Reptile
Discovering The Iranian Harlequin Newt: A Marvel Of Nature

Discovering the Iranian Harlequin Newt: A Marvel of Nature
The Iranian Harlequin Newt, Triturus karelinii, often stands out in the world of amphibians due to its striking beauty and fascinating behavior.
But beyond this captivating exterior, there is so much more to understand about these mesmerizing creatures. Let’s delve into the remarkable journey of these remarkable creatures.
Unveiling the Mystery: Origins and Etymology
The origins of the Iranian Harlequin Newt can be traced back to the mountainous regions of Iran, where their striking beauty stands in stark contrast to the austere landscapes.
The species was first described by Russian herpetologist Sergei Feofilovich Karelin, which led to its scientific name Triturus karelinii.
The word ‘Harlequin’ in its common name derives from the character in Commedia dell’arte, a reference to the dramatic black and orange patterning found on the newts’ skin.
A Nocturnal Lifestyle
Primarily nocturnal creatures, Iranian Harlequin Newts are most active during the night hours. This behavior helps them avoid the heat of the day and various predators.
They spend their nights foraging for food, exploring their environment, and interacting with other newts.
A Tale of Two Habitats
One of the most fascinating aspects of the Iranian Harlequin Newt is its ability to thrive in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. They are most commonly found near streams, ponds, and rivers, but can also be found in damp forests.
Their adaptation to both land and water is an intriguing aspect of their biology, marking them as true amphibians.
The Iranian Harlequin Newt’s Seasonal Cycle
Like many amphibians, the Iranian Harlequin Newt exhibits a unique seasonal cycle. During warmer months, they are often found in water bodies for mating and laying eggs.
When the weather cools, these newts retreat to the land, hibernating under rocks and foliage to protect themselves from the harsh winter conditions.
Communication and Social Structure
Iranian Harlequin Newts are solitary animals but can exhibit complex social behaviors during the mating season. Male newts perform elaborate courtship displays to attract females, which involves waving their tails and releasing pheromones into the water.
This sophisticated form of communication showcases the newt’s social dynamics and underlines the complexities of their behaviors.
The Beauty of Colors and Patterns
When you first lay eyes on an Iranian Harlequin Newt, you can’t help but be entranced by its vibrant colors and patterns. These newts showcase a striking combination of black and orange – reminiscent of a harlequin’s traditional costume.
The bright orange blotches stand out dramatically against their darker backdrop, giving them their unique and distinctive appearance.
Body Structure and Size
Physically, the Iranian Harlequin Newt is a robust and hardy creature. They typically measure between 12 to 16 cm in length, making them one of the larger newt species.
Their bodies are sturdy, designed for both swimming and navigating terrestrial landscapes. Males possess a more slender body compared to females and display a ridge running down their back during the mating season.
Eyes – Windows to the Environment
One of the defining features of these newts is their eyes. Large and expressive, the eyes of an Iranian Harlequin Newt are well-suited to their nocturnal lifestyle.
They offer excellent night vision, allowing the newts to effectively navigate their environment and locate prey in low-light conditions.
Skin – A Unique Sensory Organ
The skin of the Iranian Harlequin Newt is not just about stunning aesthetics. It serves as a vital sensory organ. It’s highly sensitive, facilitating a sense of touch and vibration, and plays a crucial role in their interactions with the environment.
However, their skin is also delicate, requiring a moist environment to prevent dehydration.
Tail – An Essential Tool
The tail of the Iranian Harlequin Newt is an important tool for various aspects of their life. It aids in swimming, balancing, and even plays a crucial role in the courtship rituals during the mating season.
In males, the tail becomes more pronounced and ornate, serving as a fascinating example of sexual dimorphism in the species.
The Mountainous Landscape of Iran: A Natural Habitat
Iranian Harlequin Newts are native to the mountainous regions of Iran, where they thrive in cool, damp climates.
These landscapes, characterized by high altitude and fluctuating temperatures, might seem harsh to many, but they offer the perfect habitat for these hardy newts.
Aquatic Realms: Ponds, Streams, and Rivers
In the warmer months, you’ll find these newts near bodies of water, including streams, ponds, and rivers. These aquatic habitats provide the ideal conditions for breeding, with ample food resources and shelter from predators.
During this period, they become primarily aquatic, showcasing their remarkable adaptability as amphibians.
Terrestrial Retreats: Forests and Foliage
During the colder months, Iranian Harlequin Newts make a transition to terrestrial life. They retreat to damp forests, under rocks, and foliage.
These areas offer a sanctuary where they can hibernate, protected from the cold winter weather. It’s during this time that they become elusive, making them a rare sight for the casual observer.
The Human Impact: Urban Areas and Farmland
In recent years, these newts have been spotted in more urban areas and farmland. While it showcases their adaptability, it also signifies the impact of habitat loss due to human activities.
It’s a stark reminder of the need for conservation efforts to protect these stunning creatures and their natural homes.
Iranian Harlequin Newts and Elevation
A fascinating aspect of the Iranian Harlequin Newt’s habitat is its relation to elevation. These newts are typically found at altitudes between 2000 and 3000 meters, marking them as true high-altitude dwellers.
Their ability to survive at such elevations is a testament to their resilience and adaptability.
The Season of Love: Courtship and Mating
The courtship ritual of the Iranian Harlequin Newt is an intricate ballet. During the breeding season, males transform with heightened colors and a ridge down their backs.
They perform a captivating water dance, a spectacle of tail-waving and body-quivering, releasing pheromones to attract females. This elaborate performance not only showcases their strength but also their suitability as a mate.
The Next Generation: Eggs and Fertilization
Following a successful courtship, the female newt lays her eggs one at a time, carefully wrapping each one in aquatic plant leaves for protection. Each egg is then fertilized by the male, a process that occurs externally in the aquatic environment.
The Dawn of Life: Embryo Development
The fertilized eggs develop into embryos within the safety of their leafy incubators. This period of embryogenesis lasts for approximately 2-3 weeks. During this time, the embryos transform, developing key features like gills, a tail, and, eventually, limbs.
Breaking Free: The Hatching Process
The hatching process of the Iranian Harlequin Newt is a crucial juncture in its lifecycle. Emerging from their eggs as tiny larvae, these creatures are already well-equipped for aquatic life with external gills to help them breathe underwater.
Growing Up: The Larval and Juvenile Stages
Following hatching, the larvae undergo a period of rapid growth and development. They are voracious feeders during this stage, consuming small invertebrates to fuel their growth.
As they grow, they undergo a fascinating process known as metamorphosis, during which they lose their gills and develop lungs, enabling them to survive on land.
Coming of Age: The Transition to Adulthood
After a period of approximately 4 months, the juvenile newts mature into adults. This transition is marked by the development of their characteristic black and orange coloration.
Now capable of reproduction, they join the adult population, carrying forward the cycle of life for their species.
Living Through the Seasons: The Annual Cycle
The life of an Iranian Harlequin Newt is intricately tied to the changing seasons. They breed during the spring, laying eggs that hatch into larvae by early summer.
As the colder months arrive, they retreat from their aquatic habitats to hibernate, reemerging with the return of warmer temperatures. This annual cycle illustrates the newts’ remarkable adaptability and resilience in their native habitats.
Conservation Status: A Cause for Concern
The Iranian Harlequin Newt is currently classified as “Least Concern” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). However, this status may not truly reflect the pressing threats that these fascinating creatures face.
Conservationists are concerned that due to rapid habitat loss and limited geographical distribution, these newts may be more vulnerable than what their current classification suggests.
Threats to Survival
Habitat Destruction
The most pressing threat to the Iranian Harlequin Newt is habitat destruction. Rapid urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation in Iran are causing significant damage to the natural habitats of these newts.
This not only reduces their living space but also affects the availability of food and breeding sites.
Climate Change
The impact of climate change is another significant threat to these newts. Rising temperatures, erratic weather patterns, and shifts in seasonal timings can disrupt the lifecycle of the Iranian Harlequin Newt.
It also exacerbates the risk of habitat loss, further threatening their survival.
Pollution
Pollution, particularly in aquatic habitats, can have a devastating impact on the Iranian Harlequin Newt population. Industrial waste, pesticides, and other pollutants can contaminate the water, leading to health issues and a decline in newt populations.
Pet Trade
The illegal pet trade is another problem these newts face. While they are captivating pets for experienced amphibian keepers, unregulated capture and trade can put significant pressure on their wild populations.
The Call to Action: Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts for the Iranian Harlequin Newt involve habitat preservation, strict regulation of the pet trade, and continuous monitoring of their population numbers.
It is crucial to increase awareness about these fascinating creatures and the challenges they face to encourage more active participation in their conservation.
The survival of the Iranian Harlequin Newt depends on our actions today, and every step, no matter how small, counts towards securing a future for this remarkable species.
The Allure of the Unconventional: Iranian Harlequin Newt as a Pet
The Iranian Harlequin Newt, with its vibrant colors and fascinating lifecycle, can make a captivating pet. Their nocturnal habits and unique behaviors can provide endless fascination for an amphibian enthusiast.
However, these newts are not your typical pet and require specialized care.
Creating a Suitable Home: Housing the Iranian Harlequin Newt
Aquatic Setup
Given their amphibious nature, your newt will require both aquatic and terrestrial spaces. A sizable aquarium that includes a water body deep enough for swimming, and a well-structured land area for rest, should serve well.
The water needs to be kept clean and dechlorinated, and the terrestrial area should have damp soil and hiding spots.
Temperature and Humidity Control
Temperature control is crucial for Iranian Harlequin Newts. A cooler temperature, around 16-18°C, is ideal. Since they require high humidity, regular misting may be necessary to keep the environment moist.
A Matter of Taste: Feeding the Iranian Harlequin Newt
These newts thrive on a diet of small invertebrates like earthworms, slugs, and insect larvae. They may also enjoy an occasional treat of bloodworms or brine shrimp. Feed your newts in the evening to align with their nocturnal habits.
Living with the Iranian Harlequin Newt
Handling and Interaction
Handling should be kept to a minimum as their skin is sensitive and can easily be damaged. Always ensure your hands are clean and wet before handling.
Health and Longevity
With proper care, an Iranian Harlequin Newt can live up to 20 years in captivity. However, they are susceptible to fungal and bacterial infections, often due to poor water quality or stress.
Regular water changes and a stress-free environment can prevent many health issues.
A Commitment to Respect: The Ethical Aspect
Finally, owning an Iranian Harlequin Newt is a commitment that extends beyond care requirements. It’s crucial to source your pet from a reputable breeder who practices responsible breeding to ensure you’re not contributing to the decline of wild populations.
Your decision to own a newt can be an opportunity to participate in their conservation and foster a deeper appreciation for these remarkable creatures.
Conclusion
As we explore the natural world around us, we continue to encounter fascinating species like the Iranian Harlequin Newt. Their unique life and behaviors remind us of the diversity and richness that exists within our ecosystems.
As we strive to understand and conserve these beings, we are ultimately contributing to the well-being of our planet, preserving these wonders for generations to come.
It’s our collective responsibility to care for and respect all life forms, ensuring a harmonious existence with the natural world. The Iranian Harlequin Newt’s tale is a reminder of this connection. It’s a tale of survival, beauty, and resilience that continues to inspire us all.
The Iranian Harlequin Newt is undoubtedly a mesmerizing creature, teeming with remarkable features and behaviors.
As pet owners, conservationists, or simply lovers of nature, our understanding and appreciation of these newts can significantly impact their survival.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs)
What is the lifespan of an Iranian Harlequin Newt?
With proper care, they can live up to 20 years in captivity.
What do Iranian Harlequin Newts eat?
Their diet primarily consists of small invertebrates such as insects, slugs, and worms.
Are Iranian Harlequin Newts dangerous to humans?
No, they are not dangerous. However, handling should be minimized to prevent stressing the newt and potential skin damage.
How do you differentiate between male and female Iranian Harlequin Newts?
Males generally have more vibrant colors and a jagged crest along their backs, especially visible during the breeding season.
Can you keep an Iranian Harlequin Newt as a pet?
Yes, but it requires specific conditions to mimic their natural habitat, and it’s important to source them responsibly to avoid illegal wildlife trade.
How often should you feed Iranian Harlequin Newts?
Typically, feeding them every 2-3 days with a diverse range of invertebrates is recommended.
What’s the ideal temperature for an Iranian Harlequin Newt’s habitat?
The ideal temperature range is between 16-20°C (60-68°F), to mimic the cool, damp environments they are accustomed to.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”All The Facts & Info You Need To Know About Iranian Harlequin Newt!?”
Please you should feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Reptile
Exotic Reptile Species: Unveiling the Fascinating World of Rare Reptiles

Exotic Reptile Species: Unveiling the Fascinating World of Rare Reptiles
Welcome to an enthralling adventure into the world of Exotic Reptile Species: Unveiling the Fascinating World of Rare Reptiles.
In this journey, we will embark on a remarkable exploration of some of the most extraordinary and elusive creatures that inhabit our planet.
These rare reptiles, with their unique adaptations and intriguing behaviors, invite us to peer into the awe-inspiring tapestry of the animal kingdom.
From the enchanting world of Chameleons to the resilient existence of the Alligator Snapping Turtle, we’ll unlock the secrets of these captivating reptilian marvels, unveiling the wonders of their existence.
Join us as we unravel the mysteries and celebrate the beauty of these rare reptiles.
1). The Mesmerizing Chameleon: Nature’s Master of Camouflage
When it comes to nature’s masters of camouflage, the Chameleon undoubtedly takes center stage. These enchanting reptiles, often hailed as the living art of disguise, possess a mesmerizing array of attributes that make them stand out in the world of reptiles.

Here’s an in-depth look at the captivating world of Chameleons:
- Adaptive Coloration: Chameleons are renowned for their remarkable ability to change color. This adaptation is not simply for aesthetic purposes; it serves a range of functions, from communication and thermoregulation to camouflage. Dive into the fascinating science behind this color-changing magic.
- Distinctive Anatomy: Their unique appearance, with independently mobile eyes, prehensile tails, and zygodactylous feet, sets them apart from other reptiles. Explore how these features aid in their arboreal lifestyle and insectivorous diet.
- Habitat and Diversity: Chameleons are primarily found in the tropical rainforests of Madagascar and Africa, but their range extends to other regions as well. Discover the different species, each with its own set of colors and adaptations for survival in its specific habitat.
- Feeding Behavior: Chameleons are expert insect hunters, using their specialized long, sticky tongues to capture prey. Learn about their hunting strategies and how they secure their daily meals.
- Reproduction and Lifecycle: Delve into the unique reproductive behaviors of Chameleons, including elaborate courtship displays and the intriguing incubation of eggs. Understand how these reptiles grow and develop from hatchlings to adults.
- Conservation Challenges: The Chameleon faces several conservation challenges, including habitat destruction and the illegal pet trade. Uncover the efforts being made to protect these remarkable creatures and their natural habitats.
Intriguing, mysterious, and truly mesmerizing, Chameleons are a testament to the wonders of evolution and adaptation.
Whether you’re a herpetology enthusiast or simply captivated by the beauty of the natural world, the world of Chameleons offers an endless source of fascination.
2). Meet the Alligator Snapping Turtle: A Living Fossil
In the world of reptiles, few creatures evoke the same sense of primordial fascination as the Alligator Snapping Turtle.
Often referred to as a living fossil, these reptiles have roamed our planet for millions of years, providing a captivating glimpse into prehistoric times. Let’s dive into the remarkable world of the Alligator Snapping Turtle:

- Prehistoric Lineage: The Alligator Snapping Turtle’s lineage can be traced back to the Late Miocene epoch, making them one of the oldest turtle species in existence. Explore their evolutionary history and the unique features that have remained largely unchanged over the ages.
- Gigantic Stature: These turtles are renowned for their immense size, with some individuals reaching lengths of over two feet and weighing as much as 200 pounds. Learn about their impressive physical characteristics and how they compare to other turtle species.
- Terrifying Appearance: The Alligator Snapping Turtle’s appearance is a sight to behold. Their massive head, beak-like jaws, and distinctive ridged shell give them a formidable and somewhat intimidating look. Uncover the reasons behind their formidable appearance and the role it plays in their survival.
- Habitat and Range: Native to the southeastern United States, these turtles are primarily aquatic, dwelling in slow-moving, murky waters. Explore their habitat preferences and the challenges they face due to habitat loss and water pollution.
- Feeding Strategies: Alligator Snapping Turtles are cunning ambush predators, luring fish, amphibians, and even small mammals with their worm-like appendage on their tongue. Delve into their hunting tactics and feeding behaviors, which make them apex predators in their environment.
- Conservation Status: The Alligator Snapping Turtle faces conservation concerns due to overharvesting for the pet trade, habitat destruction, and pollution. Discover the conservation efforts in place to protect and preserve these living relics.
Encountering an Alligator Snapping Turtle is like stepping back in time, offering a rare glimpse into Earth’s ancient past.
Whether you’re a wildlife enthusiast, a biology buff, or simply intrigued by the mysteries of our planet’s history, these living fossils are a testament to the enduring wonders of evolution.
3). The Enigmatic Axolotl: A Rare Amphibious Marvel
Among the remarkable creatures inhabiting our world, the Axolotl stands as a unique and enigmatic wonder. Native to the ancient lakes of Mexico, this aquatic amphibian exhibits a life strategy like no other in the animal kingdom.
Let’s dive into the extraordinary world of the Axolotl:

- Ambassadors of Neoteny: Axolotls are living examples of neoteny, a phenomenon where they reach adulthood without undergoing metamorphosis. They retain their aquatic, gilled features throughout their lives. Explore the fascinating science behind this remarkable trait.
- Intriguing Regenerative Abilities: These creatures are famous for their extraordinary regenerative capabilities. Axolotls can regrow entire limbs, spinal cord, and even portions of their heart and brain. Discover the groundbreaking research that seeks to unlock the secrets of their regenerative powers.
- Unique Appearance: Axolotls have distinctive external gills, feather-like external filaments, and a perpetual smile that adds to their charm. Learn how their unique appearance is adapted to their habitat and lifestyle in the lakes of Mexico.
- Habitat and Conservation: Indigenous to the high-altitude waters of Xochimilco and Chalco in Mexico, Axolotls face numerous conservation challenges. Explore the threats they encounter, including habitat destruction, invasive species, and pollution, and the efforts to save this endangered species.
- Behavior and Diet: Unravel the mysteries of Axolotl behavior, including their feeding habits, communication through touch, and how they navigate their underwater world.
- Keeping Axolotls as Pets: Many enthusiasts keep Axolotls as pets due to their unique appearance and manageable care requirements. Understand the basics of setting up a suitable aquarium, providing proper nutrition, and ensuring their well-being.
The Axolotl, a true amphibious marvel, holds the secrets of regenerative biology and evolutionary wonders.
Whether you’re a biology enthusiast, an aspiring herpetologist, or simply intrigued by the mysteries of the animal kingdom, the Axolotl’s unique existence is bound to captivate your imagination and inspire your appreciation for the remarkable diversity of life on Earth.
4). Exquisite Chinese Water Dragon: A Dragon in Miniature
In the realm of reptiles, the Chinese Water Dragon stands out as a captivating creature that exudes the mystique of mythical dragons.
These small but enchanting lizards, native to Southeast Asia, possess a distinctive appearance and demeanor that invoke images of the legendary beasts of ancient lore.
Let’s embark on a journey into the world of the Chinese Water Dragon:

- Dragon-Like Appearance: Chinese Water Dragons have a striking, green-scaled body, adorned with an impressive crest of spines along their back. Explore how their unique physical features draw parallels to the mythical dragons of Eastern folklore.
- Natural Habitat: Indigenous to the lush rainforests and waterways of Southeast Asia, these lizards have adapted to a semi-aquatic lifestyle. Delve into their habitat preferences, including their need for both terrestrial and aquatic environments.
- Behavior and Temperament: Discover the intriguing behaviors of Chinese Water Dragons, from their arboreal prowess to their skittish yet endearing personalities. Learn about their interactions with each other and their human keepers.
- Diet and Nutrition: These lizards are opportunistic feeders, consuming a variety of insects, small vertebrates, and plant matter. Explore their dietary requirements and the key considerations for maintaining their health in captivity.
- Reproduction and Breeding: Chinese Water Dragons engage in courtship rituals that are both fascinating and delicate. Uncover the reproductive cycle of these dragons and the nurturing care they provide to their offspring.
- Husbandry as Pets: Chinese Water Dragons are a popular choice among reptile enthusiasts as pets. Understand the essential aspects of their care, from creating an ideal enclosure to providing proper lighting, temperature, and humidity levels.
The Chinese Water Dragon, a dragon in miniature, combines the charm of a mythical creature with the accessibility of a pet lizard.
Whether you’re an avid herpetology enthusiast, a fan of fantasy, or simply intrigued by the diversity of the natural world, these remarkable reptiles offer a glimpse into a world of wonder and awe.
5). The Jeweled Lacerta: A Hidden Gem of the Reptile World
Nestled among the rich tapestry of reptile species, the Jeweled Lacerta stands out as a true hidden gem. Originating from the Mediterranean regions, these lizards boast vibrant colors and intricate patterns that make them a captivating addition to the reptile world.
Let’s unveil the secrets of the Jeweled Lacerta:

- Mediterranean Majesty: Native to the coastal areas of Southern Europe, the Jeweled Lacerta is named for its striking, jewel-like appearance. Explore the geographic range and natural habitats that these lizards call home.
- Unique Coloration: These reptiles exhibit a stunning color palette, with shades of green, blue, and turquoise combined with intricate black markings. Delve into the science behind their distinctive coloration and its role in their survival.
- Behavior and Lifestyle: Jeweled Lacertas are diurnal creatures that thrive in the warmth of the Mediterranean sun. Discover their daily routines, including basking, hunting for insects, and seeking shelter from potential predators.
- Territorial Behavior: These lizards are known for their territorial nature, fiercely defending their chosen space. Learn about their intriguing social dynamics and interactions within their own kind.
- Reproduction and Lifecycle: Explore the reproduction habits of the Jeweled Lacerta, including their courtship rituals and the process of laying and incubating eggs. Understand how these reptiles grow and develop from hatchlings to adults.
- Conservation Concerns: While not critically endangered, Jeweled Lacertas face habitat loss and potential threats due to human activities. Discover the importance of conserving their unique ecosystems and the efforts to protect their populations.
The Jeweled Lacerta, a hidden gem of the reptile world, offers a glimpse into the beauty of the Mediterranean’s diverse flora and fauna.
Whether you’re a seasoned herpetologist, a nature enthusiast, or simply captivated by the marvels of the natural world, these captivating reptiles embody the essence of hidden treasures in our ecosystems.
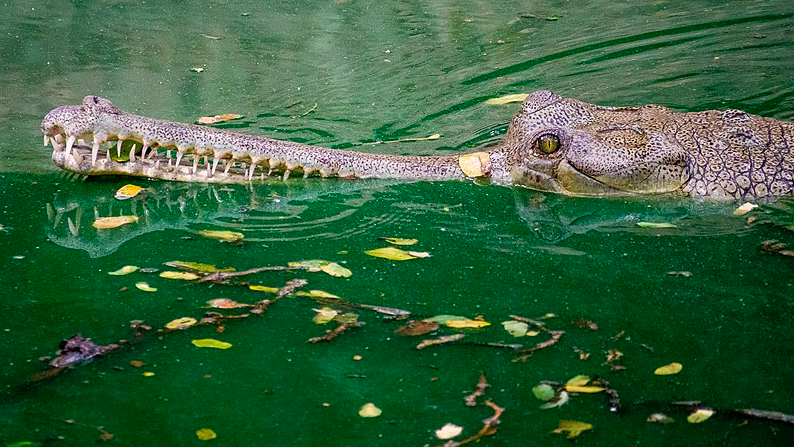
6). The Wonders of the Gharial: Nature’s Aquatic Predator
In the heart of the Indian subcontinent, a remarkable aquatic predator lurks in the waters, showcasing a distinctive appearance and a vital role in local ecosystems.
The Gharial, often dubbed the “fish-eating crocodile,” is a creature of fascination, embodying the wonders of nature’s aquatic world. Let’s embark on an exploration of the extraordinary Gharial:

- An Ancient Lineage: The Gharial is an ancient species, with roots dating back to the time of the dinosaurs. Unearth the evolutionary history of these unique crocodilians and their connections to the past.
- Distinctive Physique: Known for its long, slender snout and a bulbous knob on the tip of its snout, the Gharial’s physical attributes set it apart from other crocodilian species. Delve into the functions of these features and how they aid in its aquatic lifestyle.
- Habitat and Range: Indigenous to the major river systems of the Indian subcontinent, the Gharial’s habitat ranges from the Ganges River in India to the Indus River in Pakistan. Explore the regions they call home and the importance of these waterways to their survival.
- Feeding Behavior: As skilled aquatic predators, Gharials predominantly feed on fish, using their specialized snouts to swiftly snap up their slippery prey. Learn about their hunting tactics and the critical role they play in maintaining healthy fish populations.
- Behavior and Social Structure: Discover the behavioral patterns of Gharials, including their nesting and breeding habits. Explore how these reptiles establish territories and interact with their own kind.
- Conservation Efforts: Gharials face severe conservation challenges due to habitat loss and degradation, illegal fishing practices, and pollution. Understand the conservation initiatives in place to protect these unique reptiles and their habitat.
The Gharial, a nature’s aquatic predator, represents a living relic that continues to thrive in the rivers of the Indian subcontinent.
Whether you’re a wildlife enthusiast, a herpetologist, or simply intrigued by the complex web of life in aquatic ecosystems, the Gharial’s presence is a testament to the enduring marvels of evolution and adaptation.
7). Madagascar Giant Day Gecko: A Colorful Marvel
In the lush landscapes of Madagascar, a living rainbow of reptilian beauty thrives. The Madagascar Giant Day Gecko, often referred to as the “Colorful Marvel of the Rainforest,” captivates with its vibrant hues and stunning appearance.
Let’s delve into the world of this enchanting creature:

- Rainbow of Colors: These geckos are renowned for their kaleidoscope of colors, from vibrant greens to striking reds and blues. Explore the science behind their brilliant hues and their significance in the dense rainforest.
- Native Habitat: Indigenous to the lush rainforests of Madagascar, these geckos are well adapted to arboreal life. Discover their preferred habitats, which range from treetops to the forest floor.
- Diet and Feeding Habits: Madagascar Giant Day Geckos are insectivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, fruit, and nectar. Learn about their feeding behaviors and how they find sustenance in the wild.
- Territorial Behavior: These geckos exhibit territorial behaviors and are often solitary creatures. Understand their social dynamics and interactions within their own species.
- Reproduction and Lifecycle: Explore the fascinating aspects of their reproduction, from courtship rituals to egg-laying. Learn about the development of hatchlings and the care they receive from their mothers.
- Keeping as Pets: Madagascar Giant Day Geckos are popular as exotic pets due to their captivating appearance and manageable care requirements. Delve into the basics of setting up a suitable terrarium, providing proper lighting, temperature, and humidity levels, and their suitability as pets.
The Madagascar Giant Day Gecko, a colorful marvel of the reptile world, offers a glimpse into the vibrant ecosystems of Madagascar’s rainforests.
Whether you’re a seasoned herpetology enthusiast, an admirer of natural beauty, or simply curious about the diversity of life on our planet, these radiant geckos embody the essence of living jewels in the heart of a tropical paradise.
8). The Spectacular Uromastyx Lizard: A Desert Dweller
Amid the sun-scorched deserts of Africa and Asia, a remarkable and resilient reptile thrives – the Uromastyx Lizard. These desert-dwelling lizards, often referred to as “Spectacular Survivors of Arid Lands,” embody the spirit of adaptation and tenacity.
Join us as we journey into the world of the spectacular Uromastyx:

- Desert Oasis Dwellers: Uromastyx lizards are expertly adapted to the arid landscapes of North Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia. Explore the unique features that enable them to thrive in these harsh environments.
- Distinctive Appearance: These lizards are instantly recognizable by their spiky tails, robust build, and vibrant coloration. Delve into the functions of these physical traits and how they contribute to their survival in the desert.
- Dietary Strategies: Uromastyx lizards are herbivorous, feeding on a specialized diet of desert plants. Learn about their feeding behaviors, including their ability to utilize scarce water resources efficiently.
- Behavior and Basking: Discover their daily routines, which often include basking in the scorching sun to absorb essential warmth. Understand their burrowing habits, which help them escape extreme temperatures and predators.
- Reproduction and Lifecycle: Explore the unique aspects of their reproduction, including courtship rituals and the laying of eggs. Learn about the growth and development of Uromastyx hatchlings.
- Keeping Uromastyx as Pets: Many reptile enthusiasts keep Uromastyx lizards as pets, drawn to their desert-adapted beauty and manageable care requirements. Gain insight into creating a suitable desert terrarium, providing the right temperature and lighting, and dietary considerations for pet Uromastyx.
The Uromastyx Lizard, a true desert dweller, epitomizes the art of survival in some of the world’s harshest environments.
Whether you’re an avid herpetologist, a desert ecosystem enthusiast, or simply fascinated by nature’s ability to adapt, these spectacular lizards offer a glimpse into the resilience and resourcefulness of life in arid lands.
9). Majestic Horned Lizard: Master of Mimicry
In the arid landscapes of North America, a creature of captivating deception reigns supreme – the Horned Lizard.
These remarkable reptiles, often hailed as the “Masters of Mimicry,” possess a unique ability to blend seamlessly with their surroundings and a suite of intriguing adaptations.
Join us as we journey into the world of the majestic Horned Lizard:

- A Desert Marvel: Horned Lizards are true desert dwellers, inhabiting arid regions across North America. Explore their natural habitats and the challenges they face in these unforgiving environments.
- Distinctive Appearance: These lizards are characterized by their flattened bodies and distinctive “horns” or spines. Delve into the purpose of these physical features and their role in the lizard’s survival.
- Mimicry Mastery: Horned Lizards are masters of camouflage, often resembling rocks or pebbles in their arid surroundings. Learn about their camouflage techniques and how they expertly mimic their environment to evade predators.
- Diet and Feeding Tactics: These reptiles are insectivores, primarily feeding on ants. Discover their unique feeding strategies, including the ability to shoot blood from their eyes as a defense mechanism.
- Reproduction and Life Cycle: Explore their reproduction habits, courtship rituals, and the development of their young. Understand the growth and maturation of these remarkable lizards.
- Conservation Efforts: Horned Lizards face conservation concerns due to habitat loss and fragmentation. Discover the conservation initiatives in place to protect these unique reptiles and their ecosystems.
The Horned Lizard, a master of mimicry, showcases the art of deception and adaptation in the harsh deserts of North America.
Whether you’re an enthusiastic herpetologist, a lover of desert ecosystems, or simply intrigued by the diverse strategies of survival in nature, these majestic lizards offer a captivating window into the world of mimicry and camouflage.
10). The Adorable Leaf-Tailed Gecko: Nature’s Impersonator
In the rainforests of Madagascar, an enchanting creature of mesmerizing disguise thrives – the Leaf-Tailed Gecko. Often hailed as “Nature’s Impersonator,” these geckos are masters of camouflage and mimicry, blending seamlessly with their leafy surroundings.
Join us as we explore the world of the adorable Leaf-Tailed Gecko:

Image Source:wired.com
- Rainforest Residents: Leaf-Tailed Geckos are native to the tropical rainforests of Madagascar, where their leaf-like appearance allows them to hide in plain sight. Delve into the lush habitats they call home.
- Mimicry Marvels: These geckos are renowned for their extraordinary camouflage, which allows them to imitate leaves, twigs, and bark. Learn about the science behind their mimicry and how it aids their survival.
- Intricate Appearance: Explore the gecko’s intricate body patterns, fringed skin flaps, and cryptic coloration, all of which contribute to their remarkable impersonation of foliage.
- Nocturnal Behavior: Leaf-Tailed Geckos are primarily nocturnal, coming to life under the cover of darkness. Discover their fascinating nighttime activities, including hunting and social interactions.
- Diet and Predatory Skills: Uncover their diet, which consists of insects, and their stealthy hunting techniques. Learn how they use their remarkable disguise to ambush prey.
- Reproduction and Lifecycle: Explore the gecko’s reproduction habits, egg-laying, and the development of their offspring. Understand how the hatchlings blend seamlessly into their leafy environment.
- Conservation Considerations: Leaf-Tailed Geckos face conservation challenges due to habitat destruction and the illegal pet trade. Discover the efforts being made to protect these remarkable reptiles and their delicate ecosystems.
The Leaf-Tailed Gecko, a master of mimicry, is a testament to the art of blending in and staying hidden in the heart of Madagascar’s rainforests.
Whether you’re a herpetology enthusiast, a lover of rainforest biodiversity, or simply captivated by the wonders of adaptation in nature, these adorable geckos offer an enchanting glimpse into the realm of natural impersonation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of exotic reptile species is a fascinating and diverse realm, where each creature tells a unique story of adaptation, survival, and beauty.
From the intricate camouflage of Chameleons to the ancient lineage of Alligator Snapping Turtles, the remarkable regenerative powers of Axolotls, and the vibrant colors of the Chinese Water Dragon, we’ve explored a rich tapestry of life.
The Jeweled Lacerta, the Gharial, the Madagascar Giant Day Gecko, the Uromastyx Lizard, the Horned Lizard, and the Leaf-Tailed Gecko have each offered a window into the astounding diversity of reptilian life on our planet.
As we close this exploration, we’re reminded of the importance of conservation efforts to protect these incredible creatures and their fragile ecosystems.
Whether you’re a seasoned enthusiast or a casual observer, this journey through the world of exotic reptile species has hopefully deepened your appreciation for the beauty and complexity of the natural world.
Keep exploring, learning, and cherishing the wonders of our planet’s biodiversity.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs)
Are exotic reptile species suitable for beginner reptile keepers?
Exotic reptile species vary in terms of care requirements. Some are suitable for beginners, while others are better left to experienced keepers. Research the specific needs of the species you’re interested in before deciding.
Can I keep exotic reptile species as pets?
Yes, many exotic reptile species can be kept as pets, but it’s crucial to provide the proper habitat, diet, and care they require. Always ensure legality and ethical considerations before acquiring exotic reptiles.
What should I consider before getting an exotic reptile as a pet?
Before getting an exotic reptile as a pet, consider factors like space, time commitment, knowledge, and legal restrictions. Research the specific species thoroughly to understand its needs.
How do I create a suitable habitat for exotic reptile species?
Creating a suitable habitat involves research and careful planning. Factors to consider include temperature, humidity, lighting, enclosure size, and diet. Consult with experienced keepers or herpetologists for guidance.
Are there any conservation concerns related to exotic reptile species?
Yes, there are conservation concerns related to some exotic reptile species, especially when they are collected from the wild. It’s essential to support ethical breeding programs and avoid contributing to the illegal wildlife trade.
Explore the world of exotic reptile species, and let their charm and uniqueness enrich your understanding of the animal kingdom. Whether you’re a passionate reptile enthusiast or just starting your journey, these captivating creatures will undoubtedly leave a lasting impression.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Exotic Reptile Species: Unveiling the Fascinating World of Rare Reptiles!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Reptile
Unveiling the Marvels of the Mexican Alligator Lizard: A Fascinating Reptilian Wonder
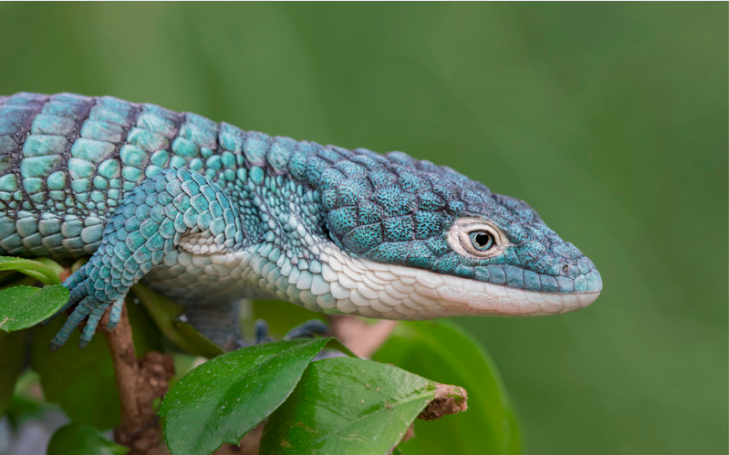

Unveiling the Marvels of the Mexican Alligator Lizard: A Fascinating Reptilian Wonder
Are you ready to embark on a thrilling journey through the mesmerizing world of the Mexican Alligator Lizard? Prepare to be captivated by the exotic allure and remarkable characteristics of this enigmatic reptile.
Join us as we delve into the hidden corners of nature and uncover the secrets of this remarkable creature.
A Closer Look: What is the Mexican Alligator Lizard?
The Mexican Alligator Lizard (Abronia) is a genus of lizards that belongs to the family Anguidae. With their distinctive appearance and intriguing behavior, these lizards have captured the hearts of reptile enthusiasts worldwide.

Let’s delve into the fascinating world of the Mexican Alligator Lizard and uncover the intriguing details that make this reptile so captivating.
Exploring Diversity: Species and Varieties
Within the realm of the Mexican Alligator Lizard (Abronia), lies a realm of astounding diversity. This group of lizards, nestled within the family Anguidae, boasts an array of distinct species and captivating varieties, each with its own unique allure.
From the vibrant and lively Green Abronia to the mesmerizing patterns adorning the Marbled Alligator Lizard, we embark on a journey to explore the remarkable range of colors, sizes, and features that grace the world of these enigmatic creatures.
Whether you’re a seasoned reptile aficionado or a newcomer to the world of lizards, the allure of this diverse array is bound to leave you enthralled.
A Colorful Kaleidoscope: The Aesthetics of the Mexican Alligator Lizard
Prepare to be entranced by the sheer visual spectacle that is the Mexican Alligator Lizard. With its kaleidoscope of colors, intricate patterns, and textured scales, it’s no wonder these reptiles are often considered living works of art.
Nature has endowed each species with a unique palette, allowing them to blend seamlessly into their surroundings with expert camouflage.
These creatures have truly mastered the art of visual deception, leaving observers awe-struck by their ability to disappear and reappear within the lush landscapes they call home.
Habitat Haven: Unveiling the Environments of Mexican Alligator Lizards
Embark on a virtual tour of the diverse habitats that play host to the Mexican Alligator Lizard.
From the dense, verdant rainforests to the mist-covered peaks of mountain ranges, these reptiles have carved out their homes in some of the most captivating landscapes in Mexico and Central America.
Discover the secrets of their chosen abodes and the remarkable adaptations that allow them to thrive in each unique environment.
From high treetops to forest floors, the Mexican Alligator Lizard has claimed its place in the intricate tapestry of nature.
Intriguing Habits: A Peek into the Life of the Mexican Alligator Lizard
Prepare to witness a day in the life of the Mexican Alligator Lizard as we uncover their captivating behaviors, feeding habits, and interactions with their surroundings.
With their adept climbing skills and fascinating behaviors, these reptiles offer us a window into the intricate dynamics of their existence.
From stealthy movements to basking under the sun’s warm embrace, we explore the various aspects of their daily routines that make them such enchanting subjects of study and admiration.
The Dance of Life: Mating and Reproduction
Step into the captivating world of courtship and reproduction as Mexican Alligator Lizards engage in their unique dance of life. Through intricate movements and displays, these reptiles communicate and navigate the delicate process of mating.
We unveil the fascinating strategies employed by these creatures to ensure successful reproduction, from the tender nurturing of eggs to the emergence of the next generation. It’s a spectacle that showcases the resilience and beauty of life itself.
Guardians of Balance: The Mexican Alligator Lizard’s Role in the Ecosystem
Explore the vital role that Mexican Alligator Lizards play in maintaining the delicate equilibrium of their ecosystems. As both predators and prey, these reptiles contribute to the intricate web of life in their natural habitats.
Delve into the relationships they share with other species, the services they provide to their ecosystems, and the ripple effects of their presence.
The Mexican Alligator Lizard’s significance extends far beyond its enchanting appearance, making it a crucial piece of the ecological puzzle.
A Call to Preservation: Safeguarding the Mexican Alligator Lizard
Amidst a rapidly changing world, the conservation of the Mexican Alligator Lizard stands as a paramount mission.
Explore the challenges these reptiles face due to habitat loss, climate shifts, and human impacts, and discover the dedicated efforts underway to ensure their survival.
Unveil the strategies, both on local and global scales, that aims to secure a future where these captivating creatures continue to roam the landscapes they’ve called home for generations.
Legends and Lore: Cultural Significance of the Mexican Alligator Lizard
Journey through the annals of cultural history and explore the myths, legends, and stories that have intertwined with the Mexican Alligator Lizard throughout time.
Discover how these reptiles have etched their presence into the fabric of local traditions and narratives, capturing the imagination of generations.
From symbolic meanings to tales of transformation, these stories shed light on the deep connections between humans and the natural world, as reflected in the Mexican Alligator Lizard’s role within cultural narratives.
Embracing the Wonder: Mexican Alligator Lizards as Pets
For those with a penchant for the extraordinary, the notion of inviting a Mexican Alligator Lizard into your life may spark intrigue. However, such a venture comes with a set of responsibilities and considerations.
Delve into the realm of caring for these captivating creatures as pets, exploring the joys, challenges, and commitments that come with welcoming a piece of the wild into your home.
From habitat setups to dietary needs, we guide you on a journey toward responsible pet ownership.
Conclusion: Embracing the Enigma of the Mexican Alligator Lizard
As we conclude our exploration of the enthralling world of the Mexican Alligator Lizard, we find ourselves steeped in wonder, admiration, and a deeper connection to the natural world.
From their stunning aesthetics to their vital role in ecosystems, these creatures remind us of the intricate tapestry of life that spans our planet. The Mexican Alligator Lizard serves as a testament to the boundless diversity and beauty that nature has to offer.
Each encounter with these reptilian wonders invites us to embrace the mysteries of the wild and nurture a sense of responsibility for the preservation of our shared heritage.
Whether you’re a seasoned biologist or an amateur naturalist, the allure of the Mexican Alligator Lizard beckons us all to become stewards of their captivating legacy.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs)
Can Mexican Alligator Lizards be kept as pets?
Absolutely, but it’s essential to provide them with a suitable habitat, diet, and care that mimics their natural environment.
What do Mexican Alligator Lizards eat?
Their diet includes insects, small vertebrates, and even fruits, making their feeding habits intriguingly diverse.
How big do Mexican Alligator Lizards grow?
Sizes vary between species, with some reaching up to 12 inches in length, tail included.
Are Mexican Alligator Lizards venomous?
No, these lizards are not venomous, and they rely on other defense mechanisms to protect themselves.
How do Mexican Alligator Lizards communicate?
They use a combination of body language, visual displays, and even vocalizations to communicate with each other.
Are Mexican Alligator Lizards endangered?
Several species of Mexican Alligator Lizards are facing threats due to habitat loss and other factors, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts.
Can Mexican Alligator Lizards regrow their tails?
Yes, like many other lizards, they have the ability to regenerate their tails if they lose them due to predation or other reasons.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Unveiling the Marvels of the Mexican Alligator Lizard: A Fascinating Reptilian Wonder!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Reptile
Tokay Gecko: Discovering the Colorful World of a Striking Reptile

Tokay Gecko: Discovering the Colorful World of a Striking Reptile
If you’re looking to add a gecko to your pet lineup, the Tokay gecko is a great option to consider. This gecko is native to parts of the eastern Mediterranean region, and as a result, it is adaptable to a variety of climates and environments.
In this guide, we’ll discuss the required supplies for caring for a Tokay gecko as well as tips for breeding and caring for these geckos.
We’ll also provide an overview of their conservation status as well as where to find them. Finally, we’ll highlight some of their key physical characteristics and behavior. Ready to get started? Let’s go!
Required Supplies For Tokay Geckos
Are you interested in adding a Tokay gecko to your pet lineup?

If so, you’ll need to be prepared to care for them properly. Feed them a small number of insects daily, set the basking light at 100-120 degrees Fahrenheit to thermoregulate, and make sure the cage has plenty of hiding spots, climbing surfaces, and water dishes.
Additionally, make sure to keep the gecko well-fed as they love food and can get quite big. In the end, Tokay gecko care is a relatively easy task that will be a rewarding experience for both you and your new pet lizard!
Tokay Gecko – A Brief Overview
Tokay geckos are small lizards that come in many colors and patterns. They’re easy to care for as long as you have the right supplies and know what to do.
Feed them live food such as crickets or worms twice a day, and give them water regularly. These lizards require a moderate amount of space – around 8 square feet is ideal.
If you have a Tokay gecko as a pet, be sure to keep an eye on their health and provide the right environment – humidity, a warm temperature, and lots of reptile-safe substrates.
Breeding And Caring For Tokay Geckos
If you’re thinking of adding a Tokay Gecko to your family, be prepared to spend some time caring for them.

They’re a great pet choice because they’re easy to breed and care for. Make sure your gecko has plenty of climbing surfaces and a well-furnished enclosure to encourage breeding.
The key to successful breeding is providing high-quality environmental conditions. Finally, be sure to read up on the care and feeding of Tokay Geckos to get the most out of your new pet!
Tips For Handling Tokay Geckos
If you’re looking for a pet that’s easy to care for, Tokay Geckos are a great option.
These geckos are also highly intelligent, making them ideal for people with busy lifestyles. While they require minimal maintenance, their territoriality tendencies make them unsuitable for housing with other small animals.
In terms of space, these geckos can live in small spaces as long as they have enough to climb and explore.
One thing to keep in mind is to provide them with a climbing surface – Tokays love to gecko on high places! And as always, be sure to provide plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables as they are known to be good eaters.
Conservation Status
Tokays are small lizard that needs specific care as a pet.
If you’re thinking of getting one as a pet, it’s important to be aware of the conservation status of this lizard as well as the specific care they need.
Tokays are small and aggressive lizard that needs a specific type of environment – one with plenty of climbing space and little to no competition. They also need a specialized diet to thrive, so make sure you purchase the correct food and feeders.
As with all pet lizards, be prepared to provide regular veterinarian checkups and treatment for health issues such as seizures and eye infections. They should also be kept with plenty of space, as they are territorial and can become aggressive with other pets.
Where To Find The Tokay Gecko
There’s no doubt that the Tokay gecko is one of the most popular pet gecko species on the market today. This small, colorful lizard is easy to care for and can make a great home companion.
They’re best suited to living in warm climates, so if you’re looking to add one to your family, be sure to check the climate requirements of the Tokay gecko before making the purchase.
As for their diet, feed them a pellet diet and provide plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables as part of their regimen. And as with all pets, be sure to keep an eye on their health and make regular check-ups. In the end, the Tokay gecko is a fun and rewarding pet to have.
Captivity
If you’re interested in keeping a gecko as a pet, there are a few things to keep in mind.
First, be sure to give your gecko some time out of its cage to get used to being around people again. Tokay Geckos are great pets for those who are interested in keeping lizards or snakes as pets.
They are easy to care for, and as long as you provide plenty of fresh fruit, insects, and other reptiles as snacks for them every day, they will be happy as can be.
Be sure to read up on gecko care to get a better understanding of what your gecko needs and how to provide it.
And last but not least, have fun! Geckos are one of the most active reptile species out there, so make sure to provide them with plenty of space to run and play.
Physical Characteristics And Behavior
If you’re considering adding a tokay gecko to your pet family, be sure to know their physical characteristics as well as their behavior.
Tokays handle warm temps well but like cool nights too – ambient room temperature should be about 75 degrees.
They come in a variety of colors including yellow-and-green striped camouflage patterns with black spots on their bellies and throats; reds, oranges, and yellows; browns with splotches or patches of gray or white; albescent whites that fade from light green to off-white tones as they age; greys with dark bands running horizontally down their backs.
And background color ranging from khaki through burnt sienna to reddish rust almost black (almost all shades have some variation).
Tokays make good pets for those who have a lot of space as they can live in as small as a 10-inch square cage as long as it’s well-ventilated.
Distribution And Habitat
Tokay geckos make great pets, but they require high humidity levels to thrive.
As a result, keep the area around your pet moist by spraying the area with a water bottle to achieve the desired humidity level. Additionally, provide a climbing structure and plenty of hiding spaces for the pet to explore.
Make sure to always provide food and water dishes for your lizard friend. Tokay geckos can be kept as pets in a variety of locations, including apartments and condos.
So, if you’re looking to add a little excitement to your life as well as some gecko fun, give these lizards a try!
Subspecies
Tokay geckos are a great pet choice for pet owners because of their small size and easy-to-handle temperament.
There are four subspecies of tokay gecko, each with its own specific set of care requirements. Make sure to research the specific needs of your chosen subspecies before buying!
Apart from providing the basics like a good diet and plenty of climbing space, you’ll need to make sure to provide your pet gecko with a chew toy and UVB light to bask in during the day.
Last but not least, always keep in mind to provide your gecko with a good name – something to call them by during their adventures!
Conclusion
Tokay geckos are one of the most popular pet lizard species and for good reason – they are beautiful, well-behaved, and easy to care for.
In this guide, we have outlined everything you need to know to keep your Tokay gecko as a pet. From required supplies to tips on breeding and caring for them, to conservation status and where to find them, we have covered it all!
Make sure to bookmark this page and come back to find the latest updates on Tokay gecko care.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs)
How Often Should I Feed My Tokay Gecko?
Tokay geckos need to be fed a small amount of insects every other day to meet their nutritional needs. Insects should only be fed to geckos if they are kept safe and out of the gecko’s reach.
A feeding window should be every other day, but this will vary depending on how active your gecko is.
How Can I Make Sure That My Tokay Gecko Is Healthy And Happy?
To ensure that your Tokay Gecko is healthy and happy, follow these tips:
1. Make sure their cage has both moisture and humidity levels, as well as plenty of hiding spots.
2. If you have more than one gecko, make sure to divide up their food evenly between them.
3. The best way to keep your Tokay Gecko healthy is by providing a proper environment and diet. Feed them crickets, super worms, or other similar-sized prey items for both meat and calcium.
What Are Some Common Problems That Geckos Face, And How Can I Prevent Them From Happening To My Pet Gecko?
Some of the most common problems geckos face are dehydration, getting tangled up in their webs, and fractures from accidents. To help avoid these problems from happening to your gecko, follow these tips:
1. Make sure your gecko has access to fresh food and water at all times.
2. Keep your gecko safe and hydrated by providing them with proper ventilation during hot weather conditions.
3. If your gecko gets tangled up in their web, immediately remove the webbing with a pair of good scissors to prevent further injury or fractures.
What Types Of Food Should I Offer My Tokay Gecko?
Offering your Tokay Gecko a varied and fresh diet is essential to their well-being. They will eat insects, vegetables, fruit, and bird food. Offer a small portion of the above every day in a hanging or wire cage or feeder.
Is It Okay To Use Heat Or Cold On A Tokay Gecko During The Winter Months?
It’s okay to use heat or cold on a Tokay Gecko during the winter months as long as you’re following some guidelines. When it comes to using heat, geckos are nocturnal animals and will be more active at night when it’s cooler outside.
So, heating the gecko’s enclosure during the day can be effective in keeping them warm. On the other hand, using cold temperatures is recommended for those days when it’s slightly below freezing and should only be used if necessary as it may cause harm to the gecko.
When it comes to keeping your Tokay Gecko healthy and comfortable in the colder months, you can either use heat or cold. Personally, I like to use cold as it seems to keep my gecko more active and awake.
How Can I Tell If My Gecko Is Sick?
If you notice any changes in your gecko’s activity or appearance, it is probably time to take him to the vet. Changes that could suggest illness for a gecko can include drooping eyes, lethargy, loss of appetite and water consumption, crusty skin around the eyes and mouth, and irregular shedding.
What Is The Best Way To Store Geckos?
When it comes to gecko care, the most important thing to remember is to keep them clean and dry. You can do this by using nontoxic and moisture-resistant products to clean their enclosure regularly.
Additionally, provide them with a gecko home that can be turned into a climbing space. Make sure the enclosure’s temperature is warm enough as geckos are arboreal animals and need a lot of climbing space.
How Can I Tell If My Tokay Gecko Is In Good Health?
When it comes to taking care of your Tokay Gecko, make sure to always consult with your veterinarian as changes in behavior or appearance may be indicative of a health issue that needs to be addressed.
Healthy geckos will typically have a glossy coat, be active and interactive, and eat regularly.
Can A Gecko Love You?
Tokay geckos are one of the best reptile choices for people who are looking for an easy-to-care-for pet. They require very little attention and as long as you have a few insects available to them, they will be just fine.
Tokays typically live around 10 years, so you’ll never have to worry about having to take care of one for too long.
What Is It Like To Have A Tokay Gecko?
If you’re curious about what it’s like to have a tokay gecko as a pet, then these gecko lovers will tell you that it’s easy to take care of and doesn’t require much attention.
Tokay Geckos are some of the most popular lizards in the world, thanks to their easy care requirements. All you need to do is provide them with a small space, fresh water every day, and enough food – which can be purchased at your local pet store.
Furthermore, tokay gecko enthusiasts will love to know that their pet needs very little care – all they need is a small space and enough food. These gecko lovers will love knowing that their pet doesn’t require any type of heating or cooling system, as well as a dark room to call home.
Should I Get A Tokay Gecko?
Yes, if you’re interested in getting a Tokay gecko as a pet. Feeding them insects on a regular basis is easy – just place them on the dish every day.
They are active and playful creatures and come in a variety of colors, so you’re bound to find one that suits your taste.
Some things to keep in mind when choosing a Tokay gecko as a pet include their size (geckos need somewhere to climb), the amount of time you’re willing to spend caring for them, and the amount of light they need each day.
Geckos need at least 12 hours of light each day, so you will have to plan your daily routine around that fact.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Tokay Gecko: Discovering the Colorful World of a Striking Reptile!?”
Please you should feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
-

 Pet Care2 years ago
Pet Care2 years agoThe Best Dog Collars For 2022
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoBichon Frise: The Happy, Playful, and Cuddly Companion
-

 Trending Pet Stories1 year ago
Trending Pet Stories1 year ago2023 ‘World’s Ugliest Dog’ Winner: Scooter’s Tale of Resilience
-

 Animals2 years ago
Animals2 years agoAre There Animals Having Down Syndrome?
-

 Pets2 years ago
Pets2 years agoThe Fascinating World Of The Red Chameleon
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Dog Breeds According To AKC.
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years ago21 Dog Breeds That Resemble Bears Or Teddy Bears!
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoEskimo Dogs from Canada – What Are They? – Find Out!