Cats
Unraveling the Importance of the Rabies Vaccine for Cats

The Vital Feline Defense: Unraveling the Importance of the Rabies Vaccine for Cats
Rabies, my fellow feline enthusiasts, is not merely a word but a dark and sinister specter that prowls in the shadows, threatening both our beloved cats and us humans.
It’s a viral disease that primarily affects mammals and is transmitted through the saliva of infected animals.
Once it takes hold, it attacks the central nervous system, leading to a cascade of neurological symptoms that are both distressing and, ultimately, fatal.
What is Rabies and Why It’s a Grave Concern
Picture this: a stealthy, enigmatic disease that affects both humans and animals, leaving a trail of neurological havoc in its wake.
That’s rabies, an ailment caused by a virus found in the saliva of infected animals. Let’s unravel why it’s a grave concern for our beloved feline companions.
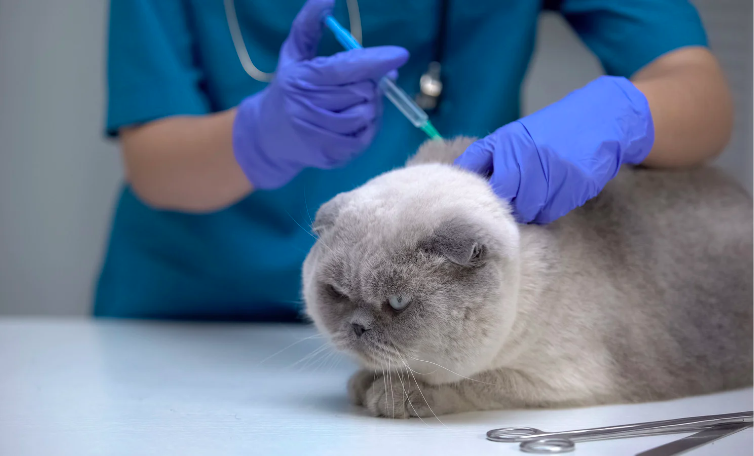
The rabies vaccine for cats is an essential preventive measure that safeguards both feline well-being and public safety. Rabies is a deadly viral disease that can affect all mammals, including humans, and is transmitted through the bite of an infected animal.
Vaccinating your cat against rabies not only protects them from this fatal disease but also helps prevent its spread to humans and other animals. Here’s why the rabies vaccine for cats is of utmost importance:
The Role of Vaccination in Feline Health
Ah, vaccines – the superheroes of the medical world! Just like our own immune systems, cats can benefit greatly from vaccinations.
They work by introducing a weakened or inactivated form of the virus to trigger a protective response. This response equips your cat’s immune system to recognize and fight off the virus if encountered in the future.
- Feline Health: Rabies is a fatal disease with no cure once symptoms appear. Vaccinating your cat against rabies ensures their protection, preventing them from contracting and suffering from this deadly virus.
- Public Safety: Rabies can be transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected animal. By vaccinating your cat, you’re contributing to the overall reduction of rabies cases, thus lowering the risk of human exposure.
- Legal Requirement: In many regions, including most states in the US, rabies vaccination for cats is legally mandated. Complying with these regulations not only avoids legal issues but also contributes to the control of the disease.
- Indoor Cats Are Not Exempt: Even if your cat is primarily indoors, they can still be at risk if they come into contact with rabid animals or if an indoor cat accidentally escapes. The vaccine offers them protection should such situations arise.
- Preventing Spread: Rabies can be transmitted not only through direct bites but also through contact with the saliva of infected animals. By vaccinating your cat, you’re preventing the potential spread of the disease through interactions with other animals or humans.
A Cross-Species Threat: Zoonotic Nature of Rabies
Now, let’s unravel the complexity of rabies’ cross-species threat. This disease doesn’t discriminate – it poses a grave danger to humans and animals alike.
Rabies is considered a zoonotic disease, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans through bites, scratches, or contact with infected bodily fluids.
This ominous characteristic underscores the urgency of addressing rabies not just for our furry companions’ sake but for the safety of our households and communities as well.
The Chilling Progression of Rabies Symptoms
The progression of rabies symptoms paints a chilling portrait of the disease’s impact. It all begins innocently enough with vague symptoms like fever and headache, which can easily be mistaken for other ailments.
However, as the virus advances, it takes a menacing turn, leading to confusion, anxiety, hallucinations, excessive drooling, and even hydrophobia – a fear of water.
Eventually, the disease reaches its cruel culmination in paralysis, convulsions, and death.
Transmission Dynamics: How Rabies Spreads
Understanding how rabies spreads is crucial to appreciating its gravity.
The virus is primarily transmitted through bites or scratches from infected animals, with the virus traveling along nerve pathways to the brain.
Once the brain is infected, the virus travels to the salivary glands, amplifying the likelihood of transmission through bites, hence cementing its reputation as a deadly menace.
The Local Threat: Rabies in Our Vicinity
It’s easy to think of rabies as a distant threat, but the reality is that this deadly disease could be lurking in your very own neighborhood.
Urban areas might seem safe, but even in bustling cities, rabid animals can emerge, posing a risk to both pets and people.
Staying informed and proactive is the key to safeguarding your feline companion and preventing the potential spread of rabies.
Why Cats are Vulnerable: An Insight into Susceptibility
But why are cats particularly vulnerable to rabies? One reason lies in their curious nature.
Cats, being natural hunters and explorers, might come into contact with potentially infected animals, making them susceptible to bites or scratches.
Moreover, their grooming habits put them at risk of ingesting the virus if it’s present on their fur, accentuating the need for protective measures like vaccination.
Beyond Borders: The Global Rabies Challenge
Rabies doesn’t adhere to geographical boundaries – it’s a global challenge that affects communities worldwide.
While some regions have managed to control rabies through widespread vaccination programs, in many parts of the world, it remains a dire public health concern.
By understanding the gravity of the situation, we can contribute to the global effort of eradicating this insidious threat.
The Unseen Enemy: Rabies and its Incubation Period
One of the most unnerving aspects of rabies is its incubation period – the time between exposure to the virus and the onset of symptoms.
This duration can vary widely, making it difficult to detect and address rabies early on.
This unseen enemy underscores the importance of proactive measures, such as timely vaccinations, to ensure your feline friend’s protection.
Tackling the Fear Factor: Rabies-Induced Hydrophobia
Hydrophobia, an aversion to water, is a chilling symptom associated with rabies.
Infected individuals, both human and animal, experience spasms in the throat muscles when attempting to swallow water, leading to a deeply unsettling fear of water.
This distinct symptom adds another layer of terror to the already formidable threat of rabies.
Conclusion
In this captivating exploration, we’ve unveiled the imperative role of the rabies vaccine for cats. It’s not just a shot – it’s a safeguard against a potentially fatal menace.
By understanding its importance, you’re not only ensuring your feline friend’s well-being but also promoting a safer environment for everyone.
So, let’s stand together in protecting our cherished companions by embracing the power of vaccination.
FAQs About Rabies Vaccine for Cats
Can indoor cats skip the rabies vaccine?
It might seem tempting to skip the rabies vaccine for indoor cats, but remember, rabies can still pose a threat if an infected animal enters your home or if your cat accidentally escapes. It’s safer to vaccinate, even if your feline friend mostly stays indoors.
Is the rabies vaccine expensive?
The cost of the rabies vaccine can vary based on factors like location and veterinary clinic. While the expense might vary, the protection it offers against a potentially life-threatening disease is invaluable.
Can kittens get the rabies vaccine?
Absolutely! Kittens can start receiving their rabies vaccine as early as 12 weeks of age. Starting them on the vaccination schedule helps ensure their safety from a young age.
Can an indoor cat transmit rabies?
A4: Rabies transmission occurs through contact with the saliva of an infected animal, usually through bites. Indoor cats have a lower risk of exposure, but it’s important to remember that the disease can still be a threat if they encounter an infected animal.
Are there alternatives to traditional vaccines?
A5: While there’s ongoing research into alternative vaccination methods, traditional vaccines are currently the most effective and widely recommended way to protect your cat against rabies and other diseases.
Can cats with health issues get vaccinated?
A6: Your veterinarian will assess your cat’s health before administering any vaccines. In most cases, even cats with certain health issues can receive vaccinations, but adjustments might be made based on their specific condition.
Can humans get rabies from vaccinated cats?
The rabies vaccine is designed to prevent the virus from replicating in an animal’s body, making it highly unlikely for vaccinated cats to transmit rabies to humans. The vaccine reduces the risk of transmission significantly.
Remember, these FAQs provide insight into common concerns, but always consult your veterinarian for personalized advice tailored to your cat’s individual needs and circumstances.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Unraveling the Importance of the Rabies Vaccine for Cats!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Cats
Clever Cats: Breeds That Learn Fast

Clever Cats: Breeds That Learn Fast
Cats have always fascinated us with their agility, independence, and sometimes enigmatic behavior. Among the vast array of feline breeds, some stand out for their remarkable intelligence and ability to learn quickly.
In this article, we will delve into the world of these exceptional cat breeds, exploring their unique characteristics, training capabilities, and what makes them such quick learners.
Whether you’re a seasoned cat owner or considering adopting a new feline friend, this comprehensive guide will help you understand the breeds that are not only intelligent but also a joy to train.
Why Intelligence Matters in Cats
Understanding Feline Intelligence
Feline intelligence is a multi-faceted trait that encompasses problem-solving abilities, social learning, and adaptability. Unlike dogs, cats often showcase their intelligence in more subtle ways, such as manipulating objects to get what they want or learning routines and commands.
Benefits of Owning Intelligent Cats
Owning an intelligent cat comes with several benefits. These cats are more interactive and engaging, making them excellent companions. They can learn tricks, follow commands, and even understand basic household rules, which makes living with them more enjoyable and less challenging.
Top Cat Breeds Known for Their Intelligence
Abyssinian

Overview
The Abyssinian is often hailed as one of the smartest cat breeds. Known for their curiosity and playful nature, Abyssinians are quick learners who thrive on mental stimulation.
Training and Activities
Abyssinians are highly trainable and enjoy interactive toys and puzzle feeders. They can learn tricks such as fetching and even walking on a leash. Their love for heights means they appreciate cat trees and climbing structures.
Siamese

Overview
Siamese cats are not only intelligent but also highly vocal and sociable. They form strong bonds with their owners and are always eager to engage in activities.
Training and Activities
Siamese cats are quick to learn tricks and commands. They enjoy interactive play and can be trained to perform simple tasks like opening doors or retrieving items. Their vocal nature also makes them responsive to verbal cues.
Bengal

Overview
Bengals are known for their striking appearance and high energy levels. Their intelligence is reflected in their ability to solve problems and learn complex tasks.
Training and Activities
Bengals enjoy activities that challenge their minds, such as agility courses and puzzle toys. They can be trained to walk on a leash and perform tricks. Providing them with interactive playtime helps in channeling their energy positively.
Burmese

Overview
Burmese cats are affectionate, people-oriented, and intelligent. They enjoy being involved in family activities and can be trained to follow various commands.
Training and Activities
Burmese cats are quick learners and respond well to positive reinforcement. They enjoy learning tricks, playing fetch, and interactive games that stimulate their minds.
Scottish Fold

Overview
Scottish Folds are known for their distinctive folded ears and sweet demeanor. Despite their calm appearance, they are intelligent and can learn quickly.
Training and Activities
Scottish Folds enjoy interactive toys and games. They can learn tricks and commands and appreciate routines that keep their minds engaged.
Training Tips for Intelligent Cats
Start Early
Begin training your cat as early as possible. Kittens are more receptive to learning new behaviors and routines.
Use Positive Reinforcement
Reward your cat with treats, praise, or playtime whenever they successfully perform a desired behavior. Positive reinforcement strengthens the association between the action and the reward.
Keep Sessions Short and Fun
Cats have shorter attention spans than dogs, so keep training sessions brief and enjoyable. Incorporate playtime to make learning fun for your cat.
Be Patient and Consistent
Patience and consistency are key when training cats. Repeat commands and routines regularly, and avoid punishing your cat for mistakes. Consistency helps reinforce learning and builds trust.
Challenges of Training Intelligent Cats
Independence and Stubbornness
Intelligent cats can sometimes be independent and stubborn. They might choose to ignore commands if they are not in the mood, so it’s important to understand their behavior and work with it.
Need for Mental Stimulation
Highly intelligent cats require constant mental stimulation. Boredom can lead to behavioral issues, so ensure they have plenty of toys, activities, and interaction to keep their minds engaged.
Managing High Energy Levels
Breeds like Bengals have high energy levels that need to be managed. Providing them with enough physical and mental exercise is crucial to prevent destructive behavior.
Living with Intelligent Cats
Creating an Enriched Environment
An enriched environment is essential for intelligent cats. This includes a variety of toys, climbing structures, scratching posts, and interactive feeders to keep them stimulated.
Social Interaction
Intelligent cats thrive on social interaction. Spend quality time playing, training, and simply bonding with your cat to ensure they feel valued and engaged.
Understanding Their Needs
Each intelligent breed has its own unique needs and preferences. Understanding these and catering to them will help you build a strong and positive relationship with your cat.
Conclusion
Owning an intelligent cat can be an incredibly rewarding experience. These quick learners bring joy, challenge, and companionship to their owners. By understanding their unique characteristics and providing the right environment and training, you can foster a deep and fulfilling relationship with your feline friend.
Whether you choose an Abyssinian, Siamese, Bengal, Burmese, or Scottish Fold, you’re sure to enjoy the remarkable intelligence and personality they bring into your home.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What makes a cat breed intelligent?
Intelligent cat breeds often show high levels of problem-solving abilities, adaptability, and social learning. They can quickly learn commands, tricks, and routines.
Can all cats be trained?
While some breeds are more receptive to training than others, all cats can be trained to some extent. Patience, consistency, and positive reinforcement are key to successful training.
What are the best toys for intelligent cats?
Interactive toys, puzzle feeders, and climbing structures are ideal for intelligent cats. These toys provide mental stimulation and keep them engaged.
How do I keep my intelligent cat from getting bored?
Provide a variety of toys, engage in regular playtime, and introduce new activities regularly. Rotating toys and creating an enriched environment also help prevent boredom.
Are intelligent cats more difficult to care for?
Intelligent cats can be more demanding in terms of mental stimulation and interaction. However, with the right approach and environment, they can be delightful companions.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Clever Cats: Breeds That Learn Fast!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Cats
The Enchanting Scottish Fold: A Guide to the Adorable Feline with Folded Ears

The Enchanting Scottish Fold: A Guide to the Adorable Feline with Folded Ears
Welcome to the world of the Scottish Fold cat, where charm and curiosity meet in an irresistibly adorable package. With their distinctive folded ears and sweet expression, Scottish Folds have captured the hearts of cat lovers around the world. Originally hailing from Scotland, these cats are known for their gentle demeanor, playful nature, and loving personality.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fascinating world of Scottish Fold cats, exploring their history, physical characteristics, personality traits, and care requirements. Whether you’re a seasoned cat owner or considering adding a feline friend to your family, the Scottish Fold’s unique charm and affectionate nature make them a delightful addition to any home. Join us as we unravel the enchanting tale of the Scottish Fold cat and discover why they are such beloved companions.
Fold
Overview
The Scottish Fold cat is a charming and distinctive breed known for its unique folded ears and sweet expression. Originating from Scotland in the 1960s, these cats have captured the hearts of many with their endearing appearance and affectionate nature. Scottish Folds are known for their gentle and loving temperament, making them wonderful companions for families and individuals alike.
History and Origins
The Scottish Fold breed traces its roots back to a white barn cat named Susie, who was found in Scotland in the early 1960s. Susie had a unique genetic mutation that caused her ears to fold forward, giving her an owl-like appearance. This trait was passed down to her kittens, and thus, the Scottish Fold breed was born. The breed quickly gained popularity for its distinctive look and friendly demeanor, and it was officially recognized by cat registries in the 1970s.
Physical Characteristics
- Folded Ears: The most distinctive feature of the Scottish Fold is its folded ears, which give the cat a sweet and owl-like appearance. Not all Scottish Folds have folded ears; some may have straight ears, known as “straights,” which are also common in the breed.
- Coat and Colors: Scottish Folds can have either a short or long coat, both of which are dense and plush. They come in a variety of colors and patterns, including tabby, tortoiseshell, and solid colors like white, black, and blue.
- Body Structure: Scottish Folds are medium-sized cats with a rounded appearance. They have sturdy bodies, round faces, and large, expressive eyes that give them a sweet and gentle expression.
Personality and Behavior
Scottish Folds are known for their calm and laid-back demeanor. They are affectionate cats that enjoy being around people and are often described as “lap cats” due to their love of cuddling. They are also known for their playful nature and enjoy interactive toys and games. Scottish Folds are generally good with children and other pets, making them a great choice for families.

Health and Care
- Ear Care: Due to their folded ears, Scottish Folds may be prone to ear infections. It’s important to regularly check and clean their ears to prevent issues.
- Grooming: Scottish Folds have dense coats that require regular grooming to prevent matting and tangling. Weekly brushing is usually sufficient to keep their coat in good condition.
- Health Concerns: Scottish Folds are generally healthy, but they may be prone to certain genetic conditions, including a skeletal disorder known as osteochondrodysplasia. Responsible breeding practices can help minimize the risk of these health issues.
Training and Activities
Scottish Folds are intelligent cats that can be trained to perform tricks and commands. They enjoy interactive play and benefit from toys that stimulate their minds and bodies. Providing them with scratching posts and other outlets for their natural behaviors can help keep them happy and healthy.
Compatibility with Families and Other Pets
Scottish Folds are known for their gentle and affectionate nature, making them great companions for families. They are good with children and other pets, including dogs, and can adapt well to different environments. Their loving and sociable nature makes them a popular choice for households looking for a friendly and affectionate pet.
Conclusion
The Scottish Fold cat is a unique and charming breed known for its folded ears and sweet expression. With their gentle demeanor and affectionate nature, Scottish Folds make wonderful companions for families and individuals alike. Whether you’re looking for a lap cat to cuddle with or a playful friend to keep you entertained, the Scottish Fold cat is sure to bring joy and companionship to your home.
FAQs about Scottish Fold Cats
Why do Scottish Folds have folded ears?
Scottish Folds have a genetic mutation that affects the cartilage in their ears, causing them to fold forward. This unique trait gives them their distinctive appearance.
Are Scottish Folds prone to ear problems due to their folded ears?
Yes, Scottish Folds may be more prone to ear infections due to the fold in their ears, which can trap dirt and moisture. Regular cleaning and monitoring of their ears can help prevent issues.
Do Scottish Folds have any health issues associated with their folded ears?
Scottish Folds may be prone to a condition called osteochondrodysplasia, which affects the development of their cartilage and bones. Responsible breeding practices can help reduce the risk of this condition.
Are Scottish Folds good with children and other pets?
Scottish Folds are known for their gentle and friendly nature, making them good companions for families with children and other pets. They enjoy socializing and being part of the family.
Do Scottish Folds require a lot of grooming?
Scottish Folds have dense coats that require regular grooming to prevent matting and tangles. Weekly brushing is recommended to keep their coat in good condition.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”The Enchanting Scottish Fold: A Guide to the Adorable Feline with Folded Ears!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Cats
The Enchanting Burmese Cat: Affectionate, Playful, and Loyal
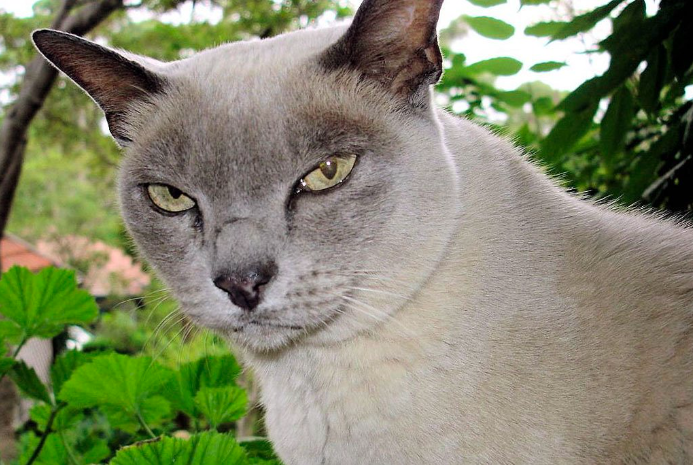

The Enchanting Burmese Cat: Affectionate, Playful, and Loyal
Enter the world of the Burmese cat, where elegance meets affection in a charming feline companion. Originating from the temples of Burma, these cats have captured the hearts of cat lovers worldwide with their striking appearance and loving nature. With their sleek coats, expressive eyes, and playful demeanor, Burmese cats are not just pets; they are cherished members of the family.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the captivating world of Burmese cats, exploring their history, physical characteristics, personality traits, and care requirements. Whether you’re a seasoned cat owner or considering adding a feline friend to your family, the Burmese cat’s unique blend of beauty, intelligence, and affection is sure to captivate you. Join us as we unravel the enchanting tale of the Burmese cat and discover why they are such beloved companions.
Burmese
Overview
The Burmese cat is a breed known for its striking appearance and affectionate nature. Originating from Burma (now Myanmar), these cats are renowned for their sleek, muscular bodies, expressive eyes, and silky coats. Burmese cats are often described as “people-oriented,” as they form strong bonds with their human companions and enjoy being part of the family. Their playful and curious nature makes them delightful companions for both children and adults alike.
History and Origins
The history of the Burmese cat can be traced back to ancient Burma, where they were considered sacred and kept by monks in temples. They were later brought to the West in the early 20th century and quickly gained popularity for their striking appearance and affectionate personality. The breed has since become a favorite among cat enthusiasts worldwide, known for its loving and loyal nature.
Physical Characteristics
- Coat and Colors: Burmese cats have short, sleek coats that lie close to the body. They come in a variety of colors, including sable, champagne, blue, and platinum. The coat is soft and silky to the touch, adding to the breed’s overall charm.
- Body Structure: Burmese cats are medium-sized with a muscular build. They have rounded heads, large, expressive eyes, and short, straight noses. Their compact bodies give them a sturdy appearance, and they move with grace and agility.
- Eyes and Ears: Their eyes are one of their most striking features, being large, expressive, and usually a deep, rich color that complements their coat. Their ears are medium-sized, slightly rounded at the tips, and set wide apart on the head.
Personality and Behavior
Burmese cats are known for their affectionate and sociable nature. They are often described as “dog-like” due to their tendency to follow their owners around the house and seek out human companionship. They are also highly intelligent and enjoy interactive play, making them great companions for families with children or other pets.
In addition to their affectionate nature, Burmese cats are also known for their vocalizations. They have a soft, sweet voice that they use to communicate with their owners, often engaging in “conversations” and expressing their needs and desires.

Health and Care
- Grooming: Burmese cats have short coats that require minimal grooming. Weekly brushing is usually sufficient to remove loose hair and keep their coat shiny. They also benefit from regular dental care to prevent oral health issues.
- Diet: A high-quality, balanced diet is essential for maintaining the health and vitality of Burmese cats. They should be fed a diet that is appropriate for their age, size, and activity level to ensure they receive the nutrients they need.
- Health Concerns: Burmese cats are generally healthy, but they can be prone to certain genetic conditions such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and diabetes. Regular veterinary check-ups and a healthy diet can help manage these risks.
Training and Activities
Burmese cats are intelligent and can be trained to perform various tricks and commands. They enjoy interactive play and thrive on mental stimulation. Providing them with toys, puzzle feeders, and opportunities for play can help keep them entertained and prevent boredom.
Compatibility with Families and Other Pets
Burmese cats are known for their loving and social nature, making them great companions for families. They get along well with children and other pets, including dogs, as long as they are properly introduced. Their affectionate demeanor and playful nature make them a popular choice for households looking for a friendly and engaging pet.
Conclusion
The Burmese cat is a breed beloved for its affectionate nature, striking appearance, and playful personality. Whether you are looking for a loyal companion or a playful friend, the Burmese cat is sure to bring joy and warmth to your home. With their loving nature and sociable demeanor, Burmese cats make wonderful pets for families and individuals alike, enriching their lives with their presence and affection.
FAQs about Burmese Cats
What is the temperament of a Burmese cat like?
Burmese cats are known for their affectionate and social nature. They are often described as “dog-like” due to their loyalty and tendency to follow their owners around the house. They enjoy being involved in family activities and form strong bonds with their human companions.
Are Burmese cats good with children and other pets?
Yes, Burmese cats are generally good with children and other pets. They are playful and enjoy interactive play, making them great companions for families with children. They also get along well with other pets, including dogs, especially if they are introduced properly.
Do Burmese cats require a lot of grooming?
Burmese cats have short, sleek coats that require minimal grooming. Weekly brushing is usually sufficient to remove loose hair and keep their coat shiny. They also benefit from regular dental care to prevent oral health issues.
Are Burmese cats vocal?
Burmese cats are known for their soft, sweet voice, but they are not excessively vocal. They use their voice to communicate with their owners, often engaging in “conversations” and expressing their needs and desires.
What kind of environment is best for a Burmese cat?
Burmese cats thrive in environments where they have plenty of opportunities for play and interaction. They enjoy being part of the family and should have access to toys, scratching posts, and other enrichment activities. They also enjoy having access to outdoor enclosures or safe outdoor spaces where they can explore and indulge their natural instincts.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”The Enchanting Burmese Cat: Affectionate, Playful, and Loyal!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
-

 Pet Care2 years ago
Pet Care2 years agoThe Best Dog Collars For 2022
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoBichon Frise: The Happy, Playful, and Cuddly Companion
-

 Trending Pet Stories1 year ago
Trending Pet Stories1 year ago2023 ‘World’s Ugliest Dog’ Winner: Scooter’s Tale of Resilience
-

 Animals2 years ago
Animals2 years agoAre There Animals Having Down Syndrome?
-

 Pets2 years ago
Pets2 years agoThe Fascinating World Of The Red Chameleon
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Dog Breeds According To AKC.
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years ago21 Dog Breeds That Resemble Bears Or Teddy Bears!
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoEskimo Dogs from Canada – What Are They? – Find Out!