Fish
Unveiling The Mysteries Of The Hammerhead Sharks: A Deep Dive

Unveiling the Mysteries of the Hammerhead Sharks: A Deep Dive
When we talk about unique marine life, hammerhead sharks undoubtedly top the list. With their peculiarly shaped heads and majestic swimming style, these creatures fascinate and intrigue.
But what is it that makes these underwater marvels so unique? Let’s embark on a deep dive into the world of hammerhead sharks.
The Hammerhead Sharks: An Overview
The hammerhead sharks, a member of the Sphyrnidae family, are one of the most distinctive species of sharks, thanks to their ‘hammer-shaped’ heads, known as cephalofoils. This unusual physical trait sets them apart, making them an intriguing subject of study among marine biologists worldwide.
Hammerhead sharks, a unique and fascinating species, are truly a sight to behold in the vast underwater world. Found globally in warm, tropical waters, these fascinating creatures of the deep have piqued the interest of scientists, divers, and marine enthusiasts alike.
This overview offers a glimpse into their captivating world, exploring their distinctive attributes, dietary habits, and fascinating behavior.
Unmistakable Appearance
The most distinguishing characteristic of hammerhead sharks is undoubtedly their oddly shaped heads, called cephalofoils.
This ‘hammer-like’ head, extending laterally from each side of the body, gives the shark its common name and sets it apart from other shark species.
Hammerheads belong to the family Sphyrnidae, which encompasses nine recognized species varying in size, from the small bonnethead to the massive great hammerhead. The latter can grow up to 20 feet in length, making it one of the larger sharks in the ocean.
Their bodies, streamlined and powerful, are built for efficient hunting. Combined with their unique head shape, hammerhead sharks are agile swimmers, capable of swift turns and sudden maneuvers.
Delving Deeper: Understanding the Hammerhead’s Distinctive Head Shape
The characteristic ‘hammer-shaped’ head or cephalofoil of hammerhead sharks is more than just an intriguing physical trait—it is a fascinating evolutionary adaptation that equips these marine predators with superior sensory abilities.
The Structural Blueprint of the Cephalofoil
To understand the benefits of the cephalofoil, we must first appreciate its unique structure. The cephalofoil’s broad, flat shape allows for a wider distribution of sensory organs across the shark’s head.
This layout improves their ability to scan larger areas in search of prey. It also provides better depth perception due to the wide spacing of the eyes on either side of the cephalofoil.
Enhancing Vision: The Binocular Overlap
Hammerhead sharks have eyes positioned on the ends of their hammer-shaped head, creating a wider field of vision compared to other sharks.
This unique arrangement also leads to binocular overlap—an area where the fields of vision from both eyes intersect. This overlap significantly enhances their depth perception and accuracy in striking prey.
The Role of Cephalofoil in Hunting and Maneuvering
The design of the hammerhead’s cephalofoil also benefits their hunting techniques and maneuvering capabilities. Hammerheads use their broad heads to pin down stingrays, one of their preferred meals, onto the ocean floor.
This allows them to attack their prey effectively, despite the stingray’s dangerous barbs.
When it comes to maneuvering, the cephalofoil acts like an airplane’s wing, providing lift and enabling the shark to make sharp turns and ascend in the water quickly.
This maneuverability is an advantage during hunting, allowing hammerheads to track and capture agile prey.
Electroreception: An Advanced Sensory System
All sharks possess a remarkable sensory system known as electroreception, which allows them to detect electric fields produced by other marine organisms. This is crucial for locating prey, even when hidden under the sand.
In hammerheads, the wide spacing of the electroreceptive organs, or the ampullae of Lorenzini, across the cephalofoil, enhances their ability to detect these electrical signals, making their hunting prowess even more impressive.
In essence, the peculiar head shape of the hammerhead sharks is a testament to the marvels of evolutionary adaptation, enhancing their sensory perception, hunting skills, and maneuverability, making them one of the ocean’s most unique and efficient predators.
A Closer Look: A Glimpse into the Behavior of Hammerhead Sharks
Hammerhead sharks are fascinating creatures with intriguing behavioral patterns that set them apart in the oceanic world.
From their unique schooling behavior to their mating rituals, each aspect of their behavior further cements their standing as unique marine species.
Schooling Behavior: An Unusual Trait Among Sharks
While many shark species are solitary predators, hammerhead sharks are known for their unusual schooling behavior. During the day, these sharks can be observed in large groups, often numbering in the hundreds, cruising along the ocean currents.
This behavior is particularly noticeable in young hammerheads, which move in schools for protection against larger predators.
The exact reason for this social behavior in adult hammerheads is still a topic of scientific debate, with theories ranging from enhanced hunting success to social learning.
Hunting Techniques: An Adaptation of Stealth and Speed
Hammerhead sharks are renowned hunters, using their unique head shape to their advantage. They are known to employ stealth, speed, and a keen sense of electroreception to locate and capture their prey.
They use their broad, flat heads to pin down stingrays, their favorite prey, onto the seafloor before delivering a fatal bite.
Migratory Patterns: Following the Seasons and Food
Hammerhead sharks also exhibit strong migratory behavior, guided primarily by the change in seasons and food availability. During the summer, they are observed to migrate to cooler waters, often traveling thousands of kilometers.
This long-distance migration, coupled with their high-energy hunting technique, testifies to their remarkable endurance and adaptability.
Reproduction: Viviparous Birth and Mating Rituals
When it comes to reproduction, hammerhead sharks display a behavior known as viviparity, where the female gives birth to live young. This contrasts with many other shark species that lay eggs (oviparity) or have eggs that hatch within the mother (ovoviviparity).
The mating process in hammerheads involves the male biting the female’s pectoral fin—a behavior that, while seemingly aggressive, is a normal part of their reproductive ritual.
Interaction with Humans: A Need for Caution and Conservation
Despite their fearsome reputation, hammerhead sharks are generally not a threat to humans. However, their curiosity and territorial behavior can lead to encounters that require caution from humans.
Unfortunately, hammerhead sharks face significant threats from human activities, such as overfishing and habitat degradation. This underlines the need for increased conservation efforts to protect these unique marine creatures.
Solitude vs. Sociability: A Deep Dive into Hammerheads’ Surprising Behavior
When we talk about sharks, an image of a solitary, menacing predator often comes to mind. However, hammerhead sharks break this mold with their interesting blend of sociability and solitude, depending on various factors such as age, time, and need for protection or hunting.
Social Butterflies of the Sea: Hammerhead Sharks in Groups
One of the most striking aspects of hammerhead sharks’ behavior is their tendency to form large schools, especially during the day.
Unlike most other sharks that lead a solitary existence, hammerheads can often be found cruising the warm ocean currents in groups that can number into the hundreds.
This schooling behavior is particularly prominent among juvenile hammerheads, which seek safety in numbers from potential predators.
But what about adults? The sociability of adult hammerheads continues to baffle scientists. Some theories suggest this schooling behavior may enhance their hunting success.
Others propose that it may facilitate social learning or serve a purpose in mating rituals. However, the exact reasons behind this behavior in adult hammerheads remain unclear and warrant further research.
The Solitary Hunters: Nighttime Behavior of Hammerheads
When the sun sets, the social hammerheads undergo a behavioral shift. They disperse from their schools and become solitary predators, navigating the vast ocean depths in search of prey.
Their unique hammer-shaped head aids them in this solitary endeavor, giving them a wide field of vision and the ability to detect electric signals from hidden prey.
The Balance Between Solitude and Sociability
The blend of solitude and sociability in hammerheads is not an ‘either-or’ situation but rather a balance that these sharks strike based on their needs.
During the day, the safety and possible advantages offered by schooling outweigh the benefits of solitude. However, as night falls, the scales tip in favor of solitary hunting.
The sociability of hammerheads is a fascinating deviation from the norm among sharks, offering a unique window into the diverse behavioral patterns within the shark world.
The balance they strike between sociability and solitude reflects their adaptability and the complex dynamics of life in the ocean.
As we continue to explore these behavioral intricacies, we come one step closer to understanding and conserving these incredible marine creatures.
Decoding the Hammerhead’s Diet
The diet of the hammerhead shark is a fascinating aspect of its biology, shedding light on its feeding habits, hunting techniques, and the ecological role it plays within its marine habitat.
Hammerheads’ Preferred Menu: A Predominantly Carnivorous Diet
Hammerhead sharks, like many other species of sharks, are carnivorous creatures.
Their menu predominantly includes a variety of marine animals that comprise both invertebrates and vertebrates. Key prey items include a variety of fishes, cephalopods like squids and octopuses, and crustaceans such as crabs.
However, the standout feature in their diet is their particular preference for stingrays. The unique design of the hammerhead’s head, known as a cephalofoil, facilitates the detection of these bottom-dwelling creatures.
Their wide-set eyes provide a better visual range, and the expansive ‘hammer’ houses numerous electroreceptors that can sense the electrical signals emitted by stingrays hiding in the sandy seafloor.
The Peculiar Case of the Bonnethead Shark
Among the hammerhead species, the bonnethead shark (Sphyrna tiburo) deserves special mention. This smaller cousin of the hammerhead has recently made headlines as the only known omnivorous shark species.
Research has found that a significant portion of its diet, around 60%, comprises seagrass, a type of marine plant. This surprising revelation challenges the conventional belief that all sharks are strictly carnivorous and underlines the diversity within the hammerhead family.
Feeding Techniques: How Hammerheads Catch Their Prey
When it comes to catching prey, hammerheads use a combination of stealth, speed, and their unique head shape. They primarily rely on surprise attacks, often approaching their prey from below or the side to maximize their chances of success.
Their distinctive head shape also allows them to pin down stingrays, their preferred meal, to the seafloor, rendering the rays’ dangerous barbs useless. The broad cephalofoil also aids in making sharp turns and agile maneuvers, making them efficient predators.
In summary, the diet of hammerhead sharks not only speaks volumes about their hunting prowess but also highlights the diversity within the species.
From consuming a variety of marine creatures to the bonnethead’s unusual omnivorous diet, hammerhead sharks showcase a wide range of dietary habits that continue to intrigue scientists worldwide.
The Conservation Status: A Cry for Help
The sobering truth about hammerhead sharks, despite their magnificent evolutionary achievements and fascinating behavior, is that they are under significant threat, with their survival hanging in the balance.
Hammerheads on the Brink: Facing Extinction Risk
Regrettably, many species of hammerhead sharks, including the Great hammerhead (Sphyrna mokarran) and the Scalloped hammerhead (Sphyrna lewini), are listed as “Endangered” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. This classification signals that these species face a high risk of extinction in the wild if current trends persist.
The Main Threats: Overfishing and Habitat Degradation
The main threats to hammerhead populations worldwide are overfishing and habitat degradation. Hammerheads are targeted for their fins, which are highly prized in certain cultures for use in shark fin soup, a traditional Asian delicacy.
This practice, known as ‘finning’, involves catching the sharks, cutting off their fins, and often discarding the still-living shark back into the ocean, where it meets a grim fate.
Habitat degradation, another significant threat, is primarily due to coastal development, pollution, and climate change. These factors affect the quality of coastal waters and can have damaging impacts on the reproductive success and survival of these sharks.
Conservation Efforts: Hope for the Hammerheads
Despite the grim outlook, there are numerous ongoing conservation efforts aimed at saving these remarkable creatures from extinction.
These include the implementation of stricter fishing regulations, the creation of marine protected areas, and campaigns to raise awareness about the ecological importance of sharks and the threats they face.
International treaties like the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) also provide some protection for hammerhead sharks by regulating international trade of these species.
However, more extensive and globally coordinated efforts are urgently needed to halt the decline in hammerhead populations and ensure the survival of these unique and important marine creatures.
Why Should We Care About Hammerhead Sharks?
There is a profound interconnectedness within nature, and the survival of every species, including the hammerhead sharks, is instrumental in maintaining a balanced ecosystem. Let’s delve deeper into why these fascinating creatures matter.
Guardians of the Marine Ecosystem
Hammerhead sharks play an indispensable role as apex predators in the ocean’s ecosystem. By controlling the population size of their prey, they help prevent the overpopulation of certain species and ensure biodiversity.
They also promote the health of these populations by typically preying on the sick or weaker individuals.
A Biological Marvel
From their distinctive head shape to their exceptional sensory abilities, hammerheads are a testament to the marvels of evolution.
Their unique characteristics provide a wealth of information for scientific research, offering insights into shark biology, behavior, and evolution.
A Source of Eco-tourism
In regions where they are known to frequent, hammerhead sharks attract divers and marine enthusiasts, thereby contributing to local economies through eco-tourism.
Dive tourism that focuses on viewing these sharks, particularly in the Galapagos Islands, Bahamas, and Cocos Island, provides sustainable economic alternatives to harmful fishing practices.
Indicator of Ocean Health
Hammerhead sharks, like other large marine species, are considered indicator species. Their well-being directly reflects the health of our oceans.
A decline in hammerhead shark populations often signals larger issues within the marine ecosystem, such as overfishing or climate change.
In essence, preserving hammerhead sharks is not only vital for maintaining ecological balance, it also has economic, scientific, and environmental significance.
Their decline should concern us all, as it not only spells a loss of biodiversity but also indicates broader challenges facing our marine ecosystems.
It is our responsibility to ensure that future generations also get to marvel at these incredible creatures and enjoy the benefits of healthy, vibrant oceans.
Conclusion
Hammerhead sharks, with their distinct appearance and fascinating behavioral patterns, continue to captivate us. As we continue to explore their world, it becomes increasingly apparent that we need to take urgent steps to protect these creatures and the oceans they call home.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs)
How many species of hammerhead sharks are there?
There are nine recognized species of hammerhead sharks.
Why do hammerhead sharks have a hammer-shaped heads?
The hammer-shaped head enhances sensory perception and aids in hunting.
Are hammerhead sharks dangerous to humans?
While any large shark can be potentially dangerous, hammerhead sharks are generally not a threat to humans.
What is the largest species of hammerhead shark?
The Great Hammerhead is the largest species, growing up to 20 feet long.
How long do hammerhead sharks live?
Hammerhead sharks can live up to 30 years in the wild.
Where are hammerhead sharks usually found?
Hammerhead sharks are found in warmer waters along coastlines and continental shelves worldwide.
What can I do to help with hammerhead shark conservation?
Supporting organizations that work towards shark conservation, spreading awareness, and advocating for policies against overfishing can contribute to hammerhead shark conservation.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Unveiling The Mysteries Of The Hammerhead Sharks: A Deep Dive!?”
Please you should feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Fish
Unlocking the Secrets of Goldfish Longevity: How Long Do Goldfish Live?
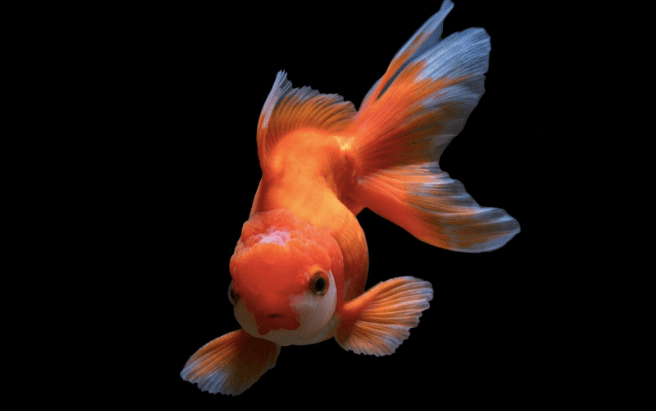

Unlocking the Secrets of Goldfish Longevity: How Long Do Goldfish Live?
Goldfish are one of the most popular and beloved pets around the world. With their vibrant colors and graceful swimming, they bring beauty and tranquility to any home or office aquarium.
But have you ever wondered how long these fascinating creatures can live?
In this article, we will explore the lifespan of goldfish and provide you with valuable insights to help you care for your aquatic companions.
Factors Affecting Goldfish Lifespan
The lifespan of goldfish can vary significantly depending on several factors. While some goldfish may live for only a few years, others have been known to live for several decades. Here are the key factors that influence the lifespan of goldfish:
1. Genetics
Just like humans, the genetic makeup of goldfish plays a crucial role in determining their lifespan. Some goldfish breeds are naturally hardier and have a longer lifespan, while others may be more prone to genetic health issues that can shorten their life expectancy.
2. Water Quality
Providing a clean and well-maintained environment is essential for the health and longevity of goldfish. Poor water quality, such as high levels of toxins or inadequate oxygenation, can significantly impact their lifespan. Regular water changes and proper filtration systems are crucial to ensure optimal water conditions.
3. Diet and Nutrition
A balanced and nutritious diet is vital for the overall health of goldfish. Feeding them a variety of high-quality commercial fish food, supplemented with occasional treats like vegetables or live food, can help support their immune system and promote a longer lifespan.
4. Tank Size and Environment
The size of the tank and the overall living environment have a direct impact on the well-being of goldfish. Providing enough space for them to swim and grow is essential. Overcrowding can lead to stress, poor water quality, and increased susceptibility to diseases, ultimately shortening their lifespan.
Average Lifespan of Goldfish
On average, goldfish can live anywhere between 10 to 15 years. However, with proper care and optimal conditions, some goldfish have been known to live up to 20 years or even longer. It’s important to note that the lifespan of goldfish can vary depending on the factors mentioned above.
Longevity Records of Goldfish
While the average lifespan of goldfish is around 10 to 15 years, there have been exceptional cases of goldfish living much longer. Here are a few notable records:
1. Tish, the Goldfish
Tish, a goldfish from the United Kingdom, held the record for the longest-lived goldfish. She lived for an impressive 43 years before passing away in 1999. Tish’s longevity was attributed to her owner’s meticulous care and a healthy environment.
2. Goldie, the Carassius auratus
Goldie, a goldfish from Australia, made headlines when she celebrated her 45th birthday in 2005. Her owner, who had inherited her from his grandmother, ensured she received excellent care and a spacious tank to thrive.
3. Fred, the Goldfish
Fred, a goldfish from the United States, lived for an astounding 41 years. His owner diligently maintained his tank, providing him with a balanced diet and a stress-free environment.
Tips for Extending Your Goldfish’s Lifespan
If you want your goldfish to live a long and healthy life, here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Provide a spacious tank with ample room for swimming.
- Maintain clean water by performing regular water changes.
- Invest in a reliable filtration system to keep the water properly oxygenated.
- Feed your goldfish a balanced diet of high-quality fish food.
- Avoid overfeeding, as it can lead to obesity and health issues.
- Monitor the water temperature to ensure it remains within the recommended range for goldfish.
- Keep an eye out for any signs of illness or distress and seek veterinary care if needed.
By following these guidelines and providing your goldfish with the care they need, you can help ensure they live a long and fulfilling life.
Conclusion
Goldfish are captivating creatures that bring joy and serenity to their owners. With proper care and attention to their needs, goldfish can live for many years, becoming cherished members of the family.
Remember to consider the genetic factors, water quality, diet, and tank size when caring for your goldfish. By providing them with a healthy and nurturing environment, you can maximize their lifespan and create a thriving aquatic habitat.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Unlocking the Secrets of Goldfish Longevity: How Long Do Goldfish Live?!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Fish
Unlocking the Secrets to Goldfish Longevity: A Comprehensive Guide
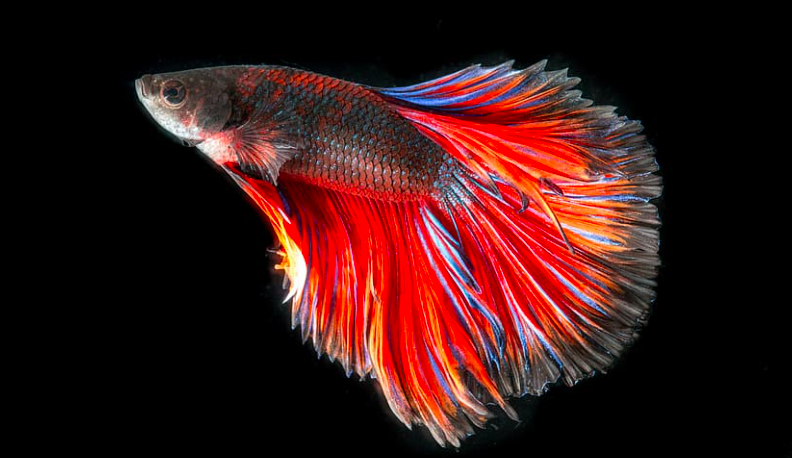

Unlocking the Secrets to Goldfish Longevity: A Comprehensive Guide
Goldfish enthusiasts, buckle up! Today, we dive deep into the fascinating world of goldfish longevity, uncovering the secrets to ensuring your aquatic companions live their happiest, healthiest, and longest lives.
Whether you’re a seasoned goldfish aficionado or a newbie to the aquatic realm, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to keep your underwater friends thriving.
Understanding the Basics: What Influences Goldfish Longevity
Goldfish, those shimmering aquatic companions adorning our homes, bring a touch of serenity to our lives. However, ensuring the longevity of these mesmerizing creatures goes beyond just feeding them regularly.

In this deep dive into the world of goldfish care, we unravel the essential factors that influence their longevity.
1. Choosing the Right Environment
Creating a conducive habitat for your goldfish is paramount. Start with an adequately sized aquarium, allowing at least 20 gallons per fish.
Proper filtration is equally crucial, maintaining water quality and reducing stress. Remember, a stress-free goldfish is a healthy goldfish.
2. Water Quality Matters
The phrase “as happy as a fish in water” holds true only when the water quality is optimal. Regular water changes, maintaining appropriate pH levels, and investing in a reliable water testing kit are indispensable practices.
These actions contribute significantly to the overall well-being and longevity of your goldfish.
3. Nutritious Diet for Longevity
Just like any pet, a goldfish’s diet plays a pivotal role in its overall health and longevity. Provide a well-balanced diet that includes high-quality flakes, pellets, and occasional treats like live or frozen brine shrimp. Avoid overfeeding, as it can lead to health complications.
4. Adequate Space for Growth
Goldfish have the potential for substantial growth. Stunting, a common issue, occurs when they are kept in cramped environments. Ensure your goldfish have enough space to grow naturally, promoting a healthier and longer life.
5. Companionship and Tank Mates
Goldfish are social creatures, and companionship can positively impact their mental well-being. However, not all fish make suitable tank mates. Research and carefully choose compatible species to avoid stress and potential conflicts.
6. Regular Health Check-ups
Prevention is better than cure, even in the underwater world. Conduct regular health check-ups, examining your goldfish for signs of illness. Promptly address any issues to prevent the spread of diseases, ensuring a longer and happier life.
7. Temperature Control
Maintaining a stable water temperature is crucial for goldfish longevity. Fluctuations in temperature can lead to stress and susceptibility to diseases. Invest in a reliable aquarium heater and monitor the temperature consistently.
8. Genetics and Breeding
The genetic makeup of your goldfish plays a vital role in determining its lifespan. Opt for reputable breeders to ensure healthier genetics. Moreover, responsible breeding practices contribute to the overall well-being of goldfish populations.
9. Environmental Enrichment
Goldfish, despite their calm demeanor, benefit from environmental enrichment. Incorporate decorations, plants, and hiding spots in the aquarium. This not only adds aesthetic value but also provides mental stimulation for your aquatic friends.
10. Regular Observations and Interaction
Understanding your goldfish requires regular observations. Take time to interact with your aquatic companions, learning their behavior patterns. Early detection of any deviations from normal behavior can be instrumental in preventing potential health issues.
Common Mistakes to Avoid: Pitfalls in Goldfish Care
Embarking on the journey of goldfish care is a rewarding experience, but pitfalls lurk along the way. To ensure the well-being and longevity of your aquatic companions, let’s delve into the common mistakes that many unwitting enthusiasts often make.

1. Overcrowded Tanks: The Space Conundrum
One prevalent mistake is underestimating the space goldfish require. Overcrowded tanks lead to stress, stunted growth, and increased vulnerability to diseases. Ensure your goldfish have ample space to swim and grow by following appropriate stocking guidelines.
2. Neglecting Water Quality: A Silent Menace
Perhaps the most critical factor in goldfish care is water quality. Neglecting regular water changes, failing to monitor pH levels, and overlooking filtration systems can result in poor water quality. This, in turn, jeopardizes the health and longevity of your goldfish.
3. Inappropriate Tank Mates: The Compatibility Quandary
While companionship is beneficial, selecting incompatible tank mates can lead to aggression, stress, and even injury. Research thoroughly to identify suitable tank mates, considering size, temperament, and environmental preferences.
4. Overfeeding Woes: Too Much of a Good Thing
The adage “less is more” holds true in goldfish feeding. Overfeeding not only pollutes the water but also contributes to health issues like swim bladder disorder. Follow a balanced feeding schedule and avoid the temptation to shower your goldfish with excessive treats.
5. Inconsistent Temperature Control: The Rollercoaster Effect
Goldfish thrive in stable environments. Fluctuating temperatures can stress your aquatic friends and make them susceptible to diseases. Invest in a reliable aquarium heater and maintain a consistent water temperature within the recommended range.
6. Lack of Observation: Ignoring Behavioral Cues
Neglecting to observe your goldfish regularly can result in late detection of health issues. Changes in behavior, appetite, or swimming patterns may indicate underlying problems. Stay vigilant and address any deviations promptly.
7. Poor Diet Choices: Nutritional Neglect
Goldfish need a well-balanced diet for optimal health. Relying solely on one type of food or feeding inappropriate treats can lead to nutritional deficiencies. Consult with experts or veterinarians to create a nutritionally balanced diet for your goldfish.
8. Overlooking Tank Maintenance: The Dirty Dilemma
A clean tank is a happy tank. Neglecting regular maintenance tasks such as cleaning filters, removing debris, and scrubbing algae can compromise water quality and create an unhealthy environment for your goldfish.
9. Ignoring Genetic Factors: The Breeder’s Impact
Choosing a goldfish from a reputable breeder is crucial. Poor breeding practices can result in genetic predispositions to illnesses and shorter lifespans. Research breeders and opt for those known for responsible breeding.
10. Skipping Quarantine: A Preventive Measure
Introducing new fish without quarantine can introduce diseases into your aquarium. Always quarantine new additions to monitor their health before introducing them to the main tank, preventing potential outbreaks.
Health Check: Identifying and Addressing Goldfish Ailments
Goldfish, with their dazzling scales and captivating swim, are delightful pets. However, even the most dedicated owners can encounter health challenges.
In this guide, we delve into the art of identifying and addressing common goldfish ailments to ensure your finned friends lead long and healthy lives.
1. Recognizing Signs of Illness
Understanding your goldfish’s normal behavior is the first step in identifying health issues. Watch for changes in appetite, swimming patterns, coloration, and the appearance of fins or scales. Any deviations from the norm may be indicative of an underlying problem.
2. Common Goldfish Ailments
a. Ich (White Spot Disease): This prevalent parasite manifests as small white dots on the skin, fins, and gills. Quarantine affected fish, gradually raise the water temperature, and treat with a suitable medication.
b. Fin Rot: Recognized by ragged fins or tail, fin rot is often caused by poor water quality. Improve water conditions, remove any decaying matter, and administer antibiotic treatments as necessary.
c. Swim Bladder Disorder: Affecting buoyancy, swim bladder issues result in floating or sinking. Adjust feeding habits, offer a diet with more fiber, and consider a temporary fasting period.
d. Dropsy: Characterized by swollen body and scales, dropsy indicates internal organ failure. Isolate the affected fish, enhance water quality, and consult a vet for antibiotics.
3. Proactive Measures for Preventing Illness
a. Maintain Water Quality: Regular water changes, proper filtration, and monitoring water parameters are fundamental in preventing a myriad of health issues.
b. Quarantine New Additions: Before introducing new fish to your aquarium, quarantine them to prevent the spread of potential diseases.
c. Balanced Diet: Provide a varied and nutritious diet to boost the immune system. Avoid overfeeding, as it can lead to digestive problems.
d. Adequate Space: Avoid overcrowding in the tank, as it can stress fish and contribute to the spread of diseases.
4. Consulting a Vet: When and Why?
Knowing when to seek professional help is crucial. If home remedies prove ineffective or if the condition worsens, consult a vet experienced in aquatic animal care. Early intervention can make a significant difference in your goldfish’s recovery.
5. Isolation and Medication
When you notice signs of illness, promptly isolate the affected fish to prevent the spread of diseases. Follow the recommended dosage of medications, and complete the treatment course even if the fish appears to recover sooner.
6. Stress Management
Goldfish are sensitive to changes in their environment. Minimize stress by maintaining a stable environment, avoiding sudden changes, and providing adequate hiding spots.
Conclusion: Nurturing the Fountain of Youth for Goldfish
In the delicate dance of goldfish care, the key to unlocking the fountain of youth lies in our hands. By avoiding common pitfalls, embracing proper nutrition, and crafting a haven of harmony, we bestow upon our aquatic companions the gift of vitality.
As custodians of their underwater world, our choices ripple through their scales, shaping a narrative of joy, longevity, and the timeless beauty found in a well-tended aquarium.
Here’s to the enduring health and happiness of our finned friends, and the shared moments that unfold within the watery embrace of their home.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can goldfish live in bowls?
Goldfish need ample space to thrive. Bowls are too small and lack proper filtration, leading to poor water conditions and health issues. Opt for a spacious tank instead.
How often should I feed my goldfish?
Feed your goldfish small, regular meals 2-3 times a day. Monitor their consumption and adjust accordingly to prevent overfeeding.
Are goldfish hardy pets?
While goldfish are hardy, they require proper care. Neglecting their needs can result in health issues. With the right care, they make resilient and long-lived companions.
Do goldfish get bored?
Yes, goldfish can get bored. Introduce toys, mirrors, and novel elements to their environment to keep them mentally stimulated.
Can I keep different goldfish breeds together?
Compatibility is crucial. Research the specific needs and temperaments of different goldfish breeds before introducing them to the same tank.
Embrace these insights, and you’ll be well on your way to unlocking the secret to goldfish longevity. Your aquatic friends will thank you with a lifetime of joy and vibrant underwater adventures.
Note: This article is not intended as veterinary advice. Consult with a qualified professional for specific concerns regarding your goldfish’s health.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Unlocking the Secrets to Goldfish Longevity: A Comprehensive Guide!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Fish
Best Tank Mates for Betta Fish: A Beginner’s Guide

Curating a harmonious aquarium for your betta fish involves choosing compatible tank mates that ensure a tranquil environment.
Bettas, with their flamboyant fins and solitary nature, require companions that respect their space and don’t compete for dominance. This beginner’s guide highlights the best tank mates that align with the betta’s need for peace and stability.
By selecting the right fish, you’ll not only enhance your betta’s wellbeing but also foster a vibrant and diverse aquatic ecosystem.
Remember, keeping a well-balanced tank is not just about aesthetics, it’s crucial for maintaining the health and happiness of all your finned friends.
Understanding Betta Fish Behavior
As a beginner, understanding the unique personality of your finned friend is critical to choosing the perfect tank mates. Let’s delve into the behavior of betta fish to set the stage for a peaceful aquarium environment.
Territorial Nature Of Betta Fish
Betta fish, also known as Siamese fighting fish, are renown for their territorial instincts. These fish often guard their space fiercely against intruders. Recognizing this trait is key. It helps prevent unwelcome confrontations in your tank.
- Males are particularly territorial.
- Display aggressive behaviors like flaring fins and gill covers.
- Small spaces amplify this nature.
Compatibility Factors To Consider
Selecting tank mates for your betta involves careful consideration. Not all fish or aquatic animals are suitable companions.
| Factor | Description |
| Temperament | Choose peaceful species that won’t provoke your betta. |
| Size | Opt for similar sized fish to prevent bullying. |
| Activity Level | Active fish may stress bettas; opt for calmer species. |
Importance Of Tank Size And Layout
A spacious tank is non-negotiable for a harmonious habitat. Smaller tanks increase tension and stress for your betta.
Good tank layout features ample hiding spots and plants. This helps diffuse tension among inhabitants.
- Opt for tanks 10 gallons or larger.
- Include caves and foliage for retreats.
- Avoid cramped conditions.
Top Tank Mate Options
Finding the perfect companions for your Betta fish calls for care. Some critters live well with Betta fish. Let’s explore the top tank mate options to make your aquarium a peaceable kingdom.
Snail Species
Bettas and snails make a great team. Snails are hardy and keep to themselves. They help clean the tank too. Look at these snail friends for your Betta:
- Nerite Snails: They eat algae and don’t breed in freshwater.
- Mystery Snails: These come in bright colors and move around a lot.
Shrimp Varieties
Shrimp can share a tank with Bettas. They are peaceful and clean up leftovers. Check out these shrimp types:
- Ghost Shrimp: Clear bodies and are good cleaners.
- Cherry Shrimp: Red color may attract Bettas, so watch them.
Neon Tetras
Neon Tetras are small and speedy. They shimmer and swim in groups. They need friends, so keep them in fives or more:
- They brighten up the tank.
- Neon Tetras avoid Betta territory.
Corydoras Catfish
Cory Catfish are peaceful bottom-dwellers. They clean up the tank and don’t bother Bettas. They are best in small groups:
- Pygmy Cory: Small and agile, perfect for a Betta tank.
- Panda Cory: Distinctive look and peaceful nature.
Rainbowfish
Rainbowfish are vibrant and active swimmers, adding a burst of color to your aquarium. Like Neon Tetras, they thrive in a group, so consider keeping them in a school of five or more:
- Their iridescent scales create a stunning display.
- Rainbowfish prefer a peaceful community tank.
- Provide a well-planted environment to mimic their natural habitat.
- Avoid aggressive tank mates, as Rainbowfish can be somewhat timid.
- Keep the water quality in check, as Rainbowfish are sensitive to changes.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Setting up a peaceful home for your betta fish means avoiding some common pitfalls. Knowing what to steer clear of will ensure a harmonious tank. Let’s dive into the key mistakes to avoid while selecting tank mates for your betta.
Overcrowding The Tank
Bettas cherish their space. They thrive in a calm, uncrowded environment.
Stick to the one-inch-of-fish-per-gallon rule for a happy tank. Keep an eye on the tank’s size and don’t add too many fish.
- A 5-gallon tank suits one betta and a few small tank mates.
- Upgrade the tank if you plan to welcome more buddies.
Selecting Aggressive Species
Bettas are known for their feisty nature.
Choosing the right tank mates is critical to avoid stress and fights.
| Safe Choices | Risky Choices |
| Snails | Tiger Barbs |
| Shrimps | Cichlids |
| Corydoras | Male Bettas |
Introducing New Tank Mates
You’ve decided to diversify your aquarium with some new friends for your Betta. However, introducing new tank mates is a delicate process that requires patience and attention to detail to ensure peace and harmony in your underwater realm.
Acclimating The New Fish Or Invertebrates
The initial step is acclimation. This helps your new tank mates adjust to their environment smoothly. Here is a simple guide:
- Isolate the new arrival in a separate container.
- Float this container in the tank to match temperature (avoid shock).
- Gradually introduce tank water to the container every 10 minutes (adjust chemistry).
- After an hour, gently release the new mate into the tank (stress-free transition).
Ensure to watch for signs of stress or discomfort.
Monitoring Behavior And Interactions
Keep a close eye on your Betta and its new companions. Look for:
- Chasing or nipping – may indicate stress.
- Hiding – a sign of fear or aggression.
- Peaceful swimming – a good sign of acceptance.
Remember, patience is key! Some fish or invertebrates may need a few days to settle. Provide plenty of hiding spaces and visual barriers to help ease the tension.
Tank Setup Tips
When it’s time to decorate your betta fish aquarium, keep your finned friend and their future tank mates in mind. A well-set-up tank means happier, healthier fish and less stress for everyone involved.
Ideal Tank Size For Betta And Tank Mates
Bettas need space to swim and thrive, especially when sharing their home. Go for a tank that can hold at least 10 gallons of water. This gives everyone plenty of room. Below, find the ideal setup:
| Tank Capacity | Bettas Only | With Tank Mates |
| 5 gallons | Yes | No |
| 10 gallons | Better | Minimum |
| 20+ gallons | Best | Recommended |
Creating Hiding Spots And Territories
Hiding spots offer safety and reduce stress. Use plants and decorations to create these areas. Here’s what works well:
- Live plants: They improve water quality.
- Smooth rocks: Great for resting spots.
- Caves: Provide secure hiding.
Divide the tank into territories. Each fish should have a space to call their own.
Proper Water Parameters For A Community Tank
Maintain ideal water conditions to keep the tank healthy. Here’s what to aim for:
- Temperature: 76-80F (24-27C)
- pH Level: 6.5-7.5
- Water Hardness: 3-4 dKH
Regularly test the water to ensure these parameters stay consistent. Use a water testing kit every week.
Conclusion
Selecting the right companions for your betta fish can ensure a harmonious tank. Remember, peaceful, non-nipping species create the best environment for your betta.
By choosing tank mates that thrive in similar conditions, your aquatic habitat will not only flourish but also become a serene underwater retreat.
A well-balanced community tank equals happy, healthy bettas and friends.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs)
What are the best tank mates for Betta fish?
Betta fish, known for their vibrant colors and flowing fins, can coexist harmoniously with certain tank mates. Ideal companions include peaceful and non-aggressive species such as small schooling fish like neon tetras, harlequin rasboras, or Corydoras catfish. Avoid aggressive or fin-nipping species to maintain a tranquil environment.
Can Betta fish live with other types of fish?
Yes, Betta fish can share a tank with other species, but compatibility is key. Peaceful community fish that inhabit different levels of the tank, such as bottom-dwellers or mid-level swimmers, are generally the best choices. Always monitor the interactions and be ready to separate them if any aggression arises.
Are there specific considerations when choosing tank mates for Betta fish?
Absolutely. Tank mates for Betta fish should share similar water parameter requirements, especially in terms of temperature and pH. Additionally, ensure that the tank is adequately sized with plenty of hiding spots and visual barriers to reduce stress and territorial disputes. Always research the specific needs of each species.
Can Betta fish live with other Betta fish?
It’s generally not advisable to house male Betta fish together, as they tend to be territorial and aggressive towards each other. However, female Betta fish can coexist peacefully in a group known as a sorority, provided the tank is spacious enough and has plenty of hiding spots to establish a hierarchy without aggression.
What precautions should be taken when introducing tank mates to a Betta fish?
When introducing new tank mates, it’s crucial to monitor their interactions closely. Begin with a quarantine period for the new fish to ensure they are healthy and disease-free. Introduce them to the tank gradually, allowing the Betta fish to acclimate to their presence. Be prepared to separate them if signs of aggression or stress emerge. Regular observation and a well-thought-out tank setup contribute to a successful community aquarium.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Best Tank Mates for Betta Fish: A Beginner’s Guide!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
-

 Pet Care2 years ago
Pet Care2 years agoThe Best Dog Collars For 2022
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoBichon Frise: The Happy, Playful, and Cuddly Companion
-

 Trending Pet Stories1 year ago
Trending Pet Stories1 year ago2023 ‘World’s Ugliest Dog’ Winner: Scooter’s Tale of Resilience
-

 Animals2 years ago
Animals2 years agoAre There Animals Having Down Syndrome?
-

 Pets2 years ago
Pets2 years agoThe Fascinating World Of The Red Chameleon
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Dog Breeds According To AKC.
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years ago21 Dog Breeds That Resemble Bears Or Teddy Bears!
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoEskimo Dogs from Canada – What Are They? – Find Out!