Pet Care
All The Facts & Info You Need To Know About American Bison

Everything Facts & Info You Need To Know About American Bison
If you’ve ever wondered what makes a bison so unique, you’ve come to the right place. Bison are ruminants, a type of mammal that is both diurnal and polygynous.
Among their other characteristics, bison have large hearts and lungs and are faster than cattle. Hence, they make excellent hunters, though they can’t be used for meat.
Habitat OF The Animal
The habitat of the American bison is one of the most endangered ecosystems on the planet.

This enormous animal shaped the ecosystems of North America by surviving in a diverse range of ecosystems and grazing in dry grasslands.
As a result, bison have impacted the ecosystems in a variety of ways, including influencing the diversity and processes of plants. They are also considered a keystone species for the prairie communities.
The habitat of American bison varies from part of the country to the next. Although they are most commonly found on open plains, they can also be found in river valleys and semi-wooded areas.
Occasionally, these large mammals will roam into mountainous and foothill areas to eat a variety of plants.

Although their habitat is different from other animals, they prefer grassy areas and are often found in the midst of national parks.
Conservation efforts have resulted in a new plan for bison that will allow bison populations to flourish on large public lands. This plan is important for two reasons.
It will help protect the bison from further extinction and will lead to economic benefits for Native communities.
In addition, the plan will make bison more likely to survive, which will be good news for all. But there is a catch: bison are very hardy animals and can survive in many environments.
There are 500,000 bison in North America today. However, only about 1% of their historic range remains.

They are highly mobile and could be accidentally introduced into an area they aren’t adapted to. The unconfined herds of bison could potentially spread the disease to neighboring populations.
Bison historically lived in grasslands, such as the prairies in the Great Plains. However, they also frequent mountain meadows and aspen parklands in Canada.
Size Of The Animal
The American bison is one of the largest land animals in North America.

It is the largest mammal of its kind and also the heaviest. This species is also the second tallest animal in the world after the moose.
Bison’s size can be deceiving, so let’s look at some facts about this animal. Here, we’ll discuss its size and where it lives. The bison lives in open, grasslands in North America.
They tend to live in parks with enough grass for their diet. The bison fossil record spans over 40,000 years, so the relationship between global temperature and bison body size has been studied.
It shows a strong inverse correlation between body mass and climate. Bison were bigger when the temperature was cooler.
The warming of the planet will decrease bison’s body mass by a factor of six, meaning it will be significantly smaller than it was during the last glacial maximum.

The current global temperature is about 5degC cooler than the last glacial maximum. Bison were around 910 kg at the Last Glacial Maximum, and if the global temperature rises another 4degC, their body mass will fall to 357 kg.
A previous study used skull metrics to determine bison’s size and weight. Although skull metrics are more susceptible to sexual selection, they are also highly variable among species.
Bison’s sexual dimorphism is clearly evident in modern contexts but lost in the fossil record.
The same holds true for osteometrics, which can’t determine intermediate size because the proportion of adult females to immature bulls overlaps.
Predators
Predators of American Bison include the northern saber-toothed cat and the American lion.

The bison was once an iconic species of western North America and were among the few survivors of a catastrophic extinction event.
Overhunting by humans was the primary cause of the bison’s decline, but a few surviving species still exist. Bison have been a part of the landscape for over 250,000 years.
Bulls dominate the bison population, with males defending the female from rival bulls. Bulls will sometimes use their horns to protect a female.
Female bison mate several times before giving birth to a single calf. During early spring, the female is pregnant with a single calf. A bison calf is born weighing fifty pounds, and its fur is reddish in color.

The calf’s first two months are crucial for its development. After birth, a bison calf will stand and walk, demonstrating its strength and endurance.
Although bison were not considered to be significant threats by the modern-day wolf, they were shaped by human predators.
In the late Ice Age, the bison faced ambush predators as well as large packs of pursuit predators. During this period, the bison evolved defensive mechanisms to prevent these predators from pursuing them.
Once these predators had vanished, gray wolves were the main threat to bison. Mountain lions are reported to hunt bison, but attacks on adult bison are rare.

Because they are large and have sharp horns, bison become dangerous when threatened. Bison often stay together in herds, and a predator may have to battle several bison at once.
If a predator is unable to kill a single bison, the whole herd may be attacked. This is why predators should be wary of bison in the wild.
Life Cycle
The bison played a critical role in the development of the North American landscape.

They were extremely adaptable to various ecosystems and survived in the harshest conditions. Their vast range allowed them to move from one part of the continent to the next, seeking food.
Because of this, bison feces were rich in nutrients, which were then decomposed by bacteria and insects. Bison also helped maintain the integrity of ecosystems by regulating the flow of nutrients.
The bison’s life cycle is relatively short. Females live in herds with males for breeding. The males leave the herd when they are three years old and form bachelor herds.

They do not mix with the females again until breeding season. During the first year of life, female bison are largely weaned.
Female bison go through a seasonal cycle of estrus (ejaculation), which can last between nine and 28 hours.
The bison’s weight varies from 318 to 460 kilograms (660 to 1,747 lb). Males are larger than females, and both genders are able to produce a male.
Male bison range in size from seven to ninety centimeters (2.3-four feet) in length, and female bison typically weigh between 360 and 640 kg.
Female bison have a shorter life span than males, but can be a little less tall than the male bison. The American bison’s reproductive cycle is similar to that of other large mammals.

The female gives birth to one calf in an isolated area. The calf is born reddish brown and can stand soon after birth.
The mother and calf spend a couple of days away from the herd before returning to the herd. It is not uncommon for one or two bisons to have a white calf, though it’s extremely rare.
Bison Is The National Mammal Of The United States
The American bison is set to become the country’s first national mammal, joining the bald eagle and oak as symbols of the U.S.
This mammal is a symbol of the American west and has deep cultural and conservation significance for many Indian tribes.

The National Bison Legacy Act will help preserve this national symbol. Listed below are a few of the facts about the bison that you should know.
Historically, bison were hunted to near extinction when the United States moved west. In fact, only about a thousand bison were left in the mid-19th century.
Fortunately, President Theodore Roosevelt, a famous conservationist, launched efforts to revive the bison’s population.
In 1907, he had 15 bison shipped by train from the Bronx Zoo to the Wichita Mountains Wildlife Refuge. The bison’s long history and cultural significance has influenced many American tribes.
Bison is the national mammal of the United States because of the role it plays in Native American culture and in the economy.

Bison is also the symbol of the American West and are recognized by federal law as an iconic animal. However, bison is not the only mammal in the world to have national significance.
The American bison once numbered in the tens of millions but is now a mere few dozen. Their extinction almost occurred in one century.
In fact, bison is now the first national mammal in the United States. As the nation’s first national mammal, the American bison has a unique role in history. It helped shape the Great Plains and the Native American way of life.
Despite its small population, bison is now widespread across the country and serves as a symbol of unity, resilience, and healthy lifestyles.
It Is A Ruminant
American Bison are ruminants, meaning they have a four-chambered stomach and even-toed hooves.

They molt twice a year with the changing seasons, and their short tails are useful for fly-swatting and indicating excitement. Because bison are prone to ticks and biting flies, they frequently roll in the dirt to relieve their itching and scratch their itchy skin.
Although bison are a threatened species, their numbers are slowly increasing. There are still significant wild herds in Yellowstone National Park, and some ranchers have begun raising semi-domestic bison.
The meat is lower in cholesterol than beef, and the bison can be a tourist attraction.
Because bison is a ruminant, they can be difficult to tame and require careful management, including robust fencing.
The American Bison is highly susceptible to a variety of pathogens and toxins. Common diseases include calf scours, infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, Johne’s disease, and Mannheimia pneumonia.

Bison are also susceptible to listeriosis, brucellosis, and emphysema. In the UK, MCF is a major threat to bison populations and is a serious disease among the species.
While bison have four stomachs, they can’t eat four times as much as animals with just one.
Bison are highly sensitive to stress, and overstocking a pasture can degrade forage quality and lead to increased parasites. Because of this, bison should only be raised for food.
A well-managed bison herd is the most productive mammal in North America. Bison are ruminants. This means that they live in their habitats and don’t live in crowded areas.
Bison graze in forests, grasslands, and deserts. Their diets consist primarily of grasses, lichens, berries, and twigs, and a little bluestem.
Bison are also ruminant creatures, meaning that they can live up to forty years in captivity.
It Is A Diurnal Animal
Like other diurnal animals, bison are also active during the day.

Their diet consists mostly of grasses and they are diurnal. Bison roam for about 2 miles a day and live in herds or alone. They communicate with each other by grunting, and bison bulls can be heard from three miles away.
They can run up to 35 mph and use their matted fur as cushioning when fighting. They also use their shoulder hump to plough through the snow.
Bison are primarily grazers, and they feed on grasses and sedges. Their diet also includes berries and lichen. Despite its diurnal nature, bison also use their horns to move snow.
They mate when they are between two and three years old, while male bison do not mature until about six years of age.
Mating season begins in July and may last until the middle of September. Male bison move into female groups to select their mates and tend them.
In the wild, bison live in herds consisting of thousands or millions of animals. Although traditionally associated with grasslands, bison also live in mountainous areas and open forests.

In addition to grasslands, bison also graze during the day, with an average dry matter intake of 1.6 percent of body weight per day.
Bison also spend a large part of their day feeding on the grasses and sedges that grow in their range. The female American bison gives birth to a single calf at a time of year, after about two to three years.
The mother and calf are usually isolated from the herd for a few days, and the calf will begin to develop shoulder humps and horns at two months.
By about seven months, the calf is fully weaned and ready to take on the world. Bison spend their warmest hours of the day resting, eating cud, or wallowing in the dirt.
It Is Polygynous
Bison exhibit polygyny, the female-dominance form of matrilineal reproduction.

The mature male defends a female until she enters estrus and breeds. He produces several threat displays including scent-urination, pawing, and rubbing.
Males can guard the female for hours. The dominant male will eventually mate with a female of equal size. Male bison are polygynous and may have up to six partners.
The polygynous reproductive system of the American bison may be responsible for the outbreeding of the species.
It indicates that management should aim to maintain a high effective breeding population. However, bison are highly intensively managed.
However, studies have shown that bison are polygynous, and a breeding strategy that emphasizes female reproduction can be beneficial for conservation.
Bison can be polygynous and can be used to inform other polygynous species. Males with greater node centrality were more likely to mate and produce more offspring.

These males were also heavier. This may explain why males with a high node centrality ranking sired more calves.
Despite being polygynous, bison are able to produce more offspring by investing more energy in mating than females with low social centrality.
This behavior is important for establishing dominance and siring offspring. Previously, bipeds were thought to have a single season of breeding, but bison have two or three estrous cycles per season.
The female bison may mate several times a season, resulting in multiple lactating female bison.
Successful copulation is evident by the way a cow arches and expels secretions from the vulva. It is common to see bison cows with multiple offspring.
It Is Near Threatened With Extinction
The American bison, sometimes colloquially called the buffalo, is a species of bison native to North America.

It is one of two species of bison still in existence, along with the European bison. Unfortunately, the American bison is near-extinct due to habitat destruction and hunting.
To learn more about why the bison is endangered, read on. Here are some tips on saving this unique animal.
First of all, bison population numbers are dropping, but they are not yet in a serious threat of extinction. Hunting has reduced bison populations to a few thousand by the nineteenth century.
As the United States government sought to control bison-dependent First Nations, it reintroduced bison to their habitat. This reintroduction has to be managed carefully.
Bison conservation efforts can help bring the bison back to their natural habitat. The American bison were once plentiful throughout the American continent.

After European settlers began to move west, however, the bison became the target of exploitation on a huge scale. In the east, bison were nearly extinct by 1825.
The military realized they had to remove the bison as a source of food to control the Native Americans. The military slaughtered thousands of bison for their hides and tongues.
This mass slaughter would not have been possible without the newly constructed railroads.
In 2010, private citizens petitioned the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to protect the plains bison from extinction.
The agency acknowledged the petition in 2011 but refused to recognize the bison’s historic range, arguing that its status should only be considered within the current habitat.
The Center is now pursuing the case against the Service. It is unclear how many bison will survive, but it remains a hopeful possibility.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”All The Facts & Info You Need To Know About American Bison!?”
Please you should feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Pet Care
Dog Trapped in Locked Car Crying for Help During Scorching 90-Degree Heat
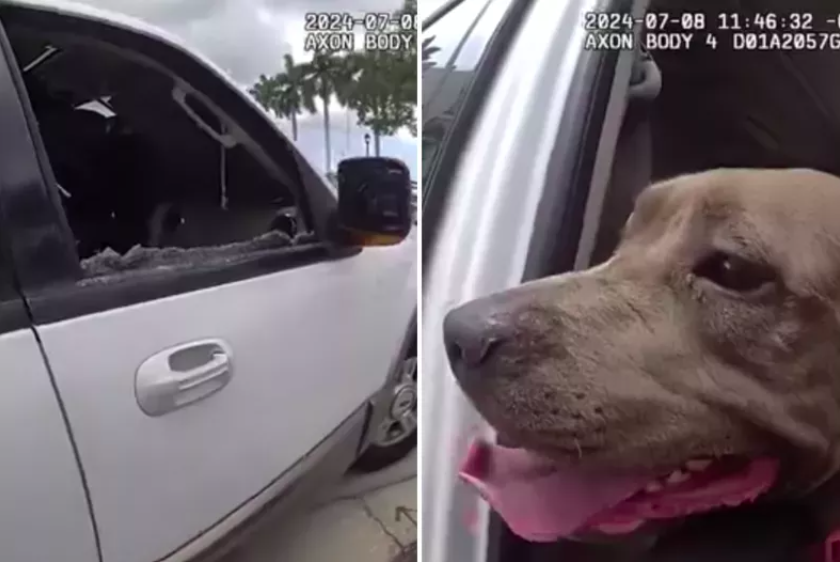

Dog Trapped in Locked Car Crying for Help During Scorching 90-Degree Heat
In a distressing incident that underscores the dangers of leaving pets in hot cars, a dog was found locked inside a vehicle, crying desperately for help amid a sweltering 90-degree heat. This heart-wrenching situation highlights the critical need for pet owners to understand the severe risks associated with leaving animals in parked cars, especially during hot weather.
The Harrowing Incident: A Dog in Peril
The Scene of the Distress
The situation unfolded on a scorching day when a concerned bystander noticed a dog trapped inside a locked car. With temperatures soaring to 90 degrees, the inside of the vehicle quickly became an oven-like environment, putting the dog’s health and safety at serious risk. The dog’s constant cries for help drew attention, prompting immediate action from witnesses.
Immediate Response and Rescue Efforts
Witnesses acted swiftly, contacting local authorities and animal rescue organizations to address the situation. Emergency responders arrived at the scene, assessing the situation and taking necessary measures to free the distressed animal. Their quick response was crucial in preventing a potential tragedy.
Understanding the Dangers: Heatstroke and Its Effects
How Heat Affects Animals
Animals, like humans, are vulnerable to heatstroke, especially when confined in a hot, enclosed space. The temperature inside a parked car can rise rapidly, even with the windows slightly open. Heatstroke can cause severe health issues in dogs, including dehydration, organ failure, and, in extreme cases, death.
Signs of Heatstroke in Dogs
Heatstroke symptoms in dogs include excessive panting, drooling, lethargy, vomiting, and confusion. If not addressed promptly, heatstroke can lead to serious health complications. Pet owners should be vigilant about these signs, especially during hot weather.
Preventing Heatstroke: Essential Tips for Pet Owners
Never Leave Pets in a Parked Car
The simplest and most effective way to prevent heatstroke is never to leave pets unattended in a parked car, even for short periods. Temperatures inside vehicles can escalate quickly, making it extremely dangerous for animals.
Provide Adequate Shade and Water
If pets must be outside, ensure they have access to shade and plenty of fresh water. Creating a cool and comfortable environment for pets can help prevent overheating and ensure their well-being.
Be Mindful of Exercise and Activity
Limit outdoor activities with pets during the hottest parts of the day. Opt for early morning or late evening walks when temperatures are cooler. Always monitor your pet for signs of overheating and adjust activities accordingly.
The Legal Perspective: Laws and Regulations
Legal Consequences for Animal Cruelty
Leaving a pet in a hot car can have serious legal repercussions. Many jurisdictions have laws that specifically address animal cruelty and neglect, including leaving pets in dangerous conditions. Violators may face fines, criminal charges, and other legal consequences.
Reporting and Enforcement
If you encounter an animal in distress, such as being locked in a hot car, it is important to report the situation to local authorities or animal control agencies. Prompt reporting can lead to timely intervention and potentially save the animal’s life.
Community Awareness: Educating and Advocating
Raising Awareness
Educating the public about the dangers of leaving pets in hot cars is crucial. Awareness campaigns, social media posts, and community events can help spread the message and prevent future incidents.
Advocating for Change
Advocacy efforts can also focus on improving laws and regulations related to animal welfare. Supporting initiatives that promote stronger protections for animals can lead to safer conditions and better outcomes for pets in distress.
Conclusion: A Call for Compassion and Responsibility
The distressing case of a dog locked in a hot car crying for help is a sobering reminder of the serious risks associated with leaving pets unattended in vehicles during hot weather. It underscores the importance of vigilance, education, and compassion in ensuring the safety and well-being of our animal companions. By taking proactive steps to prevent heatstroke and advocating for stronger animal protection laws, we can help create a safer and more compassionate world for all pets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the dangers of leaving a dog in a hot car?
Leaving a dog in a hot car can lead to heatstroke, dehydration, and even death. The temperature inside a vehicle can rise rapidly, creating a dangerously hot environment for pets.
How can I tell if my dog is suffering from heatstroke?
Signs of heatstroke in dogs include excessive panting, drooling, lethargy, vomiting, and confusion. If you notice these symptoms, seek immediate veterinary attention.
What should I do if I see a dog locked in a hot car?
If you see a dog locked in a hot car, contact local authorities or animal control immediately. Provide as much information as possible to facilitate a swift response and rescue.
Are there any laws against leaving pets in hot cars?
Yes, many jurisdictions have laws that address animal cruelty, including leaving pets in hot cars. Violators may face fines, criminal charges, and other legal consequences.
How can I prevent heatstroke in my pet during hot weather?
To prevent heatstroke, never leave pets in a parked car, provide access to shade and fresh water, and limit outdoor activities during the hottest parts of the day. Monitor your pet for signs of overheating and take appropriate actions to keep them cool.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Dog Trapped in Locked Car Crying for Help During Scorching 90-Degree Heat!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
References: Newsweek Article
Pet Care
5 Reasons Why Lifetime Pet Insurance Is a Must-Have Investment!

Secure Your Furry Friend’s Future: 5 Reasons Why Lifetime Pet Insurance Is a Must-Have Investment!
Are you a devoted pet owner seeking the best care and protection for your furry friend? The quest for ensuring your pet’s health and well-being can be met with unforeseen challenges, especially when it comes to managing unexpected medical expenses. In our comprehensive guide on pet insurance, we delve into the crucial aspects of why investing in lifetime pet insurance is a must for every responsible pet parent.
From offering peace of mind and financial security to navigating the intricate details of insurance coverage, we’re here to empower you with the knowledge needed to safeguard your pet’s future. Join us as we explore the nuances of pet insurance plans, the importance of tailored policies, and the invaluable support provided by trustworthy pet insurance providers.
Embark on this journey towards securing your furry friend’s future with lifetime pet insurance, ensuring that your beloved companion receives the best possible care without worrying about financial burdens. Take the first step towards comprehensive protection and unwavering support for your pet’s health and happiness.
Lifetime Coverage: Ensuring Ongoing Protection for Pets with Chronic Conditions
When it comes to pet insurance coverage, opting for a lifetime plan is a wise choice. Lifetime coverage ensures that your furry friend remains protected even if they develop a chronic illness or condition that requires ongoing treatment.
Imagine your beloved dog is diagnosed with diabetes or your cat develops a heart condition. With a lifetime pet insurance plan, you can rest assured that your pet will receive the necessary care and treatment for their condition without the added stress of worrying about the financial burden.
The Benefits of Lifetime Coverage
1. Continuous Protection
Lifetime coverage provides ongoing protection for your pet, even if they develop a chronic condition that requires long-term treatment.
2. Peace of Mind
Knowing that your pet is covered for life gives you peace of mind, allowing you to focus on providing them with the best possible care.
3. Financial Security
With lifetime coverage, you can avoid the financial strain of unexpected veterinary bills, ensuring that your pet receives the treatment they need without compromising your budget.
Planning Ahead: The Necessity for Unexpected Veterinary Bill Coverage

As a responsible pet owner, it’s crucial to plan ahead for unexpected veterinary expenses. Accidents and illnesses can happen at any time, and without proper financial protection, the cost of treatment can quickly become overwhelming.
Imagine your curious kitten ingests a foreign object, requiring emergency surgery, or your active dog tears a ligament during playtime. These unexpected situations can lead to substantial veterinary bills, putting a strain on your finances.
By investing in a pet insurance policy that covers unexpected veterinary expenses, you can ensure that your furry friend receives the necessary care without the added worry of how you’ll pay for it.
The Importance of Planning Ahead
1. Financial Preparedness
Planning ahead with pet insurance allows you to be financially prepared for unexpected veterinary bills, giving you peace of mind.
2. Access to Quality Care
With the right insurance coverage, you can provide your pet with access to the best possible care without hesitation, ensuring their health and well-being.
Customizing Your Pet Insurance: Tailored Policies for Every Pet’s Need
Every pet is unique, and their insurance coverage should be too. Tailored pet insurance policies allow you to customize your coverage plan to meet your pet’s specific needs, ensuring that they receive the best possible care.
Whether your pet requires alternative therapy, such as acupuncture or hydrotherapy, or has a pre-existing condition that needs special attention, a customized insurance plan can provide the necessary coverage.
Benefits of Tailored Pet Insurance Policies
1. Personalized Coverage
Tailored policies allow you to choose the coverage options that best suit your pet’s individual needs, ensuring that they receive the care they require.
2. Flexibility
With customizable plans, you can adjust your coverage as your pet’s needs change over time, providing ongoing protection throughout their life.
Trustworthiness and Reliability of Pet Insurance Providers
When choosing a pet insurance company, it’s essential to select a trustworthy and reliable provider. Look for a company with a proven track record of providing excellent customer support and timely claims processing.
A reputable pet insurance provider will be transparent about their coverage options, exclusions, and limitations, ensuring that you have a clear understanding of what your policy covers.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Pet Insurance Provider
1. Customer Reviews
Read customer reviews and testimonials to gauge the experiences of other pet owners with the insurance provider.
2. Claims Processing
Inquire about the company’s claims processing timeline and procedures to ensure that you can receive reimbursement for your pet’s medical expenses in a timely manner.
Comprehensive Support: UK-Based Teams and Online Quotation Systems
When selecting a pet insurance provider, consider the level of customer support they offer. Look for a company with a UK-based support team, ensuring that you can easily reach out with any questions or concerns.
Additionally, an online quotation system allows you to quickly and conveniently compare coverage options and prices, making it easier to find the best pet insurance plan for your furry friend.
What is Pet Insurance? Definition and Essential Insights
Pet insurance is a type of insurance coverage designed to help pet owners manage the financial costs associated with their pet’s health care. It provides a safety net against unexpected veterinary expenses, ensuring that your furry friend receives the necessary medical attention without putting a strain on your finances.
The Financial Benefits of Investing in Pet Insurance
Investing in pet insurance coverage provides numerous financial benefits for pet owners. By protecting against unexpected veterinary expenses, pet insurance helps maintain financial stability and allows you to focus on providing your pet with the best possible care.
💡 Key Takeaways: Pet insurance offers financial protection and security, enabling pet owners to prioritize their pet’s health without worrying about the cost of unexpected medical expenses.
Access to Quality Healthcare and Preventive Care: More Treatment Options
Comprehensive pet insurance coverage not only helps with unexpected accidents and illnesses but also provides access to quality healthcare and preventive care. With the right insurance plan, you can ensure that your pet receives regular check-ups, diagnostic tests, and necessary treatments without the financial burden.
Benefits of Comprehensive Pet Insurance Coverage
1. Preventive Care
Many pet insurance plans offer coverage for routine and preventive care, such as annual check-ups, vaccinations, and dental cleanings.
2. Diagnostic Tests
Comprehensive coverage often includes diagnostic tests, such as blood work and x-rays, allowing for early detection and treatment of potential health issues.
3. Access to Specialists
With pet insurance, you can provide your pet with access to specialized care, such as oncology or orthopedic surgery, without worrying about the high costs associated with these treatments.
💡 Key Takeaways: Comprehensive pet insurance coverage offers access to quality healthcare and preventive care, ensuring that your pet receives the necessary treatments and regular check-ups for optimal health.
Understanding Coverage Options: Accident, Illness, and Routine Care
When selecting a pet insurance policy, it’s essential to understand the different coverage options available. The three main types of coverage are accident-only, comprehensive (accident and illness), and routine care.
Accident-only coverage provides protection for unexpected accidents, such as broken bones or ingested foreign objects. Comprehensive coverage includes both accidents and illnesses, offering a broader range of protection for your pet’s health.
Routine care coverage helps with the costs of preventive care, such as annual check-ups and vaccinations.
💡 Key Takeaways: Understanding the different coverage options, including accident, illness, and routine care, allows pet owners to select the best insurance policy for their pet’s specific needs.
How to Choose the Right Pet Insurance: Comparing Providers and Plans
Choosing the right pet insurance company and plan can be overwhelming, but it’s crucial for ensuring that your pet receives the best possible care. When comparing providers and plans, consider factors such as coverage options, exclusions, premiums, and customer reviews.
Tips for Choosing the Right Pet Insurance
1. Assess Your Pet’s Needs
Consider your pet’s age, breed, and overall health when selecting a coverage plan.
2. Compare Coverage Options
Review the different coverage options offered by each provider, including accident, illness, and routine care coverage.
3. Read the Fine Print
Carefully review the policy details, including exclusions and limitations, to ensure that you have a clear understanding of what is covered.
💡 Key Takeaways: Comparing pet insurance providers and plans, while considering your pet’s specific needs, is essential for choosing the best coverage to ensure your pet receives the highest quality care.
The Importance of Early Enrollment: Insuring Pets at a Young Age
Enrolling your pet in an insurance policy at a young age can provide numerous benefits, including lower premiums and more comprehensive coverage. As pets age, they become more susceptible to health issues, which can lead to higher insurance costs or even exclusions for pre-existing conditions.
By insuring your pet at a young age, you can lock in lower premiums and ensure that they have lifelong coverage, regardless of any health issues that may arise in the future.
💡 Key Takeaways: Early enrollment in a pet insurance plan is crucial for securing lower premiums and more comprehensive coverage, providing lifelong protection for your furry friend.
The Role of Pet Insurance in Financial Stability: Budgeting for Pet Health
Pet insurance plays a vital role in maintaining financial stability for pet owners. By providing a safety net against unexpected veterinary expenses, insurance allows you to budget for your pet’s health care without the fear of a potential financial burden.
Imagine your dog suffers an unexpected accident or your cat develops a serious illness. Without insurance, the cost of treatment could quickly deplete your savings or even lead to debt. With pet insurance, you can have peace of mind knowing that you can provide your pet with the necessary care without compromising your financial well-being.
💡 Key Takeaways: Pet insurance contributes to financial stability by allowing pet owners to budget for their pet’s health care and providing protection against the potential financial burden of unexpected accidents or illnesses.
Navigating Policy Details: Understanding the Fine Print
When selecting a pet insurance policy, it’s crucial to carefully review the fine print and understand the details of your coverage. Pay close attention to exclusions, limitations, and any specific requirements for filing claims.
Tips for Navigating Policy Details
1. Read the Policy Thoroughly
Take the time to read through your pet insurance policy in its entirety, familiarizing yourself with the coverage details and any exclusions.
2. Ask Questions
If you have any questions or concerns about your policy, don’t hesitate to reach out to your insurance provider for clarification.
3. Keep Detailed Records
Maintain detailed records of your pet’s medical history, including receipts and invoices, to ensure a smoother claims process.
💡 Key Takeaways: Navigating policy details and understanding the fine print is essential for making informed decisions about your pet’s insurance coverage and ensuring a seamless experience when filing claims.
Making the Most of Your Pet Insurance: Tips for Maximizing Coverage
To make the most of your pet insurance coverage, it’s essential to be proactive and stay informed. Here are some tips to help you maximize your pet’s coverage:
Tips for Maximizing Pet Insurance Coverage
1. Stay Up-to-Date with Check-Ups
Regular check-ups and preventive care can help detect potential health issues early, allowing for prompt treatment and minimizing the risk of more severe, costly problems down the line.
2. Keep Detailed Records
Maintain a detailed record of your pet’s medical history, including receipts, invoices, and any relevant documentation. This will streamline the claims process and ensure that you have the necessary information readily available.
3. Understand Your Coverage
Familiarize yourself with your pet insurance policy’s coverage details, including any exclusions or limitations. This will help you make informed decisions about your pet’s care and avoid unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
4. Plan for Follow-Up Visits
If your pet experiences an unexpected accident or health issue, be sure to schedule any necessary follow-up visits and treatments. Your insurance coverage may extend to these additional appointments, helping you maintain your pet’s health without added financial strain.
💡 Key Takeaways: By staying proactive, keeping detailed records, understanding your coverage, and planning for follow-up visits, you can maximize your pet insurance coverage and ensure that your furry friend receives the best possible care.
Coverage Exclusions and Limitations: What You Need to Know
When choosing a pet insurance policy, it’s essential to be aware of any coverage exclusions and limitations. These can vary depending on the provider and the specific plan you select.
Common exclusions may include pre-existing conditions, hereditary disorders, or certain types of preventive care. Some policies may also have age limitations or breed-specific exclusions.
Understanding Exclusions and Limitations
1. Pre-Existing Conditions
Most pet insurance policies do not cover pre-existing conditions, which are health issues that were present before enrollment or during the waiting period.
2. Hereditary Disorders
Some policies may exclude or limit coverage for hereditary disorders, which are conditions that are common within certain breeds.
3. Preventive Care
While some comprehensive coverage plans include preventive care, others may exclude routine check-ups, vaccinations, and dental cleanings.
💡 Key Takeaways: Familiarizing yourself with coverage exclusions and limitations is crucial for making an informed decision when selecting a pet insurance policy, as these factors can impact your out-of-pocket expenses and the level of care your pet receives.
The Future of Pet Health Insurance: Trends and Innovations
As the pet insurance industry continues to grow, new trends and innovations are emerging to provide better care and more comprehensive coverage for our furry friends. From telemedicine services to wellness programs, the future of pet health insurance looks promising.
Emerging Trends in Pet Insurance
1. Telemedicine
Many pet insurance providers are now offering telemedicine services, allowing pet owners to consult with veterinarians remotely for minor issues or follow-up care.
2. Wellness Programs
Some insurers are expanding their coverage to include wellness programs, which focus on preventive care and early detection of potential health issues.
3. Flexible Coverage Options
As pet owners’ needs evolve, insurance providers are offering more flexible coverage options, allowing for customization based on individual pet requirements.
💡 Key Takeaways: The future of pet health insurance is focused on providing better care and more comprehensive coverage through innovative options such as telemedicine, wellness programs, and flexible coverage plans.
From Pet Parent to Informed Consumer: Taking a Closer Look at Insurance Options
As a pet parent, it’s essential to take a closer look at the various insurance options available to you. By becoming an informed consumer, you can make the best decision for your pet’s health and well-being while also protecting your financial stability.
Tips for Becoming an Informed Pet Insurance Consumer
1. Research Different Providers
Take the time to research and compare different pet insurance providers, evaluating their coverage options, exclusions, and customer reviews.
2. Consider Your Pet’s Unique Needs
Assess your pet’s specific needs, including their age, breed, and any pre-existing conditions, to determine the type of coverage that would be most beneficial.
3. Understand the Claims Process
Familiarize yourself with the claims process for each potential insurance provider, ensuring that you understand the steps involved and any required documentation.
4. Evaluate the Cost-Benefit Ratio
Consider the monthly premiums and potential out-of-pocket expenses associated with each insurance plan, weighing them against the peace of mind and financial protection they provide.
By taking a closer look at your insurance options and becoming an informed consumer, you can make the best choice for your pet’s health and your financial well-being. Remember, investing in pet insurance is not just about protecting your wallet – it’s about providing your furry friend with the best possible care and ensuring their long-term health and happiness.
Conclusion
In securing your furry friend’s future with lifetime pet insurance, you’ve embarked on a journey towards ensuring their health, happiness, and well-being for years to come. By exploring the crucial aspects of lifetime coverage, unexpected veterinary bill protection, and the customization options available, you’ve empowered yourself as a responsible pet owner.
Trustworthiness and reliability in pet insurance providers, coupled with comprehensive support systems and essential insights into coverage options, have equipped you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
As you navigate the complexities of pet insurance, remember the financial benefits and early enrollment advantages that come with it. Access to quality healthcare, preventive care, and understanding the policy details are vital components in maximizing coverage for your beloved companion. By choosing the right pet insurance plan and familiarizing yourself with coverage exclusions and limitations, you pave the way for a financially stable future for your furry family member.
Embrace the role of a well-informed consumer, taking a closer look at insurance options that best suit your pet’s needs. The peace of mind, financial protection, and better care that pet insurance offers are invaluable aspects of being a pet parent. Act now and make use of this essential coverage to safeguard your pet’s health and secure their future with love and protection.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Parvo Symptoms: What Every Pet Parent Needs to Know!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Pet Care
Bernese Mountain Dog’s Unique Car Entry: ‘Spoiled’ or Just Special?

Bernese Mountain Dog’s Unique Car Entry: ‘Spoiled’ or Just Special?
Introduction: The Charming Bernese Mountain Dog
Bernese Mountain Dogs are known for their large size, gentle demeanor, and loyalty. These characteristics make them a beloved breed among dog owners. This article explores the unique and amusing method one Bernese Mountain Dog uses to get into a car, a routine that has captured the hearts of many and sparked a discussion about whether this behavior is a sign of being ‘spoiled’ or just part of their charm.
Meet Bella: The Bernese Mountain Dog
Bella, a three-year-old Bernese Mountain Dog, has become an internet sensation due to her unusual way of getting into her owner’s car. Her owner, Mike, a dog lover from Colorado, shared videos of Bella’s routine on social media, which quickly went viral. The videos show Bella insisting on being lifted into the car, despite her size and ability to jump in herself.
The Background: How It All Started
Bella’s Initial Hesitation
Bella’s reluctance to jump into the car started when she was a puppy. Initially, Mike thought it was due to her young age and small size. However, as Bella grew, her hesitation remained. Mike tried various methods to encourage Bella to jump into the car on her own, but she consistently refused.
Establishing the Routine
After several attempts and consultations with veterinarians, Mike decided to lift Bella into the car himself. This routine soon became a habit, and Bella now expects to be lifted every time they go for a ride. Mike shares that lifting Bella has become a bonding experience for them, despite the physical effort involved.
Understanding the Behavior: Is Bella ‘Spoiled’?
Physical Considerations
One of the primary reasons dogs like Bella might refuse to jump into a car is due to physical discomfort. Despite their size, Bernese Mountain Dogs are prone to joint issues and hip dysplasia, which can make jumping painful or uncomfortable. Mike ensured Bella had no underlying health issues, but her preference for being lifted could be related to past discomfort.
Behavioral Factors
Bella’s insistence on being lifted can also be attributed to behavioral factors. Dogs are creatures of habit, and once a routine is established, they can become quite insistent on maintaining it. Bella may have learned that refusing to jump results in being lifted, reinforcing the behavior over time.
The Viral Sensation: Reactions from the Public
Adoration and Amusement
When Mike shared videos of Bella’s car entry routine online, the response was overwhelmingly positive. Viewers were charmed by Bella’s unique behavior and praised Mike for his patience and dedication. Comments often highlighted the bond between Bella and Mike, noting how their routine exemplified the lengths owners go to for their pets.
Criticism and Concern
Despite the general adoration, some viewers expressed concern about Bella’s behavior, labeling her as ‘spoiled’. Critics argued that Bella should be trained to jump into the car to avoid potential health issues for Mike. However, Mike defended their routine, emphasizing the importance of understanding and catering to individual pet needs.
Training Tips for Large Dogs
Encouraging Independent Car Entry
For owners who prefer their dogs to jump into the car independently, there are several training techniques that can be effective. Using positive reinforcement, such as treats and praise, can encourage dogs to overcome their hesitation. Gradually increasing the height they need to jump can also help build their confidence.
Using Ramps or Steps
Another practical solution is to use ramps or steps. These tools can make it easier for dogs to get into the car without needing to jump, reducing the risk of joint strain. Ramps and steps are particularly useful for older dogs or those with mobility issues.
The Bond Between Bella and Mike
Building Trust Through Routine
Bella and Mike’s routine has not only provided a solution to a practical problem but has also strengthened their bond. Lifting Bella into the car has become a ritual that they both look forward to, showcasing the deep trust and affection between them.
Understanding and Acceptance
Mike’s acceptance of Bella’s unique needs demonstrates a compassionate approach to pet ownership. By understanding Bella’s preferences and adjusting his behavior accordingly, Mike ensures that Bella feels safe and loved, which is the ultimate goal for any pet owner.
Concluding Thoughts: Celebrating Unique Pet Behaviors
Bella’s story highlights the importance of understanding and celebrating the unique behaviors of our pets. While some might see her routine as a sign of being ‘spoiled’, it’s clear that Bella’s behavior stems from a place of comfort and trust. By catering to her needs, Mike has created a loving and supportive environment for Bella, setting an example for dog owners everywhere.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why does my dog refuse to jump into the car?
There could be several reasons, including physical discomfort, fear, or simply a preference for being lifted. It’s important to assess your dog’s health and behavior to understand the underlying cause.
How can I train my dog to jump into the car on their own?
Use positive reinforcement techniques, such as treats and praise, to encourage your dog to jump. Gradually increase the height they need to jump and ensure they are physically comfortable with the activity.
Are ramps or steps effective for helping dogs get into cars?
Yes, ramps and steps can be very effective, especially for larger dogs or those with joint issues. They provide a gentle incline that is easier for dogs to navigate.
Is it okay to lift my large dog into the car?
While it can be physically demanding, lifting your dog is acceptable if it’s necessary for their comfort and safety. However, ensure you are lifting correctly to avoid injury to yourself or your dog.
How can I ensure my dog is comfortable with car travel?
Make sure your dog has a comfortable and secure spot in the car. Use familiar blankets or toys, and take short trips initially to build their confidence and comfort with car travel.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Bernese Mountain Dog’s Unique Car Entry: ‘Spoiled’ or Just Special?!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
References: Newsweek. (2024). Bernese Mountain Dog’s Backbreaking Method for Getting Into Car: ‘Spoiled’.
-

 Pet Care2 years ago
Pet Care2 years agoThe Best Dog Collars For 2022
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoBichon Frise: The Happy, Playful, and Cuddly Companion
-

 Trending Pet Stories1 year ago
Trending Pet Stories1 year ago2023 ‘World’s Ugliest Dog’ Winner: Scooter’s Tale of Resilience
-

 Animals2 years ago
Animals2 years agoAre There Animals Having Down Syndrome?
-

 Pets2 years ago
Pets2 years agoThe Fascinating World Of The Red Chameleon
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Dog Breeds According To AKC.
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years ago21 Dog Breeds That Resemble Bears Or Teddy Bears!
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoEskimo Dogs from Canada – What Are They? – Find Out!