Frogs
The Magnificent Tree Frog: Nature’s Tiny Jewel

The Magnificent Tree Frog: Nature’s Tiny Jewel
The Magnificent Tree Frog, also known as the Magnificent Treefrog (Litoria splendida), is a captivating amphibian species native to the rainforests of northern Australia.
Renowned for its vibrant appearance, remarkable life cycle, and distinctive vocalizations, this tree frog stands as a testament to the wonders of the natural world.
In this detailed overview, we delve into its unique characteristics, habitat, life cycle, significance, and conservation status.
This article covers All The Facts & Info You Need to Know About the Magnificent tree frog, Red-eyed tree frog, White tree tadpole, and Growling grass tadpole.
If you are planning a trip to the wild, you will find lots of interesting facts and information about this frog species.
Magnificent Tree Frog
The Magnificent tree frog is a native of North Western Australia.

Its scientific name is Litoria splendida. Its appearance is emerald, olive, or bright green, with yellow blotches on its sides and underbelly.
These beautiful frogs are about 10 centimeters (4 inches) in length and live on rock crevices. Their diet includes insects, worms, and small fish, and they are known for being very playful.
The green tree frog has cryptic coloration. Its color ranges from olive to bright green, with white-yellow spots on its back and undersides.
The female tree frog is slightly larger than the male and has bright yellow undersides of its feet. Its appearance makes it difficult to spot in a crowd.
The Magnificent tree frog is found in forests and other types of wooded areas close to water. The Magnificent tree frog is found in forests and is about 10 centimeters long.
It is easily distinguished from its green counterpart and has a large paranoid gland on its head. These frogs can be found throughout Australia, and they live in low-rainfall environments.
The bright colors of this frog deter predators and make them shy away. Male tusked frogs have large tusks, and they use them in fights to establish their dominance.
This frog is also known as the water-holding frog. It burrows up to a meter underground and surrounds itself with a watertight cocoon. The white-lipped tree frog is the largest tree frog in the world and reaches 14 centimeters in length.
Red-Eyed Tree Frog
You’ve probably heard of the red-eyed tree frog, but did you know all about it?

This arboreal hylid, Agalychnis callidryas, ranges from Mexico to Colombia. Its scientific name is derived from the Greek words kalos and dryas, which mean “red-eyed” and “dryas,” respectively.
Though the red-eyed tree frog is not an endangered species, its habitat is being lost at an alarming rate. While its numbers are not in danger of extinction, climate change and deforestation are endangering their habitat.
Although they are not toxic, they are prey to a variety of predators, from eggs to adults.
They are also a target of the pet trade. While red-eyed tree frogs live primarily in the forests of Central America, they can be found near bodies of water, such as ponds.
These frogs start life as tadpoles in ponds and eventually make their way to tree branches. Due to their neon-colored bodies, they are often easy to spot and avoid predators.
Read on to learn more about this interesting animal. In addition to the bright red eyes, red-eyed tree frogs have green eyelids to blend in with their surroundings.
Their bright eyes can also be seen in low-light areas. While frogs may appear red or brown, their bodies change color depending on their mood.
They are active during the day and rest at night, searching for insects to feed on. There are a few facts about the red-eyed tree frog that you should know about before seeing them.
White’s Tree Frog
You may be interested in learning more about the White’s Tree Frog and how to keep one in your home. This species of frog is a popular pet and is surprisingly easy to take care of.

Its appearance is similar to that of its cousin the White-Lipped Tree Frog, but the White’s does not jump as often, and will only leap if startled.
It is a perfect first frog to keep as a pet and can be kept by children with parental supervision. While White’s Tree Frogs may seem like jungle dwellers, you can find them in city reservoirs, suburban yards, and even your yard.
You’ll find these frogs in urban environments, too, as they can enter your home and feed on roaches, moths, and locusts. You’ll find a white tree frog in your yard – it’s a charming and unique pet to own.
White’s Tree Frogs are native to Australia and New Guinea. Although they prefer forests with moist environments, they are not native to tropical rainforests. They can live in tree-top habitats near bodies of water, but they also prefer to live in terrestrial habitats.
They prefer to live in old Eucalyptus trees with hollows.As far as conservation goes, they aren’t under any threat in the wild and are not designated as threatened species.
Growling Grass Frog
If you’re interested in learning about this fascinating animal, this is the article for you. This species has a variety of interesting facts that you may find interesting.

Tadpoles of the Growling Grass Frog have yellow fins and hide in the aquatic vegetation. If disturbed, they move to deeper water. During their tadpole stage, the Growling Grass Frog changes its coloring from yellow to green and gold.
It spends the warmer months of the year active, basking in the sun and feeding after dark. They eat a variety of insects and small lizards.
The female Growling Grass Frog’s call is a low, warty growl, which attracts a male. The female deposits up to 1,500 eggs, and the eggs develop in the waterbody.
The tadpoles eventually metamorphose into adults. During the breeding season, they feed on small fish, lizards, and invertebrates. Their habitats are becoming increasingly impacted by pollution, habitat destruction, and introduced species.
There are several threats to the growling grass frog’s survival, and many of them have a definite ecological impact. Introduced mosquitofish may affect tadpoles because they breed prolifically and tolerate poor water quality.
Another threat to the Growling Grass Frog is the increased ultraviolet-B radiation caused by climatic change and atmospheric ozone depletion. While there are other threats to the growing population of this frog, there are many proven methods that help to protect it.
Southern Corroboree Frog
When you see this species of frog, you will be impressed by the beauty and uniqueness of its habitat.

The Southern Corroboree frog breeds during the summer months, spending a year as an embryo and two years as a juvenile. After copulating, males deposit sperm directly onto the eggs.
Once mature, the tadpoles develop in the water for about seven to eight months. During the winter, this species will hibernate and not molt. The distribution of southern corroboree frogs is relatively limited and their population is declining.
The southern species is found only in the snowy mountains of Kosciuszko National Park while the northern varieties occur near the Fiery Range and Brindabella Ranges.
Their habitats vary according to the season, and they can shift up to 300 meters (984 ft) to find the right conditions to reproduce. The Corroboree frog reaches sexual maturity after four years.
The species breeds during a brief period during the summer, during which the females lay eggs. The female lays between ten and 40 pearl-sized eggs in her clutch. To protect her eggs, she oozes an alkaloid-based toxin from her skin.
While the Southern Corroboree frog has no natural predators, it is at risk due to the impacts of humans, fire, feral animals, and chytrid fungus.
Waxy Monkey Tree Frog
When it comes to Waxy Monkey Tree Frog facts and information, it’s important to know how they breed.

The frogs breed at the end of the summer, after a period of heavy rainfall when the temperature is 65degF and the humidity level is at 50 percent.
This temperature and humidity combination simulates the cooler winter season. The water temperature will drop to 65-70degF during brumation.
Once the breeding cycle is restored, the temperature and light cycle will return to normal. The frogs are small, slow-moving amphibians with short muzzles. They should be housed in pairs or small groups.
A suitable enclosure will be large enough to give them ample room to move. Eco earth, coco fiber, or sphagnum moss should be used as the substrate.
Make sure to allow sufficient ventilation to keep the environment cool and damp, and use an overhead heat source to control humidity levels.
The Waxy Monkey Tree Frog is a member of the phyllomedusid family, which is also known as leaf frogs. They are closely related to tree frogs in New Guinea and Australia.
In fact, there are only 16 species in the Phyllomedusa family. The Waxy Monkey Tree Frog is classified as an insectivore, which means that they eat insects.
Questions People Also AsK: (FAQs)
What is the Magnificent Tree Frog, and what does it look like?
The Magnificent Tree Frog is a medium-sized tree frog known for its dazzling emerald-green dorsal coloration, bright orange thighs, and contrasting blue stripes running down its sides.
This striking appearance, combined with its large, expressive eyes, makes it a visually stunning amphibian.
Where is the Magnificent Tree Frog found in its natural habitat?
This species primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of northern Australia, particularly in regions of Queensland and the Northern Territory. It is often found near water bodies, such as ponds, swamps, and streams.
What is unique about the life cycle of the Magnificent Tree Frog?
One of the most remarkable aspects of this tree frog is its breeding behavior. Unlike many frogs, it lays its eggs on leaves or overhanging branches above water.
When the tadpoles hatch, they drop into the water below, completing their development in aquatic environments.
What are the vocalizations of the Magnificent Tree Frog like?
The Magnificent Tree Frog is known for its melodious and distinctive calls, which vary depending on the sex and circumstances.
Males produce a series of loud, repetitive calls during the breeding season, resembling a rhythmic “creeek-creeek.” These calls serve to attract females and establish territory.
What is the conservation status of the Magnificent Tree Frog?
While the Magnificent Tree Frog is not currently listed as globally threatened, habitat destruction due to deforestation and urbanization poses a significant threat to its populations.
Conservation efforts focus on preserving its rainforest habitat and studying its biology to better understand its needs and behavior.
In summary, the Magnificent Tree Frog stands as a testament to the beauty and uniqueness of the natural world.
With its striking appearance, unique breeding behavior, captivating vocalizations, and presence in the lush rainforests of northern Australia, this tiny jewel of an amphibian continues to inspire awe and highlight the importance of conservation efforts to protect its habitat.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”All The Facts & Info You Need To Know About Magnificent Tree Frog!?”
Please you should feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Frogs
The Tomato Frog: Unveiling the Vibrant World of Nature’s Little Marvels
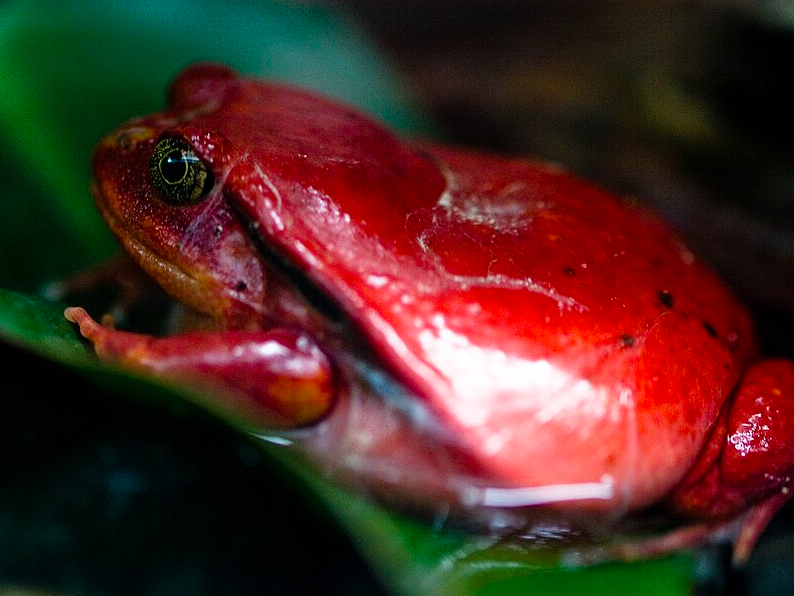

The Tomato Frog: Unveiling the Vibrant World of Nature’s Little Marvels
Nature has a way of surprising us with its incredible diversity, and one such marvel is the fascinating Tomato Frog. In the vast tapestry of amphibians, the Tomato Frog stands out as a vibrant and captivating species.
Join us on this journey as we delve into the enchanting world of these tiny wonders, exploring their unique characteristics, habitat, and the crucial role they play in maintaining ecological balance.
Understanding the Tomato Frog: A Splash of Color in Nature
The Tomato Frog, scientifically known as Dyscophus species, is a small-sized amphibian native to the captivating landscapes of Madagascar.
What immediately captures the eye is their vivid coloration, resembling the ripest tomatoes in your garden. The vibrant red, orange, or even yellow hues serve as a natural warning to potential predators, indicating the presence of toxic skin secretions.
Habitat and Lifestyle: Where Do Tomato Frogs Call Home?
In the dense rainforests of Madagascar, Tomato Frogs find their ideal homes. Their semi-aquatic lifestyle allows them to thrive near freshwater bodies, creating a delicate balance between land and water ecosystems.

These remarkable creatures spend their days hidden among the foliage, emerging during the night to hunt for small insects and invertebrates.
1. The Lush Canopy: Arboreal Retreats
Tomato Frogs, with their vibrant hues and distinct personalities, find their haven in the lush canopies of Madagascar’s rainforests. These arboreal retreats offer a multifaceted environment that caters to the various needs of Tomato Frogs.
The dense foliage provides ample hiding spots during the day, allowing these tiny amphibians to escape the prying eyes of predators.
2. Freshwater Oases: The Amphibian Playground
Nestled within the heart of the rainforest, Tomato Frogs thrive in the proximity of freshwater oases. These amphibians are semi-aquatic, making the presence of ponds, streams, and other water bodies vital to their lifestyle.
The combination of terrestrial and aquatic environments creates a dynamic setting for Tomato Frogs to exhibit their diverse range of behaviors, from foraging for food to engaging in intricate mating rituals.
3. Nightfall Revelry: Tomato Frogs Under the Moonlight
As the sun dips below the horizon, the nocturnal symphony of the rainforest begins, and Tomato Frogs emerge from their daytime retreats.
Nightfall transforms the rainforest into a realm of activity for these vibrant creatures. Under the soft glow of the moonlight, Tomato Frogs embark on their nightly adventures, hunting for small insects and invertebrates that become the sustenance for their colorful existence.
4. Microcosm of Biodiversity: Ecosystem Harmony
Madagascar’s rainforests, the natural habitat of Tomato Frogs, represent a microcosm of biodiversity. These ecosystems are home to a myriad of plant and animal species, creating a delicate balance that underscores the importance of preserving these habitats.
Tomato Frogs contribute to this intricate dance by playing their part in controlling insect populations, thereby influencing the health of the entire ecosystem.
Adaptations to Rainforest Living: Tomato Frogs’ Survival Toolkit
1. Cryptic Coloration: Blending In to Stand Out
While Tomato Frogs are known for their conspicuous colors, they also possess the ability to blend in when needed. Cryptic coloration, a form of camouflage, allows them to merge with their surroundings, especially during daylight hours.
This adaptive strategy helps them avoid detection by diurnal predators, emphasizing their versatility in navigating the challenges of rainforest living.
2. Ample Moisture: The Lifeline for Tomato Frogs
The rainforests of Madagascar provide a constant source of moisture, a lifeline for Tomato Frogs. Their semi-aquatic nature ensures that they can easily transition between terrestrial and aquatic environments, maintaining the delicate balance of hydration crucial for their survival.
The availability of freshwater bodies facilitates breeding and provides a sanctuary for tadpoles during their developmental stages.
3. Environmental Threats: Navigating Challenges in the Rainforest Realm
While the rainforest offers a rich tapestry of life for Tomato Frogs, it is not without its challenges. Habitat loss due to deforestation, climate change, and the encroachment of human activities pose significant threats to the delicate ecosystems they call home.
Conservation efforts are imperative to mitigate these challenges and secure a sustainable future for Tomato Frogs and the entire rainforest community.
The Lifecycle of Tomato Frogs: A Tale of Metamorphosis
Like many amphibians, Tomato Frogs undergo a fascinating metamorphosis from tadpole to adult. This intricate process involves a series of stages, each marked by distinct physiological changes.
From tiny eggs laid in aquatic environments to the tadpole’s aquatic phase and finally the emergence of the vibrant adult, every step in their lifecycle is a testament to the wonders of nature.
1. Egg-laying in Aquatic Nests: The Beginning of a Cycle
The lifecycle of Tomato Frogs commences with the delicate process of egg-laying. Female Tomato Frogs carefully select suitable aquatic environments, typically near freshwater bodies in their rainforest habitats, to deposit their eggs.
These aquatic nests serve as the initial sanctuary for the developing embryos, providing a stable environment for the next stage of the lifecycle to unfold.
2. Tadpoles: Aquatic Explorers in the Early Stages
Once the eggs hatch, the aquatic exploration of Tomato Frogs begins with the tadpole stage. Tadpoles are a distinct departure from the adult form, equipped with a tail for swimming and gills for breathing underwater.
In this developmental phase, Tomato Frogs exhibit a remarkable adaptability to their aquatic surroundings, feeding on algae and detritus as they grow and mature.
3. Transitioning from Water to Land: The Challenging Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a pivotal phase in the lifecycle of Tomato Frogs, marking the transition from aquatic tadpole to terrestrial adult. During this transformation, internal and external changes occur rapidly.
Limbs develop, the tail diminishes, and lungs replace gills as the primary respiratory organs. This metamorphic journey is a demanding and energy-intensive process, emphasizing the resilience ingrained in Tomato Frogs.
4. The Emergence of Juvenile Tomato Frogs: A New Chapter
As the metamorphosis concludes, juvenile Tomato Frogs emerge onto the land. These miniature versions of their adult counterparts are now equipped to navigate both terrestrial and aquatic environments.
Their colors, though not as vibrant as those of adults, start to manifest, providing a glimpse into the breathtaking hues that will characterize them as they reach maturity.
5. Maturity and Reproduction: Completing the Lifecycle Circle
Maturity signals the completion of the Tomato Frog’s lifecycle, and they are now ready to engage in the reproductive cycle themselves.
Adult Tomato Frogs return to their favored breeding grounds, repeating the cycle by laying eggs and initiating a new generation.
The lifecycle, characterized by its intricate stages, reflects the adaptability and resilience necessary for survival in Madagascar’s dynamic rainforest ecosystems.
Survival Strategies: How Tomato Frogs Thrive in the Wild
Nature equips every species with unique survival strategies, and Tomato Frogs are no exception. Their vibrant coloration not only serves as a warning to predators but also as a form of communication within their community.
The toxic skin secretions, while deterring predators, also play a crucial role in establishing territory and dominance among individuals.
1. Toxic Skin Secretions: A Chemical Defense Mechanism
The bold colors of Tomato Frogs are not just for show; they serve as a visual warning of their toxic nature. These frogs possess specialized skin glands that secrete toxic substances, making them unpalatable or even harmful to predators.
Potential threats learn quickly to associate the vibrant hues with a potential toxic encounter, creating a natural defense mechanism that enhances their chances of survival in the wild.
2. Nocturnal Lifestyle: Thriving Under the Moonlight
Tomato Frogs are primarily nocturnal creatures, and this lifestyle choice provides them with a strategic advantage in the rainforest. By emerging under the cover of darkness, Tomato Frogs avoid many diurnal predators.
The night becomes their domain, and they navigate the rainforest floor, hunting for insects and invertebrates while leveraging the darkness as a shield against potential threats.
3. Mimicry and Camouflage: Juvenile Survival Tactics
Juvenile Tomato Frogs take survival strategies to the next level by adopting mimicry and camouflage. Their colors and patterns mimic the environment, providing a natural camouflage that helps them evade detection by predators.
This mimicry is a temporary strategy that gradually transforms as they mature into their more vibrant adult coloration, showcasing the versatility and adaptability ingrained in their survival toolkit.
4. Vocal Communication: Establishing Territory and Mating Rituals
In the realm of Tomato Frogs, vocal communication plays a pivotal role in survival. Males, in particular, utilize distinct calls to establish territory and attract potential mates during the breeding season.
These calls serve as auditory markers, helping individuals identify and navigate their communal spaces while contributing to the intricate social dynamics within the Tomato Frog population.
Vocalization is not only a survival strategy but also a means of sustaining their species.
5. Selective Feeding: Dietary Choices for Optimal Health
Tomato Frogs exhibit selective feeding habits, targeting specific prey items that contribute to their overall health and well-being. By carefully choosing their diet, they ensure the intake of essential nutrients while minimizing exposure to potential toxins.
This selective feeding strategy underscores the importance of dietary choices in the intricate balance of their rainforest ecosystem.
6. Territorial Behavior: Maintaining Ecological Harmony
Territorial behavior is a crucial survival strategy for Tomato Frogs. By establishing and defending territories, individuals delineate spaces for feeding, breeding, and other essential activities.
This territoriality not only contributes to individual survival but also plays a role in maintaining ecological harmony by preventing overcrowding and resource competition within their rainforest habitat.
Conservation Concerns: Navigating the Threats to Tomato Frog Populations
Despite their intriguing nature, Tomato Frogs face various threats to their survival. Habitat loss, climate change, and collection for the pet trade contribute to the decline of their populations.
Conservation efforts are crucial to preserving the delicate balance of biodiversity and ensuring the Tomato Frog continues to enchant future generations.
1. Habitat Loss: The Looming Shadow
One of the most significant threats facing Tomato Frogs is the ongoing loss of their natural habitat. Deforestation, driven by agricultural expansion, logging, and human settlements, encroaches upon the rainforest sanctuaries these frogs call home.
As the lush canopies diminish, Tomato Frogs lose critical breeding and foraging grounds, disrupting their lifecycle and leading to population decline.
2. Climate Change: A Global Menace
The specter of climate change casts a shadow over the rainforests of Madagascar. Alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns impact the delicate ecosystems that Tomato Frogs depend on.
These changes can disrupt breeding cycles, alter food availability, and expose these amphibians to new diseases. The ramifications of climate change pose a formidable challenge to the long-term survival of Tomato Frog populations.
3. Human Activities: A Double-Edged Sword
While human activities contribute to habitat loss, they also directly impact Tomato Frogs through pollution and collection for the pet trade.
Pesticides, herbicides, and pollutants find their way into freshwater bodies, affecting the water quality crucial for the survival of Tomato Frog tadpoles.
Additionally, the demand for Tomato Frogs as exotic pets poses a threat to wild populations, as overcollection can lead to declines in numbers.
4. Invasive Species: An Unseen Menace
The introduction of invasive species poses an indirect but potent threat to Tomato Frog populations. Invasive plants, animals, or pathogens can disrupt the delicate balance of the rainforest ecosystem.
For Tomato Frogs, the presence of non-native species can introduce new diseases, predators, or competitors, exacerbating the challenges they face in their natural habitats.
5. Disease Dynamics: Emerging Threats
Disease dynamics, particularly the spread of chytrid fungus, present an emerging threat to Tomato Frogs. Chytridiomycosis, caused by the Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis fungus, has devastated amphibian populations worldwide.
The fungus affects the skin of Tomato Frogs, disrupting their ability to absorb water and leading to fatal consequences. Monitoring and managing disease outbreaks are critical components of effective conservation strategies.
Conservation Initiatives: A Glimmer of Hope
Amidst these challenges, several conservation initiatives strive to protect and preserve Tomato Frog populations:
1. Habitat Restoration Programs
Efforts to restore and protect rainforest habitats are crucial for the survival of Tomato Frogs.
Conservation organizations collaborate with local communities to implement reforestation projects, creating corridors that reconnect fragmented habitats and provide essential breeding and foraging areas.
2. Climate Change Adaptation Strategies
Conservationists are developing and implementing strategies to help Tomato Frogs adapt to the changing climate.
This includes monitoring weather patterns, studying the frogs’ responses to climate shifts, and implementing habitat management practices that enhance resilience.
3. Community Education and Engagement
Raising awareness and involving local communities in conservation efforts are integral to success. Educating residents about the importance of preserving Tomato Frogs and their habitats fosters a sense of stewardship.
Engaging communities in sustainable practices helps mitigate the impact of human activities on these amphibians.
4. Legislation and Regulation
Implementing and enforcing legislation to regulate the collection and trade of Tomato Frogs is vital for their protection.
Conservation organizations work alongside governments to establish and enforce measures that ensure the responsible and sustainable management of wild populations.
5. Disease Monitoring and Research
Ongoing research into disease dynamics, particularly chytridiomycosis, enables conservationists to implement targeted measures to prevent and manage outbreaks.
Disease monitoring programs provide critical data for understanding and addressing emerging threats to Tomato Frog populations.
Tomato Frogs in Captivity: A Glimpse into Responsible Pet Ownership
Captivated by their vibrant colors and unique personalities, many enthusiasts are drawn to the idea of keeping Tomato Frogs as pets. However, responsible pet ownership is paramount to ensure the well-being of these captivating amphibians.
Let’s take a closer look at the essentials of caring for Tomato Frogs in captivity, from creating suitable enclosures to understanding their dietary needs.
1. Enclosures: Crafting a Comfortable Habitat
Creating a suitable environment is crucial for the health and happiness of Tomato Frogs in captivity. Opt for spacious, well-ventilated terrariums that mimic their natural rainforest habitat.
Include live plants to provide hiding spots and maintain humidity. A substrate of coconut coir or sphagnum moss can replicate the moisture-rich conditions Tomato Frogs thrive in.
2. Temperature and Humidity: Mimicking Rainforest Conditions
Tomato Frogs are accustomed to the warmth and humidity of Madagascar’s rainforests. Maintain temperatures between 75-80°F (24-27°C) during the day and a slight drop at night.
Humidity levels should range from 60% to 80%, replicating the conditions of their native habitat. Regular misting and a reliable heat source contribute to creating a comfortable microclimate within the enclosure.
3. Dietary Needs: A Varied and Balanced Menu
Tomato Frogs are insectivores, and providing a diverse and nutritious diet is essential for their well-being. Offer a range of live insects such as crickets, fruit flies, and small worms.
Dusting these with a calcium supplement ensures they receive the necessary nutrients. Be mindful of portion sizes and frequency to maintain a healthy balance.
4. Water Requirements: Hydration and Breeding Spaces
Fresh, dechlorinated water is vital for Tomato Frogs. Ensure a shallow water dish is available for them to soak in, as they absorb water through their skin.
Adequate hydration is essential for their overall health and can also serve as a breeding space if you decide to keep a pair. Regularly clean and replenish the water to prevent bacterial growth.
5. Handling Considerations: Limited Interaction
While Tomato Frogs are captivating to observe, they are not particularly fond of handling. Their skin is sensitive, and the oils on human hands can be harmful.
Limit interactions to necessary activities such as health checks or habitat maintenance. If handling is unavoidable, ensure your hands are clean and moist to minimize stress on the frogs.
6. Veterinary Care: Regular Health Checks
Regular veterinary check-ups are integral to maintaining the health of Tomato Frogs. Find a veterinarian with experience in exotic amphibian care.
Watch for signs of stress, skin issues, or changes in behavior. Early detection of health issues can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment.
7. Educating Yourself: Ongoing Learning
Responsible pet ownership includes ongoing education. Stay informed about the latest research, husbandry practices, and any advancements in amphibian care.
Join online communities, forums, or local herpetological societies to exchange knowledge and experiences with fellow Tomato Frog enthusiasts.
8. Conservation Advocacy: Supporting Wild Populations
As responsible pet owners, it’s essential to contribute to the conservation of Tomato Frog populations in the wild. Avoid purchasing frogs collected from the wild, and instead, choose captive-bred specimens.
Support reputable conservation organizations working to preserve the natural habitats of Tomato Frogs and other amphibian species.
Conclusion: Embracing the Marvels of Nature
In the intricate tapestry of the natural world, Tomato Frogs stand out as vibrant gems, captivating our imagination and instilling a sense of wonder.
From their striking appearance to their essential role in ecosystem balance, these tiny creatures remind us of the interconnectedness of all life forms on Earth.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of nature, let us strive to be responsible custodians of the planet we call home.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs)
Can Tomato Frogs Change Their Color?
Yes, Tomato Frogs can change their color to some extent, adapting to their surroundings. However, their vibrant hues are primarily a result of genetics.
Are Tomato Frogs Dangerous as Pets?
While Tomato Frogs are not inherently dangerous, their skin secretions can be toxic. Responsible handling and proper care are essential to ensure the safety of both the frog and the owner.
How Long Do Tomato Frogs Live in Captivity?
With proper care, Tomato Frogs can live up to 6-8 years in captivity. Adequate housing, nutrition, and environmental conditions contribute to their longevity.
Are Tomato Frogs Endangered?
Several species of Tomato Frogs are currently classified as near-threatened or vulnerable due to habitat loss and other environmental threats. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect their populations.
Can Tomato Frogs Survive in Different Climates?
Tomato Frogs are adapted to the specific climate of Madagascar’s rainforests. Attempts to keep them in vastly different climates may pose challenges, making it essential to replicate their natural habitat in captivity.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”The Tomato Frog: Unveiling the Vibrant World of Nature’s Little Marvels!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
References:
- AmphibiaWeb. (https://amphibiaweb.org)
- IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. (https://www.iucnredlist.org)
Remember, our understanding and appreciation of nature contribute to the preservation of its wonders. Let this exploration of Tomato Frogs be a reminder of the marvels that surround us and the responsibility we share in protecting the delicate balance of our planet.
Frogs
The Enchanting World of the Amazon Milk Frog: A Comprehensive Guide
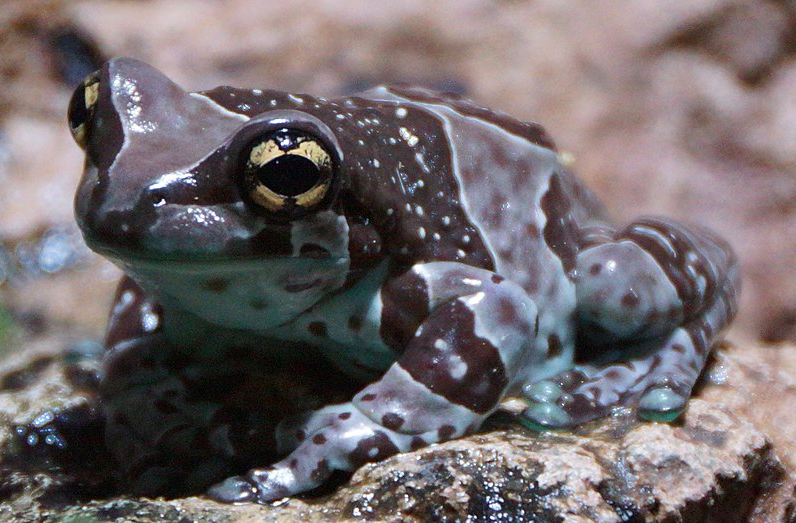

The Enchanting World of the Amazon Milk Frog: A Comprehensive Guide
The Amazon Rainforest, a treasure trove of biodiversity, is home to some of the most captivating creatures on our planet. One such mesmerizing resident is the Amazon Milk Frog (Trachycephalus resinifictrix).
Join us on a journey through the lush greenery as we uncover the secrets of this enchanting amphibian.
Getting to Know the Amazon Milk Frog
In the verdant embrace of the Amazon Rainforest resides a creature that captivates the hearts of nature enthusiasts – the Amazon Milk Frog (Trachycephalus resinifictrix). Delve into the intricacies of its existence as we unravel the layers of this fascinating amphibian.

Appearance and Size
Visual Symphony
The Amazon Milk Frog is a living masterpiece, adorned with vibrant hues of green and intricate patterns. Its striking appearance serves both aesthetic and survival purposes, blending seamlessly with the lush foliage of its rainforest habitat.
Dimensions Unveiled
Mature individuals typically reach sizes ranging from 2.5 to 4 inches. This compact size makes them an ideal choice for amphibian aficionados looking to add a touch of exotic charm to their collections.
Habitat and Range
Amazonian Haven
These enchanting frogs call the Amazon Rainforest home, specifically favoring lowland areas adjacent to slow-moving water bodies. Ponds and streams become their playgrounds, providing the perfect backdrop for their vibrant existence.
Geographical Tapestry
Spanning parts of Ecuador, Peru, Brazil, and Colombia, the Amazon Milk Frog’s distribution mirrors the expansive reach of the Amazon Rainforest. Exploring the nooks and crannies of these regions unveils the wonders of their natural habitat.
Distinctive Features
Milk-Like Secretions
One of nature’s ingenious defense mechanisms is showcased by the Amazon Milk Frog. When confronted with danger, it secretes a milky substance from its skin, believed to deter predators. This unique adaptation contributes to its intriguing nomenclature.
Chameleon-Like Coloration
A true marvel unfolds as these amphibians showcase their color-changing abilities. Adapting to their surroundings, their chameleon-like camouflage aids in evading predators. Witnessing this metamorphosis adds to the allure of these captivating creatures.
Keeping Amazon Milk Frogs as Pets: Creating a Tropical Haven
Embracing the charm of the Amazon Milk Frog in your own living space requires a meticulous understanding of their needs. Join us as we unravel the secrets to creating a tropical haven for these delightful amphibians.
Housing and Enclosure
Terrarium Design
Crafting a suitable habitat for Amazon Milk Frogs involves a well-ventilated terrarium. Opt for a vertical setup, providing ample climbing opportunities for these agile creatures. Incorporate live plants to mimic the lush vegetation of their natural environment.
Ventilation and Security
Ensuring proper ventilation is essential for maintaining optimal humidity levels. Additionally, secure the enclosure with tight-fitting lids, as these adept climbers are known for their escapades.
Diet and Feeding
Insectivorous Delights
Amazon Milk Frogs are avid insectivores, relishing a diet of crickets, fruit flies, and other small insects. Offer a variety of prey to provide a balanced nutritional profile. Dusting their food with calcium supplements ensures their skeletal health.
Frequency of Feeding
Feed these frogs 3 to 4 times a week, adjusting portion sizes based on their age and size. Observing their feeding habits can offer insights into their overall well-being.
Water Requirements
Shallow Water Dish
Include a shallow water dish in the terrarium to meet their hydration needs. Ensure the dish is easily accessible and cleaned regularly to prevent bacterial growth. Amazon Milk Frogs are not proficient swimmers, so a shallow dish is sufficient.
Humidity Control
Maintain a humidity level of 50% to 80% within the enclosure, replicating the moist conditions of their rainforest habitat. Regular misting helps achieve this, with attention to preventing waterlogged substrates.
Temperature and Lighting
Thermoregulation
Amazon Milk Frogs thrive in temperatures ranging from 75°F to 85°F (24°C to 29°C). Implement a gradient within the terrarium, allowing them to thermoregulate by moving between warmer and cooler areas.
Full-Spectrum Lighting
While these frogs don’t require direct exposure to sunlight, a full-spectrum UVB light can simulate natural daylight, aiding in calcium metabolism and overall well-being.
Social Dynamics and Handling
Social Creatures
Amazon Milk Frogs are social beings and can be kept in small groups. Ensure there’s enough space and hiding spots for each frog to minimize potential conflicts. Observe their interactions and ensure a harmonious living environment.
Minimizing Handling
These frogs are sensitive to human touch, and excessive handling can cause stress. Limit interaction to essential activities, such as feeding and health checks, to maintain their well-being.
Breeding and Reproduction of Amazon Milk Frogs: Nature’s Love Symphony
Delving into the realm of breeding and reproduction offers a glimpse into the intricate courtship rituals and fascinating life cycle of the Amazon Milk Frog (Trachycephalus resinifictrix).
Join us as we explore the nuances of nature’s love symphony in these captivating amphibians.
Courtship Rituals
Vocal Serenades
Breeding begins with the male Amazon Milk Frogs serenading potential mates through distinctive vocalizations.
These calls, resembling a melodic symphony, serve to attract females. Each male’s unique call contributes to the diverse chorus echoing through the Amazon Rainforest.
Visual Displays
In addition to their enchanting calls, males showcase vibrant colors to entice females. This visual spectacle is an integral part of their courtship ritual, with the frogs adopting striking hues to stand out in the lush greenery.
Egg-Laying Process
Selecting Suitable Sites
Once courtship is successful, females select suitable sites for laying eggs. Overhanging leaves above water bodies, such as ponds or streams, become the chosen locations.
The careful selection of sites ensures the tadpoles’ smooth transition from aquatic to terrestrial life.
Egg Clutches
Females deposit egg clutches on the chosen leaves, where they adhere securely. These clutches can contain a variable number of eggs, and the entire process is orchestrated to optimize the tadpoles’ chances of survival.
Tadpole Development
Aquatic Phase
Upon hatching, tadpoles enter an aquatic phase, where they rely on the water for nourishment and development. A well-planned transition to terrestrial life awaits these tadpoles as they undergo metamorphosis into fully-formed frogs.
Parental Absence
Unlike some amphibians, Amazon Milk Frog parents do not provide direct care to their offspring. Instead, the survival of tadpoles and subsequent froglets relies on the environmental conditions of their aquatic habitat.
Tadpole Care
Aquatic Environment
Raising tadpoles in captivity involves providing a suitable aquatic environment. A shallow, clean water source with appropriate water quality parameters is crucial for their well-being. Regular monitoring ensures optimal conditions for growth.
Metamorphosis to Froglets
As tadpoles undergo metamorphosis, transitioning from water to land is essential. A gradual change in the enclosure from aquatic to terrestrial, complete with suitable hiding spots, facilitates this transformation.
Conservation Implications
Preserving Biodiversity
Understanding the breeding and reproduction of Amazon Milk Frogs carries significant conservation implications.
By appreciating their life cycle, we become advocates for preserving the biodiversity of the Amazon Rainforest, a vital habitat for these remarkable amphibians.
Health and Well-being of Amazon Milk Frogs: Nurturing Nature’s Marvels
Ensuring the health and well-being of Amazon Milk Frogs (Trachycephalus resinifictrix) requires a holistic approach.
Join us on a journey into the intricacies of maintaining the vitality of these captivating amphibians, from common health considerations to mindful handling practices.
Common Health Issues
Vigilance is Key
While Amazon Milk Frogs are generally hardy, it’s crucial to stay vigilant for potential health issues. Skin infections and parasitic infestations can arise, necessitating regular veterinary check-ups. Early detection and prompt intervention are vital for their overall well-being.
Skin Infections
Moist environments, while essential for these frogs, can also create conditions conducive to skin infections. Redness, swelling, or abnormal discoloration may indicate an issue.
Maintaining proper humidity levels and a clean environment helps prevent skin-related ailments.
Diet and Nutrition
Balanced Diet
A well-balanced diet is fundamental to the health of Amazon Milk Frogs. Varied insect offerings, such as crickets and fruit flies, should be appropriately sized for the frogs.
Dusting their food with calcium supplements ensures the maintenance of robust skeletal health.
Hydration and Water Quality
In addition to their diet, proper hydration is essential. The water dish in their enclosure should be regularly cleaned to prevent bacterial growth. Adequate hydration contributes to overall health and supports essential physiological functions.
Environmental Considerations
Optimal Temperature Range
Maintaining an optimal temperature range of 75°F to 85°F (24°C to 29°C) within the terrarium is crucial. This thermoregulation ensures the frogs can metabolize nutrients efficiently and remain active and healthy.
Humidity Management
Balancing humidity is an art. While Amazon Milk Frogs thrive in humid conditions, excess moisture can lead to respiratory issues. Regular misting and ensuring proper ventilation help strike the delicate balance required for their well-being.
Handling with Care
Sensitivity to Touch
Amazon Milk Frogs are sensitive to human touch. Minimizing handling is essential to prevent stress, as excessive contact can adversely affect their delicate skin. Reserve handling for necessary activities like feeding or health assessments.
Observational Interaction
While minimizing direct contact, observational interaction provides valuable insights into their behavior. Monitoring their activities and noting any deviations from normal behavior aids in the early identification of potential health issues.
Conservation Efforts for Amazon Milk Frogs: Preserving Rainforest Harmony
As stewards of Earth’s biodiversity, it is incumbent upon us to actively engage in conservation efforts.
In this segment, we delve into the crucial role of preserving the natural habitat of Amazon Milk Frogs (Trachycephalus resinifictrix), emphasizing the interconnectedness of their existence with the delicate ecosystem of the Amazon Rainforest.
Deforestation Threats
The Alarming Reality
The Amazon Rainforest, the primary habitat of these enchanting frogs, faces the ominous threat of deforestation.
As trees fall to the advance of human activities, the intricate balance of this ecosystem is disrupted, jeopardizing the survival of countless species, including the Amazon Milk Frog.
Impact on Amphibians
Amphibians, with their sensitivity to environmental changes, suffer disproportionately from habitat loss. Preserving the Amazon Rainforest is not merely an ecological concern but a critical step in safeguarding the future of Amazon Milk Frogs and countless other species.
Conservation Initiatives
Preserving Pristine Wilderness
Supporting organizations dedicated to rainforest preservation is a tangible way to contribute to conservation efforts. These groups work tirelessly to protect large expanses of the Amazon, creating sanctuaries where biodiversity can flourish undisturbed.
Community Engagement
Empowering local communities plays a pivotal role in conservation. Initiatives that promote sustainable practices, alternative livelihoods, and education foster a harmonious coexistence between human communities and the delicate ecosystems they inhabit.
Reforestation Projects
Healing the Green Lungs
Recognizing the importance of the Amazon Rainforest as the “lungs of the Earth,” reforestation projects aim to restore areas affected by deforestation.
By planting native trees and vegetation, these projects contribute to the revival of crucial habitats for Amazon Milk Frogs and other species.
Creating Corridors
Creating ecological corridors is another innovative approach. These pathways connect fragmented habitats, allowing for the movement of species and maintaining genetic diversity. Such initiatives are essential for the long-term survival of Amazon Milk Frogs.
Education and Advocacy
Raising Awareness
Educating the public about the value of rainforests and the species they harbor is fundamental. Awareness campaigns highlighting the unique attributes of Amazon Milk Frogs and their role in maintaining ecological balance garner support for conservation initiatives.
Advocating Policy Changes
Engaging in advocacy to influence policy changes at local and international levels is imperative.
Policies that promote sustainable land use, enforce anti-deforestation measures, and address the root causes of habitat loss are essential for the continued well-being of Amazon Milk Frogs.
Conclusion
In the heart of the Amazon Rainforest, the Amazon Milk Frog stands as a testament to nature’s creativity. From their vibrant appearance to unique behaviors, these frogs have rightfully earned their place in the hearts of amphibian enthusiasts.
As we strive to understand and appreciate these incredible creatures, let’s also advocate for the conservation of their precious habitat.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs)
Can Amazon Milk Frogs be kept in groups?
Yes, they are social creatures and can thrive in small groups. Ensure the enclosure provides enough space and hiding spots for each frog.
What is the lifespan of an Amazon Milk Frog?
In captivity, with proper care, these frogs can live up to 10 to 15 years.
Are Amazon Milk Frogs venomous?
No, they are not venomous. The milky secretion they produce is not harmful to humans.
How often should I feed my Amazon Milk Frog?
Feed them 3 to 4 times a week, offering a variety of appropriately sized insects.
Can Amazon Milk Frogs be housed with other amphibian species?
It is recommended to keep them in a species-specific enclosure to avoid stress and potential conflicts.
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”The Enchanting World of the Amazon Milk Frog: A Comprehensive Guide!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
Frogs
Decoding the Enigma of Frog Poop: What Does It Really Look Like?

Decoding the Enigma of Frog Poop: What Does It Really Look Like?
When it comes to the intriguing world of amphibians, frogs have always held a special place in our hearts. From their mesmerizing croaks to their acrobatic leaps, these slimy creatures never fail to captivate us.
But today, dear readers, we are embarking on a journey to explore a rather peculiar aspect of frog life that often goes unnoticed: their excrements!
Yes, you heard it right – frog poop! In this article, we’ll dive deep into the realm of frog droppings and unravel the secrets they hold. So, brace yourselves for an eye-opening adventure into the mysterious world of “What Does Frog Poop Look Like?”
The Importance of Understanding Frog Poop
Before we delve into the specifics, you might wonder, “Why should I care about frog poop?” Well, my dear readers, the answer lies in its ecological significance.
Frog excrement plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems. It serves as a rich source of nutrients for plants and aquatic organisms, contributing to the health of wetland habitats.
Additionally, studying frog droppings can help researchers gain valuable insights into the health and diet of these amphibians, which can aid in conservation efforts.
Identifying Frog Poop: A Closer Look
Frog droppings come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the species and their diet. Generally, they are small, cylindrical pellets, much like those of rodents.

However, their appearance can differ based on whether the frog is herbivorous, insectivorous, or carnivorous.
Herbivorous frog poo may be brownish or greenish, reflecting their plant-based diet, while insectivorous and carnivorous species may have darker-colored excrements due to their protein-rich meals.
The Diet Chronicles: Clues Within Frog Poop
Oh, the mysteries that lie hidden in a frog’s diet, all concealed within their feces! If you’re an amateur detective of the animal kingdom, deciphering a frog’s excrement might just become your favorite pastime.
Insectivorous frogs leave behind a trail of dark-colored droppings, often sprinkled with the remnants of exoskeletons. Meanwhile, carnivorous frog poo boasts an even darker shade, sometimes offering hints in the form of tiny bones or fur remnants.
On the other hand, herbivorous frog droppings might have a touch of green or brown, reflecting their plant-based feasts.
Texture Tales: The Scoop on Frog Poop Consistency
The texture of frog droppings can tell us a lot about their health and lifestyle. Healthy frogs typically produce firm yet moist excrements, indicating a well-hydrated and balanced diet.
However, occasional variations may occur due to factors such as diet changes or environmental conditions. Understanding these subtle texture tales can assist frog enthusiasts in monitoring their pet’s well-being.
Decoding Frog Poop: Color Clues and Beyond
Every frog species has its unique blend of colors, and this extends to their fecal masterpiece as well! Besides their diet, pigments in their skin contribute to the color variations in their droppings.
This kaleidoscope of colors allows us to identify frog species and gain insights into their diverse lifestyles. It’s a marvelous way of connecting with nature and the inhabitants of the wild.
Frog Poo and Environmental Indicators
Beyond being an interesting topic for amphibian enthusiasts, frog droppings can serve as vital environmental indicators. Researchers often study the presence and characteristics of frog excrement in wetland areas to assess the health of ecosystems.
By understanding the connections between frog populations and their droppings, scientists can better comprehend the impacts of pollution, habitat loss, and climate change on these amphibians.
Frog Poop Frequency: How Often Do Frogs Do Their Business?
Curious about the bathroom habits of our froggy friends? Now that you’re well-versed in identifying frog poo, you might wonder about the frequency of their bathroom visits. Well, my friends, the answer isn’t as straightforward as you might think.
The frequency of frog defecation varies based on factors like species, size, and diet. Generally, frogs tend to be quite punctual with their toilet trips, and some might even leave droppings daily to maintain a healthy digestive rhythm.
Frog Poop Detective: Identifying Species through Droppings
Calling all wildlife detectives! Here’s a fun challenge for you – identifying frog species through their droppings.
Armed with the knowledge of color, size, and shape variations, you can embark on an adventure to spot the telltale signs left behind by these elusive amphibians. Become a frog poop detective, and the natural world will reveal its hidden wonders to you!
Fascinated by the idea of decoding your frog’s diet through their droppings? We’ve got you covered! Here’s a handy guide to interpreting the dietary clues hidden in their poo:
- Insectivorous Frog Poo: Dark-colored with insect exoskeleton fragments.
- Carnivorous Frog Poo: Even darker, possibly with bones or fur remnants.
- Herbivorous Frog Poo: Greenish or brownish, containing plant matter.
How to Keep Track of Your Frog’s Droppings?
If you’re an avid frog keeper, monitoring your pet’s droppings can be a rewarding and informative practice.
By keeping a “poo log,” you can track any changes in frequency, texture, or color, which may signal potential health issues. Remember, it’s essential to know your frog’s normal droppings to spot any abnormalities early on.
Questions People Also Ask: (FAQs)
Can I tell if my frog is sick by examining its droppings?
While changes in frog droppings can be an indicator of health issues, they are not the sole factor. Always consider other signs, such as appetite, behavior, and appearance, and consult a veterinarian if you suspect your frog is unwell.
How do I clean my frog’s habitat from droppings effectively?
Regularly clean your frog’s enclosure, removing droppings and soiled substrate. Use a safe disinfectant, and ensure the habitat is dry before returning your frog.
Can I use frog poo as fertilizer for my garden?
Yes, frog droppings are rich in nutrients and can be an excellent natural fertilizer for plants. However, avoid using droppings from wild frogs, as they may carry parasites.
Is it normal for my frog to eat its own poop?
Yes, some frogs engage in coprophagy, the act of consuming their own feces. It may sound strange to us, but it’s a common behavior for certain species.
How can I tell if my frog is constipated?
If your frog hasn’t pooped for an extended period, appears bloated, or displays discomfort, it might be constipated. Seek veterinary assistance if the issue persists.
Can frogs get diarrhea?
Yes, frogs can experience diarrhea, usually caused by dietary changes or infections. Ensure your frog has access to clean water and consult a veterinarian if the diarrhea persists.
Are there any risks associated with handling frog droppings?
While frog droppings are generally safe, it’s crucial to wash your hands thoroughly after handling them or cleaning your frog’s enclosure to prevent potential disease transmission.
Conclusion
Congratulations, dear readers! You’ve now mastered the art of deciphering frog poo mysteries and understanding its significance in the world of frogs.
By recognizing the valuable insights hidden in their droppings, you can enhance your connection with these fascinating creatures and contribute to their well-being.
Remember to share your knowledge with fellow frog enthusiasts and continue exploring the wonders of the natural world. Until next time, hop on and keep exploring the captivating realm of frogs and their mysterious poo!
We appreciate you for taking the time to read this article!
Finally, we hope you found this article interesting? And what do you think about ”Decoding the Enigma of Frog Poop: What Does It Really Look Like?!?”
Please feel free to share or inform your friends about this article and this site, thanks!
And let us know if you observe something that isn’t quite right.
-

 Pet Care2 years ago
Pet Care2 years agoThe Best Dog Collars For 2022
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoBichon Frise: The Happy, Playful, and Cuddly Companion
-

 Trending Pet Stories1 year ago
Trending Pet Stories1 year ago2023 ‘World’s Ugliest Dog’ Winner: Scooter’s Tale of Resilience
-

 Animals2 years ago
Animals2 years agoAre There Animals Having Down Syndrome?
-

 Pets2 years ago
Pets2 years agoThe Fascinating World Of The Red Chameleon
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoTop 10 Most Popular Dog Breeds According To AKC.
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years ago21 Dog Breeds That Resemble Bears Or Teddy Bears!
-

 Dogs2 years ago
Dogs2 years agoEskimo Dogs from Canada – What Are They? – Find Out!