
Safety and Well-being
- Trained parrots are more likely to respond to basic commands, such as “step up” or “come here,” which can be crucial in emergency situations.
- This training ensures that your parrot’s safety is prioritized and reduces the risk of accidents or escapes.
Enrichment and Mental Stimulation
- Parrots are naturally curious and thrive on mental stimulation. Behavior training provides an excellent avenue for them to exercise their cognitive abilities.
- It keeps their minds active and engaged, preventing boredom and related behavioral problems.
Social Interaction
- Training encourages social interaction and engagement. It gives your parrot a sense of purpose and accomplishment.
- Parrots that are trained to interact positively with people and other pets are more likely to be well-adjusted and happy.
Prevention of Problematic Behavior
- Many parrots develop undesirable behaviors, such as excessive screaming, biting, or feather plucking, which can be stressful for both the parrot and the owner.
- Behavior training allows you to address and modify these behaviors effectively, creating a harmonious living environment for everyone.
In summary, parrot behavior training is not only a means to teach tricks and commands; it is the cornerstone of a fulfilling and enriching life for your feathered friend.
It enhances communication, reduces stress, ensures safety, stimulates mental activity, promotes social interaction, and prevents problematic behavior.
Investing time and effort in training your parrot can lead to a happier and healthier relationship between you and your avian companion.
Getting Started with Parrot Behavior Training
Parrot behavior training is a journey that begins with foundational steps. To ensure a successful training experience, it’s essential to start on the right foot.
Let’s explore the key components of getting started with parrot behavior training:
Create a Safe Environment
- Before commencing any training, it’s crucial to establish a secure and safe environment for your parrot. Remove any potential hazards, such as toxic plants, chemicals, or small objects that your parrot could ingest.
- Ensure that your parrot’s cage or play area is well-maintained and free from potential dangers. Safety is paramount to successful training.
Positive Reinforcement
- Parrots, like many animals, respond well to positive reinforcement. This technique involves rewarding your parrot for desired behaviors, thereby encouraging them to repeat those actions.
- Positive reinforcement can take the form of verbal praise, physical affection, or favorite treats. Use what motivates your parrot the most as a reward.
Basic Commands as a Foundation
- Begin your training journey with fundamental commands that lay the foundation for more advanced behaviors. These include commands like “step up,” “stay,” and “come here.”
- These basic commands not only enhance your parrot’s understanding but also build the framework for further training.
Consistency is Key
- Consistency is a fundamental principle in parrot behavior training. To ensure your parrot grasps the desired behaviors, use the same words or gestures consistently for each command.
- This consistency helps your parrot understand what is expected of them and eliminates confusion.
Patience and Respect
- Training a parrot requires patience and respect for the individuality of your bird. Each parrot is unique, and their progress will vary.
- Avoid using force or punishment in training, as it can lead to fear and mistrust. Instead, be patient and respectful of your parrot’s boundaries and pace.
Training Sessions
- Keep training sessions short and focused. Parrots have relatively short attention spans, so training for about 10-15 minutes at a time is ideal.
- Multiple short sessions throughout the day are more effective than a single lengthy session.
Use of Clicker Training
- Clicker training is a useful method for parrot behavior training. It involves using a clicker to mark the precise moment your parrot performs the desired behavior.
- The click sound signals to your parrot that they’ve done something right, and a reward follows.
Expand Gradually
- Once your parrot has mastered basic commands, gradually introduce more advanced training techniques and behaviors.
- This could include teaching tricks, vocalizations, or addressing specific behavioral issues.
By focusing on creating a safe environment, employing positive reinforcement, and mastering basic commands with patience and consistency, you’ll set a solid foundation for successful parrot behavior training.
Remember that every parrot is unique, and their progress may vary. Be respectful of their individuality and enjoy the rewarding journey of training your feathered companion.
Advanced Parrot Behavior Training
Once your parrot has grasped the basics of behavior training, it’s time to take things to the next level. Advanced parrot behavior training offers an opportunity to challenge your feathered friend mentally, enrich their life, and reinforce the bond you share.
Let’s explore the intricacies of advanced training:
Teaching Intriguing Tricks
- Parrots are natural performers, and they love to show off their skills. Teaching your parrot entertaining tricks like waving, ringing a bell, or even simple math tasks can be incredibly rewarding for both you and your parrot.
- These tricks stimulate your parrot’s cognitive abilities and provide them with hours of fun and mental stimulation.
Behavior Modification and Problem Solving
- Some parrots may develop undesirable behaviors, such as excessive screaming, biting, or feather plucking. Advanced behavior training can help address and modify these behaviors.
- If your parrot is struggling with problematic behaviors, consider consulting with a professional avian behaviorist for guidance and tailored solutions.
Speech and Vocalization Training
- Many parrot species are renowned for their ability to mimic human speech. Advanced training can help you teach your parrot specific words, phrases, and even sentences.
- Patience and consistent training are key when it comes to teaching your parrot to talk. Remember that not all parrots will become proficient talkers, and some may have a limited vocabulary.
Target Training
- Target training is an advanced technique that involves teaching your parrot to touch or “target” a designated object, typically a stick or a finger.
- This technique has various applications, from teaching your parrot to follow a target stick to assisting in behavior modification for specific issues.
Advanced Recall Training
- Recall training takes basic recall commands like “come here” to the next level. You can teach your parrot to return to you even when they are at a distance.
- This skill can be particularly valuable for outdoor interactions, ensuring your parrot’s safety.
Complex Puzzle Solving
- Challenge your parrot’s problem-solving abilities by presenting them with complex puzzles and toys.
- These activities not only provide mental stimulation but also offer a sense of accomplishment when your parrot successfully solves them.
Flight Training
- Flight training is an advanced skill that allows your parrot to fly and return to you safely.
- If you choose to engage in flight training, it’s essential to do so in a controlled and safe environment.
Building on Foundation Behaviors
- Advanced training builds upon the basic commands your parrot has already mastered. Remember to maintain those foundational behaviors while introducing more complex ones.
- Consistency is key to ensuring that your parrot doesn’t forget what they’ve already learned.
Advanced parrot behavior training is an exciting journey that can bring a new level of engagement, mental stimulation, and interaction to your relationship with your feathered companion.
Remember that patience and positive reinforcement remain essential, and the key to success lies in understanding your parrot’s individual needs and abilities.
With dedication and the right approach, you can unlock your parrot’s full potential and enjoy a fulfilling partnership.
Common Parrot Behavior Issues and Solutions
Parrots are complex and intelligent birds, and like all pets, they can occasionally exhibit behavior issues. Recognizing and addressing these issues is crucial for maintaining a harmonious relationship with your feathered friend.
Let’s delve into some common parrot behavior problems and their solutions:
Screaming
Issue: Parrots are known for their vocal nature, but excessive screaming can be problematic and disruptive.
Solution:
- Identify the cause of the screaming. Is your parrot seeking attention, feeling anxious, or just bored?
- Address the underlying issue to reduce excessive noise. Spend more quality time with your parrot, provide mental stimulation, or change their environment to alleviate stress.
Biting
Issue: Biting is a natural behavior for parrots, but it can be a problem if it’s aggressive or frequent.
Solution:
- Determine the trigger for biting. Is it fear, aggression, territorial behavior, or something else?
- Remain calm and avoid reacting negatively to bites. Use positive reinforcement for good behavior and consult with an avian behaviorist if biting persists.
Feather Plucking
Issue: Feather plucking can be a sign of stress, health issues, or boredom.
Solution:
- Consult with an avian veterinarian to rule out any medical causes for feather plucking.
- Offer mental stimulation, toys, and a balanced diet to keep your parrot occupied and discourage this harmful behavior.
Destructive Chewing
Issue: Parrots love to chew, and they may target items you’d rather they didn’t.
Solution:
- Provide a variety of safe chewing toys to redirect your parrot’s energy. These toys should be specifically designed for parrots.
- Ensure your parrot receives enough mental and physical stimulation to prevent boredom and destructive chewing.
Aggression
Issue: Aggressive behavior in parrots can be directed toward their owners or other pets.
Solution:
- Identify the source of aggression, which could be fear, territorial behavior, or hormonal changes.
- Consult with an avian behaviorist to create a tailored plan for addressing and modifying aggressive behavior.
Loud Vocalizations
Issue: While vocalizations are normal, excessively loud vocalizations can be disruptive.
Solution:
- Provide your parrot with an appropriate outlet for their vocalizations, such as a designated time or space for chattering and squawking.
- Use positive reinforcement for quiet behavior and avoid reinforcing loud vocalizations with attention.
Cage Aggression
Issue: Some parrots may display aggression when you approach their cage.
Solution:
- Gradually work on desensitizing your parrot to your presence near their cage by offering treats and rewards.
- Be patient and avoid sudden movements or forcing interactions.
Territorial Behavior
Issue: Parrots can become territorial over certain areas or objects in their environment.
Solution:
- Respect your parrot’s territorial boundaries and avoid encroaching on their space unnecessarily.
- Use positive reinforcement and rewards to encourage them to share or relinquish their territory.
Addressing common parrot behavior issues requires patience, understanding, and a willingness to work with your parrot’s unique personality.
Consult with an avian veterinarian or behaviorist when needed to ensure the health and well-being of your feathered companion.
With the right approach and consistent training, many of these issues can be successfully managed, fostering a happier and more balanced life for your parrot.
Conclusion
Parrot behavior training is a rewarding and essential aspect of responsible parrot ownership. It enhances the bond between you and your feathered companion while promoting a happy and well-adjusted life for your bird.
Remember, patience and consistency are the keys to successful training. With dedication and love, you can unlock your parrot’s potential and enjoy a harmonious relationship for years to come.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs)
Can all parrot species be trained?
Yes, most parrot species can be trained to some extent. However, the ease of training and the specific behaviors they can learn may vary from one species to another.
How long does it take to train a parrot?
The time it takes to train a parrot varies depending on the bird’s age, previous experiences, and the complexity of the behaviors you’re trying to teach. Simple commands may take a few weeks, while complex tricks might require several months of consistent training.
Are there specific training tools I should use?
While you don’t need specialized tools, having a clicker for clicker training and a variety of parrot-safe treats can be beneficial in the training process.
What should I do if my parrot refuses to train or seems disinterested?
If your parrot appears disinterested or uncooperative, it’s essential to assess their mood and health. Ensure they are not stressed or unwell. Sometimes, taking a break from training and revisiting it later can help reignite their interest.
Can I train an older parrot, or is it easier with a young bird?
It’s possible to train older parrots, but it may require more patience. Young parrots tend to be more receptive to training, but with consistency and positive reinforcement, older parrots can also learn new behaviors.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Mastering Parrot Behavior Training: A Comprehensive Guide!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Birds
The Ultimate Guide to White Pet Birds
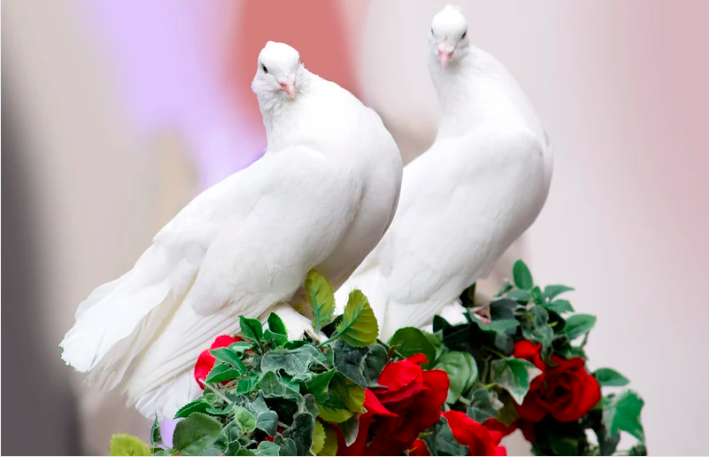

The Ultimate Guide to White Pet Birds
If you’re looking to bring some feathered friends into your life, there’s something undeniably charming about white pet birds.
These elegant creatures can make wonderful companions, and their purity and grace have captured the hearts of bird enthusiasts around the world.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about white pet birds, from their types and care to frequently asked questions.
Types of White Pet Birds
Cockatoos: Snowy Elegance
When it comes to white pet birds, few can match the majestic beauty and charm of the snowy cockatoo. These birds are often considered the epitome of elegance with their pure white plumage and enchanting personalities.

In this section, we’ll take a closer look at these captivating creatures, exploring their personality, characteristics, and the care they require to thrive as your beloved companions.
Personality and Characteristics
- Social Butterflies: Cockatoos are renowned for their social nature. They thrive on interaction and enjoy being the center of attention. If you’re looking for a feathered friend that wants to be part of your daily life, a cockatoo might be the perfect choice.
- Intelligent and Playful: These birds are incredibly intelligent, which makes them quick learners and great problem solvers. They enjoy mental stimulation through toys and puzzles, and their playful antics will keep you entertained for hours.
- Affectionate and Bonding: Cockatoos have a reputation for forming deep emotional bonds with their human companions. They often see their owners as part of their flock and crave physical affection, such as cuddling and petting.
- Vocal Talents: While not as renowned for talking as some parrot species, cockatoos can mimic sounds and words with practice. They are more likely to create a symphony of delightful chirps, whistles, and squawks.
Caring for Cockatoos
Caring for cockatoos requires dedication and commitment. Here are some essential tips to ensure the well-being of these magnificent birds:
- Spacious Living Quarters: Cockatoos need room to spread their wings and exercise. Invest in a large cage that allows them to move freely. Ensure the cage has horizontal bars for climbing.
- Mental Stimulation: Keep their intelligent minds engaged with a variety of toys and puzzles. Rotate these regularly to prevent boredom.
- Balanced Diet: Provide a balanced diet consisting of high-quality pellets, fresh fruits, vegetables, and a limited amount of seeds. Consult with an avian veterinarian to create a nutrition plan tailored to your bird’s needs.
- Social Interaction: Spend plenty of quality time with your cockatoo. They require social interaction and mental stimulation daily. If you can’t be around, consider getting a companion bird to keep them company.
- Grooming: Regularly trim your cockatoo’s nails and beak to prevent overgrowth. Ensure access to a shallow dish for bathing, as cleanliness is essential to their health.
- Safety First: Make your home bird-friendly by removing potential hazards like toxic plants, open windows, and other pets that may pose a threat to your cockatoo.
- Vet Visits: Schedule regular check-ups with an avian veterinarian to monitor your bird’s health and address any concerns promptly.
In conclusion, cockatoos offer a unique blend of elegance, intelligence, and affection that can make them outstanding companions. However, their care demands commitment and a genuine love for their spirited personalities.
If you’re ready to welcome a cockatoo into your life, be prepared to embark on a rewarding journey filled with snowy elegance and cherished moments with your feathered friend.
Budgerigars: Small and Charming
When it comes to delightful and charismatic white pet birds, budgerigars, affectionately known as budgies, are at the top of the list.

These small parrots are cherished by bird enthusiasts worldwide for their vibrant personalities, colorful plumage, and entertaining antics.
In this section, we’ll delve into the world of white budgerigars, exploring their personality, characteristics, and how to provide them with the care they need to thrive in your home.
Personality and Characteristics
- Playful and Curious: Budgies are renowned for their playful and inquisitive nature. These tiny parrots are always on the lookout for new toys, objects, or perches to explore. Their curiosity can bring endless joy to your life.
- Affectionate and Social: Despite their small size, budgies have big hearts. They form strong bonds with their human companions and thrive on social interaction. With patience and time, your budgie can become a loyal and affectionate friend.
- Mimicry Masters: While they may not reach the talking prowess of some larger parrot species, budgies are excellent mimics. With consistent training and patience, they can learn to mimic words and sounds, adding a charming touch to your home.
- Colorful Plumage: Budgerigars are available in various colors, including pure white. Their vibrant plumage adds a dash of color to any room and makes them a striking choice for bird enthusiasts.
Caring for Budgerigars
Ensuring the well-being of your budgie involves attention to their specific needs and preferences:
- Spacious Cage: Invest in a roomy cage that allows your budgie to fly and move around comfortably. Horizontal bars are preferable for climbing, and add perches and toys for mental stimulation.
- Balanced Diet: Provide a well-balanced diet that includes high-quality budgie pellets, fresh fruits, vegetables, and the occasional treat. Fresh water should always be available.
- Social Interaction: Budgies thrive on social interaction. Spend time with your feathered friend daily, talking to them, offering toys, and allowing them to explore outside the cage in a safe environment.
- Mental Stimulation: Keep your budgie’s clever mind engaged with a variety of toys, puzzles, and objects to explore. Rotating toys can help prevent boredom.
- Grooming: While budgies are generally good at self-grooming, keep an eye on their nails and beak. If needed, consult an avian veterinarian for trimming.
- Safe Environment: Ensure your home is bird-safe by removing potential hazards such as toxic plants, open windows, and other pets that may pose a threat to your budgie.
- Health Check-ups: Schedule regular visits to an avian veterinarian to monitor your budgie’s health and address any health concerns promptly.
In conclusion, budgerigars, with their small size and big personalities, make wonderful companions for bird enthusiasts of all levels of experience.
Their playful nature, cheerful disposition, and ability to form strong bonds with their owners make them a popular choice among white pet birds.
By providing proper care and attention, you can enjoy a charming and vibrant addition to your household in the form of a white budgerigar.
Doves: Symbols of Peace
When it comes to embodying the essence of peace and serenity, white doves are the ultimate ambassadors. These gentle and elegant birds have long been revered as symbols of tranquility and love.

In this section, we will explore the enchanting world of white doves, their peaceful personalities, unique characteristics, and how to provide them with the care they need to thrive as cherished companions.
Personality and Characteristics
- Calm and Gentle Nature: Doves are renowned for their peaceful demeanor. They exude a sense of calm and tranquility, making them perfect additions to events symbolizing love and unity, such as weddings and ceremonies.
- Simplicity in Beauty: The beauty of white doves lies in their simplicity. Their pristine, snow-white plumage is a sight to behold, and their graceful flight adds an elegant touch to any occasion.
- Mates for Life: Doves are known for their strong pair bonds. Once they find a mate, they often remain devoted for life, symbolizing enduring love and commitment.
- Symbolic Significance: Throughout history, doves have symbolized peace, purity, and hope. Their presence at special events signifies harmony and new beginnings.
Caring for Doves
Ensuring the well-being of your white doves involves providing them with a peaceful and secure environment:
- Spacious Enclosure: Doves need a clean and spacious enclosure that allows them to stretch their wings and fly. An outdoor aviary or an indoor space with plenty of room is ideal.
- Adequate Perches: Offer various perches of different sizes and textures to keep their feet healthy and provide mental stimulation.
- Balanced Diet: Provide a balanced diet consisting of dove pellets, seeds, and fresh water. Supplement their diet with grit for digestion.
- Gentle Social Interaction: While doves may not be as interactive as parrots, they appreciate gentle socialization. Speak softly to them, and allow them to become comfortable with your presence.
- Safe Environment: Ensure their environment is safe from potential hazards, including predators, toxic plants, and extreme weather conditions.
- Nesting Material: If you plan to breed doves, provide nesting material like twigs and straw, and ensure they have privacy during the nesting period.
- Regular Health Checks: Schedule periodic check-ups with an avian veterinarian to monitor your doves’ health and detect any issues early.
In conclusion, white doves are more than just birds; they are living symbols of peace and purity. Their presence can add a touch of grace and tranquility to your life and special events.
By providing them with a peaceful and loving environment, you can enjoy the beauty and symbolism of these gentle creatures, making them a timeless addition to your world of love and serenity.
Canaries: Serenading Songsters
When it comes to pet birds with a talent for serenading, canaries take the spotlight. These melodious songbirds are known for their enchanting tunes and charming personalities.

In this section, we’ll dive into the world of canaries, exploring their remarkable singing abilities, unique characteristics, and how to provide them with the care they need to become your delightful companions.
Personality and Characteristics
- Melodious Minstrels: Canaries are celebrated for their exceptional singing prowess. These birds have a natural gift for melody, and their songs can range from cheerful chirps to complex and captivating tunes.
- Colorful Varieties: Canaries come in various colors, including the stunning white canary. Their colorful plumage adds to their visual appeal, making them not just a treat for your ears but also for your eyes.
- Independent Nature: Canaries are relatively independent compared to some other pet birds. They don’t require constant attention and are content singing and exploring their surroundings.
- Low-Maintenance: These birds are considered low-maintenance compared to parrots or cockatoos. They are a great choice for those seeking the joy of pet bird ownership without the demands of high social interaction.
Caring for Canaries
Providing a nurturing environment for your singing canary involves considering their specific needs and preferences:
- Proper Cage: Invest in a spacious cage that allows your canary to fly and perch comfortably. Ensure the bars are horizontal for climbing, and add multiple perches at different heights.
- Nutritious Diet: Canaries thrive on a diet primarily consisting of high-quality canary pellets, fresh water, and a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables. A treat of egg food can enhance their singing abilities.
- Clean Environment: Keep the cage clean by changing the paper lining regularly. Good hygiene is crucial to prevent illness.
- Safe Surroundings: Ensure your home is safe for your canary by removing hazards like toxic plants and potential sources of drafts.
- Alone Time: Canaries appreciate time alone to practice their songs. Allow them quiet periods to hone their musical talents.
- Fresh Air and Natural Light: Provide access to fresh air and natural sunlight whenever possible. However, protect them from extreme temperatures and drafts.
- Gentle Interaction: While canaries may not seek constant companionship, they can enjoy gentle interactions with their owners. Talk to them softly and offer occasional treats.
In conclusion, canaries are like living works of art, gracing your home with both visual beauty and delightful melodies. Their songs can bring a sense of calm and happiness to your surroundings.
By providing them with proper care and a nurturing environment, you can enjoy the serenades of these charming songsters, making them a harmonious addition to your life.
White Parrot: A Majestic Avian Companion
White parrots, with their pristine plumage and charismatic personalities, hold a unique allure for bird enthusiasts. These majestic birds combine the intelligence and charm of parrots with the pure elegance of a snowy white coat.

In this section, we’ll embark on a journey into the captivating world of white parrots, exploring their unique characteristics, personality traits, and how to provide them with the care they deserve as your cherished avian companions.
Personality and Characteristics
- Intelligence and Wit: White parrots, like their colorful counterparts, are incredibly intelligent birds. They possess a sharp wit, which makes them quick learners and problem solvers. Their ability to mimic sounds and words is renowned, and they often enjoy engaging in playful banter with their human companions.
- Social Butterflies: Parrots are social creatures, and white parrots are no exception. They thrive on interaction and can form strong bonds with their owners. They often see their human caregivers as part of their flock and crave companionship.
- Playful and Energetic: These birds are bursting with energy and enjoy an active lifestyle. They appreciate a variety of toys, puzzles, and opportunities for physical and mental stimulation. Providing them with a stimulating environment is essential to their well-being.
- Longevity: Many parrot species, including white parrots, have relatively long lifespans. With proper care, they can become cherished members of your family for decades.
Caring for White Parrots
Ensuring the happiness and health of your white parrot involves providing them with a nurturing environment that caters to their specific needs:
- Roomy Accommodations: White parrots need a spacious cage that allows them to move, stretch their wings, and play. Opt for horizontal bars to facilitate climbing.
- Nutrient-Rich Diet: Offer a balanced diet that includes high-quality parrot pellets, fresh fruits, vegetables, and a limited amount of seeds. Fresh water should always be available.
- Mental Stimulation: Keep your white parrot’s brilliant mind engaged with a variety of toys, puzzles, and opportunities for exploration. Rotate toys regularly to prevent boredom.
- Social Interaction: Spend quality time with your feathered friend daily, engaging in conversations and providing them with social stimulation. Parrots can get lonely if left alone for extended periods.
- Grooming and Hygiene: Monitor their nails and beak for overgrowth and seek professional assistance for trimming if necessary. Provide a shallow dish for bathing, as cleanliness is essential.
- Safe Environment: Ensure your home is free from hazards such as toxic plants, open windows, and other pets that may pose a threat to your white parrot’s safety.
- Vet Check-ups: Schedule regular visits to an avian veterinarian to monitor your parrot’s health, detect potential issues early, and establish a wellness plan.
In conclusion, white parrots represent a harmonious blend of beauty, intelligence, and charm. Their presence can grace your life with elegance and joy.
By providing them with proper care, attention, and a loving environment, you can enjoy the companionship of these majestic avian beings, making them an enduring and cherished part of your world.
Song Canary: A Harmonious Avian Virtuoso
Song canaries are renowned for their exceptional vocal talents and melodious serenades. These avian virtuosos captivate bird enthusiasts with their enchanting songs and charming personalities.

In this section, we’ll immerse ourselves in the captivating world of song canaries, delving into their unique characteristics, singing prowess, and how to care for these harmonious feathered friends.
Personality and Characteristics
- Virtuoso Vocalists: Song canaries are celebrated for their extraordinary singing abilities. They are natural-born singers, and their songs can range from cheerful chirps to complex and captivating tunes. Each canary has its unique song, making them akin to avian maestros.
- Diverse Song Varieties: Different breeds of song canaries are known for distinct song patterns. Some produce lively and rhythmic melodies, while others offer serene and soulful tunes. The variety in their songs adds depth to the world of canary enthusiasts.
- Colorful Plumage: Song canaries come in various colors, but it’s their vocal talents that steal the show. Their plumage, while diverse, often takes a back seat to the symphony of sounds they create.
- Independent Nature: These birds are relatively independent compared to some other pet birds. While they may not seek constant attention, they appreciate a harmonious environment for practicing their melodies.
Caring for Song Canaries
Ensuring the well-being and happiness of your song canary involves providing them with a nurturing environment that caters to their specific needs:
- Proper Cage: Invest in a spacious cage that allows your canary to fly and perch comfortably. Include perches of varying sizes and textures to keep their feet healthy.
- Nutrient-Rich Diet: Song canaries thrive on a diet primarily consisting of high-quality canary pellets, fresh water, and a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables. A treat of egg food can enhance their singing abilities.
- Clean and Peaceful Environment: Keep the cage clean, changing the paper lining regularly. A serene and quiet environment is conducive to their singing practice.
- Mental Stimulation: Provide your canary with toys, mirrors, and opportunities for exploration. Mental stimulation can enhance their singing repertoire.
- Grooming and Hygiene: Monitor their nails and beak for overgrowth and seek professional assistance for trimming if necessary. Bathing options should be available.
- Safe Surroundings: Ensure your home is safe for your canary, removing potential hazards such as toxic plants and sources of drafts.
- Social Interaction: While not as social as some other parrot species, song canaries enjoy gentle interactions with their owners. Speak softly to them and offer occasional treats.
In conclusion, song canaries are not just pet birds; they are living concert performers. Their melodious tunes can bring a sense of harmony and joy to your home.
By providing them with proper care, a peaceful environment, and opportunities to practice their art, you can enjoy the enchanting world of these harmonious avian virtuosos, making them a harmonious addition to your life.
Caring for White Pet Birds: Your Guide to Avian Well-being
Caring for white pet birds, regardless of their species, requires attention to their unique needs and a genuine commitment to their well-being.
In this comprehensive section, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to ensure the health, happiness, and longevity of your beloved feathered friends.
Habitat and Housing
- Spacious Accommodations: White pet birds, like all birds, need adequate space to stretch their wings and move around. Invest in a cage or aviary that allows them to exercise and explore comfortably.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure that the bird’s habitat is well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of moisture and odors. This promotes a healthier environment for your pet.
- Cleanliness: Regularly clean the cage or aviary by changing the bedding or substrate. A clean living space is essential for your bird’s health.
- Enrichment: Provide perches, toys, and opportunities for mental stimulation. Birds need mental exercise to prevent boredom and stress.
Diet and Nutrition
- Balanced Diet: Offer a well-balanced diet that suits your specific bird species. This typically includes high-quality pellets, fresh fruits, vegetables, and a limited amount of seeds. Consult with an avian veterinarian to create a tailored nutrition plan.
- Fresh Water: Ensure a constant supply of fresh, clean water. Birds can become dehydrated quickly, so check and refill their water dishes regularly.
- Nutritional Supplements: Depending on your bird’s species and health, your veterinarian may recommend nutritional supplements to address specific dietary deficiencies.
Grooming and Hygiene
- Nail and Beak Care: Regularly check and, if necessary, trim your bird’s nails and beak. Overgrown beaks can lead to health issues and difficulty eating.
- Bathing: Many birds enjoy bathing. Provide a shallow dish of lukewarm water for your bird to splash in, or mist them lightly with a spray bottle. Cleanliness is crucial to their health.
- Feather Health: Keep an eye on your bird’s feathers. Any signs of abnormal molting, feather plucking, or damage should be promptly addressed with a veterinarian.
Social Interaction
- Time and Attention: Birds are social creatures. Spend quality time with your pet daily, talking to them, offering treats, and engaging in interactive play.
- Companionship: Depending on the species, some birds thrive with the companionship of other birds. Consider getting a companion if it suits your bird’s personality and needs.
- Training and Enrichment: Train your bird to perform tricks, follow commands, or use a litter box. Mental stimulation and training are excellent for your bird’s well-being.
Health Care
- Regular Vet Visits: Schedule regular check-ups with an avian veterinarian. These professionals can monitor your bird’s health, provide vaccinations, and address any health concerns.
- Quarantine: If you have multiple birds, quarantine new arrivals for a period to prevent the potential spread of diseases.
- Observation: Be vigilant and observant. Any changes in behavior, appetite, or droppings should be noted and reported to your veterinarian.
In conclusion, caring for white pet birds requires commitment, knowledge, and a genuine love for these avian companions.
By providing them with a clean and enriching environment, a balanced diet, social interaction, and proper health care, you can ensure that your white pet birds enjoy a long, healthy, and happy life as cherished members of your family.
Conclusion
White pet birds are not just pets; they are graceful companions that bring joy and beauty into our lives. Whether you choose a majestic cockatoo, a charming budgie, or a peaceful dove, these birds can become cherished members of your family.
Remember to provide them with love, care, and attention, and you’ll be rewarded with a feathered friend that brightens your days.
For more in-depth information and tips on caring for your white pet bird, feel free to explore our website. We’re here to assist you on your journey to becoming the best pet parent to your avian companion.
Together, let’s create a haven of happiness for your beloved feathered friend.
FAQs About White Pet Birds
Can white pet birds talk like parrots?
Some white pet birds, like cockatoos and budgies, can mimic words and sounds. Training and interaction play a significant role in their speaking abilities.
How long do white pet birds live?
The lifespan varies by species, but on average, white pet birds can live from 10 to 30 years or more with proper care.
Do white pet birds require special lighting?
Providing natural light is essential for their well-being, but supplemental full-spectrum lighting may be necessary in indoor settings.
Are white pet birds high-maintenance?
While they require attention and care, the level of maintenance depends on the species. Some, like doves, are low-maintenance, while others, like cockatoos, need more interaction.
How can I bond with my white pet bird?
Spend time with your bird daily, offering treats, gentle petting, and talking to them. Building trust is key to a strong bond.
Are white pet birds suitable for families with children?
A6: Generally, yes. However, always supervise interactions between birds and young children to ensure safety for both.
Can white pet birds be trained?
Yes, white pet birds can be trained to perform tricks, follow commands, and even potty train. Consistency and positive reinforcement are essential.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”The Ultimate Guide to White Pet Birds!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Birds
Unveiling the Fascinating World of the Kea Bird: A Masterpiece of Nature’s Artistry

Unveiling the Fascinating World of the Kea Bird: A Masterpiece of Nature’s Artistry
Welcome to the captivating realm of the Kea bird! If you’re a nature enthusiast or simply someone who marvels at the wonders of the avian world, you’re in for a treat.
Join us on this exhilarating journey as we dive into the captivating world of these intelligent parrots that call the majestic mountains of New Zealand home.
Discovering the Kea: Nature’s Mischievous Genius
Welcome to a world where intelligence and mischief converge, embodied by the charismatic and cunning Kea bird (Nestor notabilis).

Nestled within the rugged landscapes of New Zealand’s South Island, these enchanting parrots stand as a living testament to nature’s artistry and innovation. These enchanting parrots have a personality that’s as vibrant as their plumage.
Their olive-green feathers, adorned with striking orange underwings, make them a true sight to behold.
A Natural Marvel
The Kea bird’s appearance is a symphony of colors, with its olive-green plumage adorned by vibrant splashes of orange beneath its wings.
This exquisite palette is a masterpiece of evolution, seamlessly blending into the lush greenery of their alpine habitat. However, it’s not just their appearance that captivates; it’s their vibrant personality and astonishing intellect that truly set them apart.
An Enigmatic Personality
Picture this: a bird that possesses a personality akin to a mischievous child, an explorer, and a socialite all in one. That’s the Kea for you.
Renowned for their playful antics and curiosity, these birds have a reputation for engaging in activities that verge on the comical. Backpacks, vehicles, and even unsuspecting hikers become subjects of their inquisitiveness.
Masters of Adaptation
One of the defining traits of the Kea is its remarkable ability to adapt. Living in the challenging environment of the Southern Alps, they’ve become masters of innovation, crafting solutions to navigate the ever-changing landscape.
Their acute problem-solving skills have been showcased through their interactions with novel objects, including puzzle feeders devised by researchers to challenge their intellect.
Curiosity: A Double-Edged Trait
The Kea’s innate curiosity, while endearing, has also brought them into conflict with human activities. While exploring and interacting with humans can be entertaining, it has also led to their involvement in damaging scenarios.
From gnawing on car windscreen wipers to damaging infrastructure, their mischief can sometimes result in unintended consequences.
Social Creatures
In their native habitat, Kea birds are often seen in communal gatherings, socializing with each other in a way that mirrors human interaction. Playful displays, mutual preening, and even gentle “conversations” are all part of their complex social fabric.
Their vocalizations, ranging from high-pitched calls to guttural sounds, contribute to their intricate communication system.
Kea Intelligence Unveiled
Undoubtedly, one of the most fascinating aspects of Kea birds is their intelligence. Their intellect is evident in their foraging strategies, where they’ve been observed using tools to access hard-to-reach food sources.
This level of cognitive prowess has placed them among the few non-mammalian species with the capacity for tool use, showcasing their extraordinary adaptability.
A Mélange of Sounds
The Kea’s vocal repertoire is as diverse as their personalities. From melodious whistles that echo through the mountains to boisterous calls that pierce the air, their vocalizations serve a multitude of purposes.
These range from alerting their companions of potential danger to expressing their emotions, making their soundscape an integral part of their identity.
Kea Conservation: A Shared Responsibility
As we journey deeper into the world of the Kea, it becomes apparent that the delicate balance of their existence rests in the hands of both humans and nature itself.
Conservation efforts play a pivotal role in safeguarding these mischievous geniuses. Predator control, habitat preservation, and responsible tourism are essential steps in ensuring the Kea’s future in the wild.
The Grand Tapestry of Nature
In conclusion, the Kea bird is a testament to nature’s boundless creativity. Their mischievous tendencies, insatiable curiosity, and exceptional intelligence paint a vivid portrait of the wonders that await discovery in the natural world.
As we unravel the layers of their captivating personality and marvel at their resourcefulness, we are reminded of the intricate tapestry that comprises our planet’s diverse inhabitants.
A Charismatic Character: Kea’s Playful Personality
What truly sets the Kea bird apart is its extraordinary personality. These feathered entertainers are brimming with curiosity and mischief.

They’ve been known to interact with humans, investigate backpacks, steal shiny objects, and even mimic sounds. It’s as if they possess a playful spirit that adds a touch of whimsy to the wild landscape they call home.
Playfulness in Flight
From the moment you lay eyes on a Kea bird, its playful spirit is palpable.
Whether engaged in aerial acrobatics, hopping around boulders, or indulging in games with their fellow companions, these avian entertainers embody the joy of living in the present moment.
Their zest for life is infectious, reminding us to relish the simple pleasures that surround us.
Inquisitive Explorers
Picture a curious explorer with feathers – that’s the Kea in a nutshell. Their innate curiosity drives them to investigate anything that piques their interest.
Be it a shiny trinket left unattended or a backpack begging to be inspected, Kea birds approach life with a “Why not?” attitude, transforming ordinary objects into sources of amusement.
Mimicry and Vocal Play
The Kea’s mischievousness extends to their vocal prowess. Not content with a mundane repertoire, they often mimic sounds from their surroundings, both natural and human-made.
Their mimicry isn’t just about copying; it’s a form of vocal play, a way of engaging with their environment and fellow Kea in a language uniquely their own.
Social Shenanigans
Just like a social butterfly fluttering from one gathering to another, Kea birds revel in each other’s company. They engage in boisterous interactions, play-fighting, and even engaging in what seems like animated conversations.
These communal exchanges are a testament to their complex social structure, where bonds are formed through shared play and vibrant communication.
Problem-Solving Prodigies
Kea birds aren’t just about having fun; they’re also adept problem solvers. Their intelligence shines through as they tackle challenges with ingenuity.
From accessing hard-to-reach food sources to navigating complex situations, their analytical minds are always at work. Watching a Kea devise a solution is akin to witnessing a mini genius at play.
Tales of Mischief
It’s not unusual to hear anecdotes of Kea birds engaging in playful pranks. Stories of these avian comedians unscrewing bolts, unraveling shoelaces, and even swooping down to “borrow” snacks from unsuspecting picnickers abound.
Their antics remind us that the line between the animal and human worlds can sometimes blur in the most delightful ways.
A Window into Joy
In essence, the Kea bird’s playful personality serves as a window into the world of unadulterated joy. Their exuberance and spontaneity inspire us to embrace the lighter side of life, to savor the moments that bring a smile to our faces.
As you observe a Kea hop from rock to rock, engage in vocal banter, and investigate the mysteries of their environment, you’ll undoubtedly find a renewed appreciation for the art of playfulness that enriches our lives.
Kea’s Acumen: Exploring Their Intelligence
Prepare to be astonished as we delve into the intricate world of the Kea bird (Nestor notabilis) and unravel the layers of their remarkable intelligence.
These feathered geniuses have earned a reputation for their problem-solving prowess and adaptability, showcasing a level of acumen that continues to captivate researchers and enthusiasts alike.
Cognitive Marvels
Kea’s intelligence is not to be underestimated. Their ability to assess situations, devise strategies, and adapt to new challenges speaks volumes about their cognitive capabilities.
Researchers have conducted various studies that showcase Kea’s knack for navigating complex tasks, positioning them as true cognitive marvels in the avian world.
Tool Use: A Sign of Ingenuity
One of the most awe-inspiring displays of the Kea’s intelligence is their use of tools. While tool use is often associated with mammals, these parrots have shattered that perception.
Observations have revealed Kea birds fashioning sticks and other objects to access food hidden in crevices – a behavior that highlights their ingenuity and ability to think outside the box.
Puzzle Solvers Extraordinaire
Put a puzzle in front of a Kea, and you’re in for a spectacle of problem-solving brilliance.
Researchers have designed intricate puzzles that challenge the birds’ cognitive abilities, from unlocking latches to maneuvering objects to reach rewards.
The Kea’s tenacity in deciphering these puzzles showcases not only their intelligence but also their persistence in the face of challenges.
Social Learning and Innovation
The Kea’s intelligence extends beyond individual problem-solving; it permeates their social interactions as well. These birds are adept at learning from each other, often observing and mimicking behaviors to navigate novel situations.
This social learning and the subsequent innovation demonstrate their capacity for shared knowledge and the development of cultural practices within their community.
Adaptability in the Wild
Survival in the harsh alpine environment demands adaptability, and the Kea bird rises to the challenge with finesse.
Their intelligence allows them to exploit various food sources, from insects to vegetation, ensuring they have a diverse diet even in the face of changing conditions.
This adaptability is a testament to their ability to learn and adjust their behaviors to thrive in their habitat.
The Power of Observation
One remarkable facet of the Kea’s intelligence is their keen observational skills. These birds pay attention to their surroundings, fellow Kea, and even human activities.
This ability to keenly observe their environment aids in identifying potential food sources, detecting threats, and even navigating through man-made obstacles.
A Window into Evolution
The Kea’s intelligence isn’t just a quirk; it’s a glimpse into their evolutionary journey. As inhabitants of a unique and demanding environment, their intelligence has evolved as a survival strategy.
Their cognitive prowess allows them to navigate the challenges of their alpine home, find food, and interact with their fellow Kea in ways that ensure their species’ continued existence.
The Kea’s Culinary Preferences: A Gourmet Adventure
Prepare to embark on a delectable journey into the world of the Kea bird (Nestor notabilis) and its eclectic culinary choices.
These avian gourmands are anything but picky eaters, indulging in a diverse array of foods that showcase their adaptability and resourcefulness in the vibrant landscapes of New Zealand’s alpine regions.
A Whimsical Menu
The Kea’s palate is a true testament to their resourceful nature. From the moment they hatch, their taste buds are primed for adventure.
Their diet reads like a menu crafted by a curious epicurean, featuring a medley of options that span both the animal and plant kingdoms.
Insect Delights
As opportunistic feeders, Kea birds have a penchant for insects that skitter through the undergrowth.
From juicy grubs to crunchy beetles, these protein-packed morsels offer a flavorful feast that satisfies their nutritional needs and showcases their ability to exploit the abundant insect life in their environment.
Berry Bonanza
In the summertime, Kea birds indulge in the colorful bounty of berries. From the succulent sweetness of ripe fruits to the tartness of unripe ones, their taste for berries adds a burst of color to their alpine diet.
These vibrant treats provide a burst of energy, making them a sought-after delicacy in Kea’s culinary repertoire.
Carrion Connoisseurs
The Kea’s resourcefulness extends to Carrion as well. While scavenging may not sound glamorous, it’s a testament to their ability to make the most of available food sources.
Carrion offers a protein-rich option that sustains them through lean times and showcases their adaptability in a landscape where food can be scarce.
Vegetarian Ventures
Kea birds are not exclusively carnivorous; they dabble in vegetarian fare too. Their diet includes various plant matter such as leaves, flowers, and even the nectar of native New Zealand plants.
This vegetarian adventure not only diversifies their diet but also highlights their role in pollinating and shaping the ecosystems they inhabit.
High-Altitude Harvesting
Navigating the alpine landscape isn’t just about finding food; it’s also about the thrill of the hunt.
Kea birds are known to venture to high altitudes, where they nibble on alpine plants and engage in a gourmet adventure that is uniquely their own.
This high-altitude foraging showcases their ability to exploit food sources that other creatures might overlook.
Culinary Adaptations
The Kea’s culinary preferences are a testament to their adaptability. Their ability to thrive on a variety of foods highlights their resourcefulness in a challenging environment.
Whether it’s foraging for insects, feasting on berries, or exploring the treasures of the alpine heights, the Kea’s diet reflects their ability to adjust their menu based on the seasons and the availability of food.
Conservation Concerns: Protecting the Kea’s Kingdom
As we delve into the captivating world of the Kea bird (Nestor notabilis), it becomes apparent that alongside their charismatic charm and intellectual prowess, these magnificent creatures face significant conservation challenges.

Their unique alpine habitat and interactions with human activities have raised concerns, highlighting the need for concerted efforts to safeguard the Kea’s kingdom.
A Precarious Home
Nestled within the stunning landscapes of New Zealand’s Southern Alps, the Kea has carved out a niche in a rugged and challenging environment.
However, the very features that make this habitat picturesque also pose threats. Human activities, including tourism, development, and even unintentional feeding, can disturb their habitat and disrupt their natural behaviors.
Unintended Consequences
The Kea’s playful personality and inquisitive nature have endeared them to many, but these interactions come with unintended consequences.
Their penchant for investigating objects, including vehicles and equipment, can lead to damage and conflicts. Moreover, their affinity for human food can result in dependency and even health issues, further underlining the need for responsible coexistence.
Predation Predicaments
Predation poses another challenge to Kea’s survival. Introduced predators such as stoats, rats, and possums can threaten their nests and young, jeopardizing the next generation of these intelligent birds.
Conservation efforts often involve predator control to mitigate this risk and give the Kea population a fighting chance to thrive.
Ethical Eco-Tourism
Tourism can be a double-edged sword for the Kea. While visitors are drawn to these charismatic parrots, their presence can inadvertently disturb the birds’ natural behaviors.
Responsible eco-tourism practices, including maintaining a respectful distance and adhering to codes of conduct, are crucial to minimizing human impact on Kea habitats.
Preservation Initiatives
A glimmer of hope lies in the ongoing conservation initiatives aimed at protecting the Kea’s kingdom.
Researchers, conservationists, and government bodies are collaborating to implement measures that balance human interests with Kea’s well-being.
Predator control programs, habitat restoration, and public education campaigns all play pivotal roles in securing the Kea’s future.
Community Engagement
Conservation success hinges on community engagement and awareness. Efforts to foster understanding about the Kea’s importance in the ecosystem and the challenges they face are vital.
By cultivating a sense of stewardship and responsibility, we empower communities to actively participate in safeguarding these remarkable birds and their unique habitat.
A Call to Action
In conclusion, the Kea’s kingdom is a delicate balance of natural wonders and human activities. As we continue to be enchanted by their mischievous personalities and remarkable intelligence, we must also acknowledge our role in their conservation.
By promoting ethical interactions, supporting preservation efforts, and fostering a culture of coexistence, we can ensure that the Kea’s kingdom remains a haven for generations to come.
Let us unite to protect these avian wonders and preserve the magic of the Southern Alps for both the Kea and future generations to cherish.
Kea Tourism: A Glimpse into Their World
Venture into the heart of New Zealand’s Southern Alps, where a unique and captivating experience awaits – an encounter with the enchanting Kea bird (Nestor notabilis).
As you embark on a journey of eco-tourism, you’ll not only witness the Kea’s charismatic antics but also gain insights into their habitat and the delicate balance between human exploration and wildlife conservation.
A Majestic Playground
Imagine standing amidst the breathtaking alpine landscape, surrounded by rugged peaks and pristine wilderness. This is the backdrop against which the Kea thrives.
With their olive-green plumage contrasting against the snowy backdrop, these intelligent parrots add a touch of vibrancy to the awe-inspiring scenery.
Curious Companions
Kea birds are natural-born explorers, and as an eco-tourist, you have the privilege of observing their curiosity up close.
From watching them hop from rock to rock to witnessing their playful interactions with each other, you become part of a fascinating narrative that reveals the intricate social dynamics and behaviors of these charismatic creatures.
Guided Insights
Eco-tourism initiatives offer the chance to engage with knowledgeable guides who provide insights into the Kea’s world.
They share anecdotes, facts, and observations that enrich your experience, giving you a deeper understanding of the challenges these birds face and the conservation efforts that are in place to protect them.
Respectful Encounters
While the allure of observing Kea birds is strong, it’s essential to approach the experience with respect for their habitat and well-being.
Guided tours prioritize responsible wildlife viewing, ensuring that visitors maintain a safe distance and avoid actions that may disturb the birds. This commitment to ethical interactions respects Kea’s need for a peaceful environment.
Capturing Moments
Photography enthusiasts are in for a treat during Kea-focused eco-tourism outings. The chance to capture candid shots of Kea birds in their natural habitat is a rare privilege.
As you freeze moments of their playfulness, exploration, and interactions, you’re not only creating cherished memories but also sharing the beauty of these birds with a wider audience.
Leaving a Legacy
Your participation in Kea tourism goes beyond a single experience. By fostering a connection with these birds and their habitat, you become an advocate for their conservation.
Sharing your insights and experiences with others spreads awareness about the delicate balance between human enjoyment and the need to protect the Kea’s kingdom.
In Conclusion: A Tribute to Nature’s Marvel
The Kea bird stands as a remarkable testament to the diversity and brilliance of Earth’s inhabitants.
With its inquisitive spirit, vibrant plumage, and unique behaviors, this avian genius captures our hearts and fuels our admiration for the wild wonders that grace our world.
As we venture forward, let’s strive to preserve and protect the Kea’s mountain kingdom, ensuring that its playful presence continues to enchant generations to come.
FAQ: Your Kea Questions Answered
Are Kea birds endangered?
Kea birds are classified as vulnerable due to habitat loss and interactions with humans.
Do Kea birds make good pets?
Kea birds are wild creatures and are not suitable as pets due to their complex needs and protected status.
Can Kea birds imitate human speech?
While not as proficient as some parrot species, Kea birds can learn to mimic simple sounds and words.
Why are Kea birds so curious?
Curiosity is a survival trait, helping them find food and adapt to their ever-changing environment.
What is the best way to observe Kea birds without disturbing them?
Join guided eco-tours that prioritize ethical wildlife viewing and maintain a respectful distance.
Do Kea birds mate for life?
Kea birds are known to form long-lasting bonds, often choosing a lifelong mate.
What is being done to conserve Kea populations?
Conservation organizations and the New Zealand government are implementing predator control and educational initiatives to protect Kea birds.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Unveiling the Fascinating World of the Kea Bird: A Masterpiece of Nature’s Artistry!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
-

 Pet Care2 years ago
Pet Care2 years agoThe Best Dog Collars For 2022
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoBichon Frise: The Happy, Playful, and Cuddly Companion
-

 Trending Pet Stories1 year ago
Trending Pet Stories1 year ago2023 ‘World’s Ugliest Dog’ Winner: Scooter’s Tale of Resilience
-

 Animals2 years ago
Animals2 years agoAre There Animals Having Down Syndrome?
-

 Pets2 years ago
Pets2 years agoThe Fascinating World Of The Red Chameleon
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Dog Breeds According To AKC.
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years ago21 Dog Breeds That Resemble Bears Or Teddy Bears!
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoEskimo Dogs from Canada – What Are They? – Find Out!